Abstract
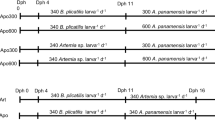
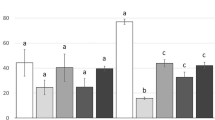
The nutritional value of Artemia sp. as food for marine fish and crustacean larvae has been linked to the level of its polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) content. Experiments in August 1984 were conducted to determine the effects of various artificial diets and algae on fatty acid composition of PUFA-deficient Artemia sp. (Utah GSL strain) and their resulting value as food for postlarvae of the prawn Penaeus monodon (Fabricius). Nauplii of the brine shrimp were grown on extracts of corn, copra, soybean and rice bran containing precursors (C18) to long-chain PUFA and also on algal species containing different levels of long-chain PUFA (C20). The nauplii were then used as food for P. monodon postlarvae. The results revealed that absence of C20 polyunsaturates from the feeds and their presence in the algae were reflected in the polyunsaturated fatty acid content of the tissues of Artemia sp. When fed with brine shrimp fed on algae, P. monodon displayed better postlarval survival and significantly higher growth; related to the content of polyunsaturated fatty acids in Artemia sp. A practical feeding approach in prawn hatcheries would be to grow Artemia sp. on a cheap diet such as rice bran, and then to enhance its nutritional value with a diet high in PUFA prior to harvesting, in order to improve hatchery production.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Beck, A. D., Bengtson, D. A. (1982). International study of Artemia XXII. Nutrition in aquatic toxicology: diet quality of geographical strains of the brine shrimp Artemia. Spec. tech. Publs. Am. Soc. Test Mater. 766: 161–169
Beck, A. D., Bengtson, D. A., Howell, W. H. (1981). International study on Artemia. V. Nutritional value of five geographic strains of Artemia effects of survival and growth of larval atlantic silversides, Menidia menidia. In: Persoone, G., Sorgeloos, P., Roels, O., Jaspers, E. (eds.) The brine shrimp Artemia. Vol. III. Ecology, culturing, use in aquaculture. Universa Press, Wetteren, Belgium, p. 249–259
Bligh, E. G., Dyer, W. J. (1959). A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can. J. Biochem. Physiol. 35: 811–917
Bottino, N. R., Gennity, J., Lilly, M. L., Simmons, E., Finne, G. (1980). Seasonal and nutritional effects on the fatty acids of three species of shrimp, Penaeus setiferus, P. aztecus and P. duorarum. Aquaculture, Amsterdam 19: 139–148
Castell, J. D., (1979). Review of lipid requirement of finfish. In: Halver, J. E., Tiews, K. (eds.) Finfish nutrition and fishfeed technology. Vol. 1 H. Heenemann GmbH & Co., Berlin, p. 59–84
Claus, C., Benjits, R., Vandeputte, G., Gardner, M. (1979). The biochemical composition of two strains of Artemia salina (L.) reared on two different algal foods. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 36: 171–183
Cowey, C. B., Sargent, J. R. (1979) Nutrition. In: Hoar, W. S., Randall, D. S. (eds.) Fish physiology. Academic Press, New York, p. 1–69
Dobbeleir, J., Adam, N., Bossuyt, E., Bruggemen, E., Sorgeloos, P. (1980). New aspects of the use of inert diets for high density culturing of brine shrimp. In: Persoone, G., Sorgeloos, P., Roels, O., Jaspers, E. (eds.) The brine shrimp Artemia. Vol. III. Ecology, culturing, use in aquaculture. Universa Press, Wetteren, Belgium, p. 249–259
Fujita, S., Watanabe, T., Kitajima, C. (1980). Nutritional quality of Artemia from different locations as a living feed for marine fish from the viewpoint of essential fatty acids. In: Persoone, G., Sorgeloos, P., Roels, O., Jaspers E. (eds.) The brine shrimp Artemia. Vol. III. Ecology, culturing, use in aquaculture. Universa Press, Wetteren, Belgium, p. 277–290
Guary, J. C., Kayama, M., Murakami, Y., Ceccalsi, H. (1976) The effects of a fat-free diet and compounded diets supplemented with various oils on moult, growth and fatty acid composition of prawn, Penaeus japonicus Bate. Aquaculture, Amsterdam 7: 245–254
Howell, B. R. (1979). Experiments on the rearing of larval turbot, Scopthalmus maximus L. Aquaculture Amsterdam 18: 215–225
Johns, D. M., Peters, M. E., Beck, A. D. (1978). International study on Artemia. I. An evaluation of five geographical strains of brine shrimp, Artemia salina, as food for larval mud crabs Rhithropanopeus harrissii. Am. Zool. 18: p. 585
Johns, D. M., Peters, M. E., Beck, A. D. (1980). International study on Artemia. VI. Nutritional value of geographical and temporal strains of Artemia. Effects on survival and growth of two species of brachyural larvae. In: Persoone, G., Sorgeloos, P., Roels, O., Jaspers, E. (eds.) The brine shrimp Artemia. Vol. III. Ecology, culturing, use in aquaculture, Universa Press, Wetteren, Belgium, p. 291–304
Kanazawa, A., Teshima, S., Ono, K. (1979). Relationship between essential fatty acid requirements of aquatic animals and the capacity for bioconversion of linolenic acid to highly unsaturated fatty acids. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 638: 295–298
Kates, M. (1972). Techniques of lipidology: isolation, analysis and identification of lipids. North Holland Publishing Co. New York, p. 347–353
Klein-Mac Phee, G., Howell, W. H., Beck, A. D. (1980). International Study on Artemia VII. Nutritional value of five geographical strains of Artemia to winter flounder Pseudopleuronectes americanus larvae. In: Persoone, G., Sorgeloos, P., Roels, O., Jaspers, E. (eds.) The brine shrimp Artemia Vol. III. Ecology, culturing, use in aquaculture, Universa Press, Wetteren, Belgium, p. 305–372
Leger, P., Bengtson, D. A., Simpson, K. L. Sorgeloos, P. (1986). The use of nutritional value of Artemia as a food source. In: Barnes, M. (ed.) Marine biology and oceanography: an annual review, Vol. 24. Aberdeen University Press, Aberdeen, Scotland, p. 29–55
Leger, P., Bieber, G. F., Sorgeloos, P. (1985a). International study on Artemia. XXXIII. Promising results in larval rearing of Penaeus stylirostris using a prepared diet as algal substitute and for Artemia enrichment. J. Wld aquacult. Soc. 16: 354–367
Leger, P., Millamena, O. M., Simpson, K. L., Sorgeloos, P. (1985b). International study on Artemia. XXIV. Factors determining the nutritional effectiveness of Artemia: the relative impact of chlorinated hydrocarbons and essential fatty acids in San Francisco and San Pablo Bays Artemia. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 93: 71–82
Morrison, W. R., Smith, L. H. (1964). Preparation of fatty acid methyl esters and dimethyl acetals from lipids with boron trifluoride-methanol. J. Lipid Res. 5: 600–608
Olney, C. E., Schauer, P. S., McClean, S., Lu, Y., Simpson, K. L., (1980). International Study on Artemia. VIII. Comparison of the chlorinated hydrocarbons and heavy metals in five different strains of newly hatched Artemia and a laboratory reared marine fish. In: Persoone, G., Sorgeloos, P. Roels, O., Jaspers, E. (eds.) The brine shrimp Artemia. Vol. III. Ecology, culturing, use in aquaculture. Universa Press, Wetteren, Belgium, p. 343–353
Schauer, P. S., Johns, D. M., Olney, C. E. Simpson, K. L. (1980). International study on Artemia IX. Lipid level, energy content and fatty acid composition of the cysts and newly hatched nauplii from five geographical strains of Artemia. In: Persoone, G., Sorgeloos, P., Roels, O., Jaspers, E. (eds.) The brine shrimp Artemia. Vol. III. Ecology, culturing, use in aquaculture, Universa Press, Wetteren, Belgium, p. 365–373
Scott, A. P., Middleton, C. (1979). Unicellular algae as a food for turbot (Scopthalmus maximus L) larvae. The importance of dietary long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acids. Aquaculture, Amsterdam 18: 227–240
Simpson, K. L., Beck, A. D., Sorgeloos, P. (1980). Workshop I. Characterization of Artemia strains for application in aquaculture. In: Persoone, G., Sorgeloos, P., Roels, O., Jaspers, E. (eds.) The brine shrimp Artemia Vol. III. Ecology, culturing use in aquaculture. Universa Press, Wetteren, Belgium, p. 409–411
Watanabe, T., Oowa, P., Kitajima, C., Fujita, S. (1978). Nutritional quality of brine shrimp, Artemia salina, as a living feed from the viewpoint of essential fatty acids for fish. Bull. Jap. Soc. scient. Fish. 44: 1115–1121
Yashiro, R. (1982). The effect of Artemia fed with different diets on the growth and survival of Penaeus monodon Fabricius postlarvae. Master's thesis, UP/SEAFDEC Graduate Study Program, University of the Philippines, Iloilo City, Philippines
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by M. Anraku, Tokyo
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Millamena, O.M., Bombeo, R.F., Jumalon, N.A. et al. Effects of various diets on the nutritional value of Artemia sp. as food for the prawn Penaeus monodon . Mar. Biol. 98, 217–221 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391197
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391197