Abstract
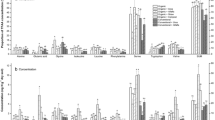
The anaerobic microbial uptake of alanine and aspartic acid was determined in 4 diverse salt-marsh soils (tall and short Spartina alterniflora, creek bank, and mud flat). Uptake in soil slurries was determined by the radioisotopic tracer technique at one substrate concentration (<250 pmoles cm-3). Dissolved free alanine and aspartic acid concentrations in the interstitial nutrient pool ranged from approximately 1 to 500 pmoles cm-3. In the short S. alterniflora soil, maximum microbial uptake of alanine was found at a depth of 10 cm (8.32 pmoles cm-3 h-1); in the tall S. alterniflora soil maximum uptake was at 20 cm (23.4 pmoles cm-3 h-1). The utilization of aspartic acid appeared constant over the depth interval investigated (0 to 60 cm). The turnover times of alanine and aspartic acid in the tall and short S. alterniflora soils ranged from 5 to 25 h and 40 to 100 h, respectively. The percent of the labeled alanine and aspartic acid taken up that was mineralized by tall and short s. alterniflora microbenthos ranged from 20 to 50% and 5 to 20%, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Burnison, B.K.: Amino acid flux in a naturally eutrophic lake, 116 pp. Ph.D. Thesis, Oregon State University, Corvallis 1971
Christian, R.R.: Regulation of a salt marsh soil microbial community: a field experimental approach, 132 pp. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Georgia 1976
— and J.R. Hall: Experimental trends in sediment microbial heterotrophy: radioisotopic techniques and analysis. In: Ecology of marine benthos, pp 67–88. Ed. by B. Coull. Columbia: University of South Carolina Press 1977. (Belle Baruch Marine Symposium Volume No. 7)
Christian, R.R. and W.J. Wiebe: Anaerobic microbial community metabolism in Spartina alterniflora soils. Limnol. Oceanogr. (In press)
Crawford, C.C., J.E. Hobbie and K.L. Webb: The utilization of dissolved free amino acids by estuarine microorganisms. Ecology 55, 551–563 (1974)
Gallagher, J.L.: Sampling macroorganic matter profiles in salt marsh plant root zones. Proc. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. 38, 154–155 (1974)
—, R.J. Reimold and D.E. Thompson: Remote sensing and salt marsh productivity. Proc. Am. Soc. Photogrammetry 38, 338–348 (1972)
Gardner, W.S.: Sensitive fluorometric procedure to determine individual amino acids in marine waters. Mar. Chem. (In press)
Hall, K., P.M. Kleiber and I. Yesaki: Heterotrophic uptake of organic solutes by microorganisms in sediments. Memorie Ist. ital. Idrobiol. (Suppl.). 29, 441–471 (1972)
Hanson, R.B.: Nitrogen fixation (acetylene reduction) in a salt marsh amended with sewage sludge and organic carbon and nitrogen compounds. Appl. envirl Microbiol. 33, 846–852 (1977a)
—: A comparison of the nitrogen-fixers in low and high Spartina alterniflora salt marsh soils. Appl. envirl Microbiol. 33, 596–602 (1977b)
— and W.J. Wiebe: Heterotrophic activity associated with particulate size fractions in a Spartina alterniflora salt-marsh-estuary, Sapelo Island, Georgia, USA, and the continental shelf waters. Mar. Biol. 42, 321–330 (1977)
Harrison, M.J., R.T. Wright and R.Y. Morita: Method for measuring mineralization in lake sediments. Appl. Microbiol. 21, 698–702 (1971)
Hobbie, J.E. and C.C. Crawford: Respiration corrections for bacterial uptake of dissolved organic compounds in natural waters. Limnol. Oceanogr. 14, 528–533 (1969)
Kadota, H.Y., Y. Hata and H. Miyoshi: A new method for estimating the mineralization activity of lake water and sediment. Mem. Res. Inst. Fd Sci. Kyoto Univ. 27, 28–30 (1966)
King, G.M. and W.J. Wiebe: Methanogenesis in soils of a Georgia salt marsh. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta
Munro, A.L.S. and T.D. Brock: Distinction between bacterial and algal utilization of soluble substances in the sea. J. gen. Microbiol 51, 35–42 (1968)
Oshrain, R.: Aspects of sulfur metabolism in salt marsh soils, 153 pp. M. Sci. Thesis, Department of Microbiology, University of Georgia, Athens 1977
Pomeroy, L.R.: Algal productivity in salt marshes of Georgia. Limnol. Oceanogr. 4, 386–397 (1959)
Sherr, B.: The ecology of denitrifying bacteria in salt marsh soils: an experimental approach, 154 pp. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Zoology, University of Georgia, Athens 1977
Teal, J.: Energy flow in the salt marsh ecosystem of Georgia. Ecology 43, 614–624 (1962)
Williams, P.J. LeB: Heterotrophic utilization of dissolved organic compounds in the sea. I. Size distribution of population and relationship between respiration and incorporation of growth substrates. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 50, 859–870 (1970)
—: The validity of the application of simple kinetic analysis to heterogeneous microbial populations. Limnol. Oceanogr. 18, 159–165 (1973)
— and C. Askew: A method for measuring the mineralization by micro-organisms of organic compounds in sea water. Deep-Sea Res. 15, 365–375 (1968)
Wood, L.W.: The role of estuarine sediment micro-organisms in the uptake of organic carbon under aerobic conditions, 75 pp. Ph.D. Thesis, Department of Zoology, North Carolina State University, Raleigh 1970
— and K.E. Chua: Glucose flux at the sediment water interface of Toronto Harbour, Lake Ontario, with reference to pollution stress. Can. J. Microbiol. 19, 413–420 (1973)
Wright, R.T.: Some difficulties in using 14C-organic solutes to measure heterotrophic bacterial activity. In: Estuarine microbial ecology, Vol. 1 pp 199–217. Ed. by H.L. Stevenson and R.R. Colwell. Columbia, S.C.: University of South Carolina Press 1973
— and J.E. Hobbie: The use of glucose and acetate by bacteria and algae in aquatic ecosystems. Ecology 47, 447–464 (1966)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J.M. Lawrence, Tampa
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hanson, R.B., Gardner, W.S. Uptake and metabolism of two amino acids by anaerobic microorganisms in four diverse salt-marsh soils. Mar. Biol. 46, 101–107 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391525
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391525