Abstract
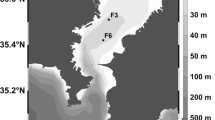
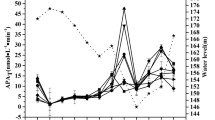
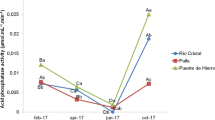
Alkaline phosphatase activity in seawater samples taken from Tokyo Bay was measured by both spectrophotometric and fluorometric methods. A stratified distribution pattern of the enzyme was observed in August, a vertically mixed pattern in December. The distribution of phosphatase activity in the eutrophic seawater was paralleled by variations in other parameters, such as viable counts of bacteria, chlorophyll a content, inorganic and total phosphorus concentrations, amounts of seston, particulate deoxyribonucleic acids (DNA) and protein. A significant correlation between phosphatase activity and these measurements indicated that the enzyme was a good indicator of the degree of eutrophication. The positive relationship between phosphatase and inorganic phosphorus indicates that enzyme activity was not inhibited at inorganic phosphorus levels present in the bay and that production of phosphatase by microorganisms inhabiting the bay was not repressed at the inorganic phosphorus levels in the bay. Culture experiments revealed that the formation of repressible phosphatase by bacteria isolated from the bay was not affected by the inorganic phosphorus levels in the bay.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Aaronson, S. and N.J. Patni: The role of surface and extracellular phosphatases in the phosphorus requirement of Ochromonas. Limnol. Oceanogr. 21, 838–845 (1976)
Armstrong, F.A.J. and H.W. Harvey: The cycle of phosphorus in the waters of the English Channel. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 29, 145–162 (1950)
Berman, T.: Alkaline phosphatase and phosphorus availability in Lake Kinneret. Limnol. Oceanogr. 15, 663–674 (1970)
Hewitt, E.G. and P. Tatham: Interaction of mineral deficiency and nitrogen source on acid phosphatase activity in leaf extracts. J. exp. Bot. 11, 367–376 (1960)
Holm-Hansen, O.: Determination of microbial biomass in ocean profiles. Limnol. Oceanogr. 14, 740–747 (1969)
Jones, J.G.: Studies on fresh water bacteria—association with algae and alkaline phosphatase activity. J. Ecol. 60, 59–75 (1972a)
—: Studies on freshwater microorganisms — phosphatase activity in lakes of differing degrees of eutrophication. J. Ecol. 60, 777–791 (1972b)
Kadner, R.J., J.F. Nyc and D.M. Brown: A repressible alkaline phosphatase in Neurospora crassa. J. biol. Chem. 243, 3076–3082 (1968)
Kuenzler, E.J. and J.P. Perras: Phosphatases of marine algae. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 128, 271–284 (1965)
Lowry, O.H., N.J. Rosebrough, A.F. Farr and R.J. Randall: Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. biol. chem. 193, 265–275 (1951)
Marumo, R. and M. Murano: Succession of plankton diatoms in Tokyo Bay. La Mer (Bull. Soc. franco-jap. Océanogr.) 11, 70–82 (1973)
Murphy, J. and J.P. Riley: A modified single solution method for the determination of phosphate in natural waters. Analytica chim. Acta 27, 31–36 (1962)
Parker, A.B.C.: Classification of Micrococci and Staphylocci based on physiological and biochemical tests. J. gen. Microbiol. 30, 409–427 (1963)
Perry, M.J.: Alkaline phosphatase activity in subtropical Central North Pacific waters using a sensitive fluorometric method. Mar. Biol. 15, 113–119 (1972)
Reichardt, W., J. Overbeck and L. Steubing: Free dissolyed enzymes in lake waters. Nature, Lond. 216, 1345–1347 (1967)
Shah, D.B. and H. Blobel: Repressible alkaline phosphatase of Stapylococcus aureus. J. Bact. 94, 780–781 (1967)
Simidu, U., E. Kaneko and N. Taga: Microbiological studies of Tokyo Bay. Microb. Ecol. 3, 173–191 (1977)
Stewart, W.D.P., T. Mague, G.P. Fitzgerald and R.H. Burris: Nitrogenase activity in Wisconsin lakes in differing degrees of eutrophication. New Phytol. 70, 497–509 (1971)
Strickland, J.D.H. and T.R. Parsons: Determination of the weight of microscopic materials in seawater. In: A practical handbook of seawater analysis, rev. ed. pp 181–184, Ottawa: Fisheries Research Board of Canada 1972. (Bull. Fish. Res. Bd Can. No. 167)
Taga, N.: Some ecological aspects of marine bacteria in the Kuroshio Current. Bull. Misaki mar. biol. Inst. (Kyoto Univ.) 12, 65–76 (1968)
Torriani, A.: Influence of inorganic phosphate in the formation of phosphatases by Escherichia coli. Biochim. biophys. Acta 38, 460–479 (1959)
Wai, N., T.C. Hung and Y.H. Lu: Alkaline phosphatase in Taiwan sea water. Bull. Inst. Chem. Acad. sin. 3, 1–10 (1960)
Yentsch, C.S. and D.W. Menzel: A method for the determination of phytoplankton chlorophyll and phaeophytin by fluorescence. Deep-Sea Res. 10, 221–231 (1963)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by M. Anraku, Nagasaki
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Taga, N., Kobori, H. Phosphatase activity in Eutrophic Tokyo Bay. Marine Biology 49, 223–229 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391134
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391134