Abstract
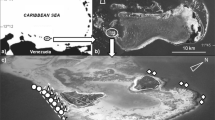
I examined whether patterns of settlement of planktonic juveniles determined the size and composition of adult populations of three Caribbean surgeonfishes (A canthurus bahianus, A. chirurgus and A. coeruleus) on six isolated patch-reefs in Panamá. I monitored settlement monthly on six reefs (0.14 to 0.67 ha) for 8 yr (1978–1986), and censused adults on those reefs annually. Year-to-year fluctuations in the absolute and relative abundances of settlers arriving on each reef were not extreme. Densities of adults in 1986 were not correlated with the densities of settlers that arrived between 1979 and 1984. Survival of settlers, although apparently unrelated to the density of adults, was negatively related to the density of settlers per unit of adult habitat (but not per unit of settlement habitat) for each species. Changes in adult populations of each species between 1978 and 1986 were not correlated with the abundance of settlers relative to the initial number of adults. The relative abundances of adults of each species in 1986 did not reflect the relative abundances of settlers (1979–1984); these abundances were due to both spatial variation and interspecific variation in survival. In some cases, relocation of adults between isolated patch-reefs (as much as 100 m from other reefs) substantially altered the size and composition of surgeonfish populations. Thus, either post-settlement mortality or relocation overrode effects of settlement patterns in determining adult abundances on the six reefs. Relocation is important in organizing reef-fish communities and must be further examined, particularly in large habitat mosaics.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Aldenhoven, J. M. (1986). Local variation in mortality rates and life-expectancy estimates of the coral-reef fish Centropyge bicolor (Pisces: Pomacanthidae) Mar. Biol. 92: 237–244
Bohnsack, J. A. (1983). Species turnover and the order versus chaos controversy concerning reef fish community structure. Coral Reefs 1: 223–228
Brock, R. E., Lewis, C., Wass, R. C. (1979). Stability and structure of a fish community on a coral patch reef in Hawaii. Mar. Biol. 54: 281–292
Choat, J. H., Bellwood, D. R. (1985). Interactions amongst herbivorous fishes on a coral reef: influence of spatial variation. Mar. Biol. 89: 221–234
Clavijo, I. E. (1974). A contribution on feeding habits of three species of acanthurids (Pisces) from the West Indies. M. S. thesis, Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton
Cowen, R. K. (1985). Large scale pattern of recruitment by the labrid, Semicossyphus pulcher: causes and implications. J. mar. Res. 43: 719–742
Doherty, P. J. (1982). Coral reef fishes: recruitment-limited assemblages? Proc. 4th int. coral Reef Symp. 2: 465–470 [Gomez, E. D. (ed.) Marine Sciences Center, University of the Philippines, Quézon City]
Doherty, P. J. (1983). Tropical terriotorial damselfishes: is density limited by aggression or recruitment? Ecology 64: 176–190
Ebersole, J. P. (1985) Niche separation of two damselfish species by aggression and differential microhabitat utilization. Ecology 66: 14–20
Gundermann, N., Popper, D. (1975). Some aspects of recolonization of coral rocks in Eilat (Gulf of Aqaba) by fish populations after poisoning. Mar. Biol. 33: 109–117
Itzkowitz, M. (1985). Aspects of the population dynamics and reproductive success in the permanently terriotorial Beaugregory damselfish. Mar. Behav. Physiol. 185: 57–69
Johannes, R. E. (1978). Reproductive strategies of coastal marine fishes in the tropics. Envir. Biol. Fish. 3: 65–84
Munro, J. L. (1983). Epilogue: progress in coral reef fisheries research, 1973–1982. In: Munro, J. L. (ed.) Caribbean coral reef fishery resources. ICLARM, Manila, Philippines, p. 249–276
Munro, J. L., Williams, D. McB. (1985). Assessment and management of coral reef fisheries: biological, environmental and socio-economic aspects. Proc. 5th int. coral Reef Congr. 4: 543–478. [Gabrie, C. et al. (ed.) Antenne Museum-EPHE, Moorea]
Nolan, r. S. (1975). The ecology of patch reef fishes. Ph.D. thesis, University of California, San Diego
Ogden, J. C., Quinn, T. P. (1984). Migration in coral reef fishes: ecological significance. In: McCleave J. D., Arnold, G. P., Dodson, J. J., Neill, W. H. (eds.) Mechanisms of migration in fishes. Plenum Press, New York, p. 293–308
Randall, J. E. (1962). Tagging reef fishes in the Virgin Islands. Proc. Gulf Caribb. Fish. Inst. 14:201–241
Randall, J. E. (1963). An analysis of the fish population of artificial and natural reefs in the Virgin Islands. Caribb. J. Sci. 2:31–47
Randall, J. E. (1967). Food habits of reef fishes of the West Indies. Stud. trop. Oceanogr., Miami 5:655–847
Randall, J. F. (1983). Caribbean reef fishes. 2nd ed. T.F.H. Publications, Neptune City, New Jersey
Reeson, P. H. (1983). The biology, ecology and bionomics of the surgeonfishes, Acanthuridae. In: J. L. Munro (ed.) Caribbean coral reef fishery resources. ICLARM, Manila, Philippines, p. 178–190
Robertson, D. R. (1974). A study of the ethology and reproductive biology of the labrid fish, Labroides dimidatus, at Heron Island, Great Barrier Reef. Ph.D. thesis, University of Queenslan, Brisbane, Australia
Robertson, D. R. (1983). On the spawning behaviour and spawning cycles of eight surgeonfishes (Acanthuridae) from the Indo-Pacific. Envir. Biol. Fish. 9:192–223
Robertson, D. R. (1987). Responses of two coral reef toadfishes (batrachoididae) to the demise of their primary prey, the sea urchin Diadema antillarum. Copeia 1987, 637–642
Robertson, D. R., Foster, S. A. (1982). Off-reef emigration of young adults of the labrid fish Epibulus insidiator. Copeia 1982:227–229
Robertson, D. R., Gaines, S. G. (1986). Interference competition structures habitat use in a local assemblage of coral reef surgeonfishes. Ecology 67:1372–1383
Russell, B. C., Talbot, F. H., Domm, S. (1974). Patterns of colonization of artificial reefs by coral reef fishes. Proc. 2nd int. coral Reef Symp 1:207–215. [Cameron, A. M. (ed. Great Barrier) Reef Commitec, Brisbane]
Sale, P. F. (1979). Recruitment, loss and coexistence in a guild of territorial coral reef fishes. Oecologia 42:159–177
Sale, P. F. (1980). Assemblages of fish on patch reefs-predictable or unpredictable? Envir. Biol. Fish. 5:243–249
Sale, P. F., Dybdahl, R. (1978). Determinants of community structure for coral reef fishes in isolated coral heads at lagoonal and reef slope sites. Oecologia 34:57–74
Shulman, M. J., Ogden, J. C., Ebersole, J. P., McFarland, W. N., Miller, S. L., wolf, N. G. (1983). Priority effects in the recruitment of juvenile coral reef fishes. Ecology 64:1508–1513
Smith, C. L., Tyler, J. C. (1975). Succession and stability in fish communities of dome-shaped patch reefs in the West Indies. Am. Mus. Novit. 2572:1–18
Springer, V. G., McErlean, A. J. (1962). A study of the behavior of some tagged South Florida coral reef fishes. Am. Midl. Nat. 67: 386–397
Stier, F. (1977). Fishing in the Eastern San Blas community. Unpublished preliminary report for the Smithsonian Tropical Research Institute
Sweatman, H. (1985). The influence of adults of some coral reef fishes on larval recruitment. Ecol. Monogr. 55:469–485
Thresher, R. E. (1983). Habitat effects on reproductive success in the coral reef fish, Acanthochromis polyacanthus (Pomacentridae). Ecology 64:1184–1199
Victor, B. (1983). Recruitment and population dynamics of a coral reef fish. Science, N.Y. 219:419–420
Victor, B. (1986). Larval settlement and juvenile mortality in a recruitment-limited coral reef fish population. Ecol. Monogr. 56: 145–160
Wellington, G. M., Victor, B. C. (1985). El Niño mass coral mortality: a test of resource limitation in a coral reef damselfish population. Oecologia 68:15–19
Williams, D. McB. (1981). Dynamics of the pomacentrid community on small patch reefs in One Tree Lagoon (Great Barrier Reef). Bull. mar. Sci. 30:159–170
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. M. Lawrence, Tampa
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robertson, D.R. Abundances of surgeonfishes on patch-reefs in Caribbean Panamá: due to settlement, or post-settlement events?. Marine Biology 97, 495–501 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391045
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00391045