Abstract
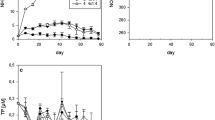
The effect of ambient ammonium concentration on the nitrate uptake rate of marine phytoplankton was investigated. These studies consisted of laboratory experiments using unialgal species and field experiments using natural phytoplankton communities. In laboratory experiments, ammonium suppressed the uptake rates of nitrate and nitrite. Approximately 30 min were required for ammonium to exhibit its fully inhibitory effect on nitrate uptake. At high ammonium concentration (>3 μg-at/l), a residual nitrate uptake rate of approximately 0.006 h-1 was observed. When the ambient ammonium concentration was reduced to a value less than 1 μg-at/l, the suppressed nitrate uptake rate subsequently attained a value comparable to that observed before the addition of ammonium. A range of 25 to 60% reduction in the nitrate uptake rate of natural phytoplankton communities was observed at ambient ammonium concentrations of ∼1.0 μg-at/l. A mechanism is proposed for the suppression of nitrate uptake rate by ammonium through feedback control of the nitrate permease system and/or the nitrate reductase enzyme system. The feedback control is postulated to be regulated by the level of total amino acids in the cell.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Armstrong, F.A.J., C.R. Stearns and J.D.H. Strickland: The measurement of upwelling and subsequent biological processes by means of the Technicon Analyzer® and associated equipment. Deep-Sea Res. 14, 381–389 (1967)
Bongers, L.H.J.: Aspects of nitrogen assimilation by cultures of green algae. (Chlorella vulgaris, strain A, and Scenedesmus) Meded. LandbHoogesch. Wageningen 56, 1–52 (1956)
Conway, H.L., P.J. Harrison and C.O. Davis: Marine diatoms grown in chemostats under silicate or ammonium limitation. II. Transient response of Skeletonema costatum to a single addition of the limiting nutrient. Mar. Biol. 35, 178–199 (1976)
Davis, C.O., P.J. Harrison and R.C. Dugdale: Continuus culture of marine diatoms under silicate limitation. I. Synchronized life cycle of Skeletonema costatum. J. Phycol. 9, 175–180 (1973)
Dixon, M.R. and E.C. Webb: Enzymes, 950 pp. New York: Academic Press 1964
Dugdale, R.C. and J.J. MacIsaac: A computational model for the uptake of nitrogen in the Peru upwelling regions. Investigación pesq. 35, 299–308 (1971)
Eppley, R.W. and J.L. Coatsworth: Uptake of nitrate and nitrite by Ditylum brightwellii-kinetics and mechanisms. J. Phycol. 4, 151–156 (1968)
—— and L. Solorzano: Nitrate reductase in marine phytoplankton. Limnol. Oceanogr. 14, 194–205 (1969)
— and J.N. Rogers: Inorganic nitrogen assimilation of Ditylum brightwellii, a marine plankton diatom. J. Phycol. 6, 344–351 (1970)
Guillard, R.R.L. and J.H. Ryther: Studies of marine plankton diatoms. I. Cyclotella nana (Hustedt) and Detonula confervacea (Cleve) Gran. Can. J. Microbiol. 8, 229–239 (1962)
Harrison, P.J., H.L. Conway and R.C. Dugdale: Marine diatoms grown in chemostats under silicate or ammonium limitation. I. Cellular chemical composition and steady-state growth kinetics of Skeletonema costatum. Mar. Biol. 35, 177–186 (1976)
Koroleff, F.: Direct determination of ammonia in natural waters as indophenol blue. Int. Counc. Explor. Sea Comm. Meet. C:9, p. 19 (1969)
Ludwig, C.A.: The availability of different forms of nitrogen to a green alga (Chlorella). Am. J. Bot. 25, 448–458 (1938)
Lycklama, J.C.: The absorption of ammonium and nitrate by perennial ryegrass. Acta bot. neerl. 12, 361–423 (1963)
MacIsaac, J.J. and R.C. Dugdale: Interactions of light and inorganic nitrogen in controlling nitrogen uptake in the sea. Deep-Sea Res. 19, 209–232 (1972)
Pavlou, S.P., G.E. Friederich and J.J. MacIsaac: Quantitative determination of total organic nitrogen and isotope enrichment in marine phytoplankton. Analyt. Biochem. 61, 16–24 (1974)
Prochazkova, L.: Spectrophotometric determination of ammonia as rubazoic acid with dispyrazalone reagent. Analyt. Chem. 36, 865–871 (1964)
Shields, D. and E. Pollack: Chemostat laboratory operating system. Decoscope 12 (3), 1–15 (1972)
Sims, A.P., B.J. Folkes and (in part) A.H. Bussey: Mechanisms involved in the regulation of nitrogen assimilation in micro-organisms and plants. In: Recent aspects of nitrogen metabolism in plants, pp 91–114, Ed. by E.J. Hewitt and C.V. Cutting. New York: Academic Press 1968
Slawyk, G. and J.J. MacIsaac: The comparison of two automated ammonium methods in a region of coastal upwelling. Deep-Sea Res. 19, 521–524 (1972)
Strickland, J.D.H., O. Holm-Hansen, R.W. Eppley and R.J. Linn: The use of a deep tank in plankton ecology. I. Studies of the growth and composition of phytoplankton crops at low nutrient levels. Limnol. Oceanogr. 14, 23–34 (1969)
Syrett, P.J.: The assimilation of ammonia by nitrogen-starved cells of Chlorella vulgaris. II. The assimilation of ammonia to other compounds. Ann. Bot. 17, 20–36 (1953)
—: The assimilation of ammonia and nitrate by nitrogen-starved cells of Chlorella vulgaris. II. The assimilation of large quantities of nitrogen. Physiologia Pl. 9, 19–27 (1956)
— and I. Morris: The inhibition of nitrate assimilation by amonium in Chlorella. Biochim. biophys. Acta 67, 566–575 (1963)
University of Washington: R.V. T.G. Thompson Cruise 67 (Mescal-I, Outfall-I). Part II: Outfall-I — Hydrography and productivity. Compiled by T. Whitledge and D. Bishop. Spec. Rep. Dep. Oceanogr. Univ. Wash. 51, 1–391 (1972)
Whitledge, T.E.: The regeneration of nutrients by nekton in the Peru upwelling system, Ph.D. dissertation, 114 pp. University of Washington, Seattle 1972
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J.S. Pearse, Santa Cruz
Contribution No. 936 from the Department of Oceanography, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington 98195, USA. This paper represents a portion of a dissertation submitted to the Department of Oceanography, University of Washington, Seattle, in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the Ph.D. degree.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Conway, H.L. Interactions of inorganic nitrogen in the uptake and assimilation by marine phytoplankton. Mar. Biol. 39, 221–232 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00390996
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00390996