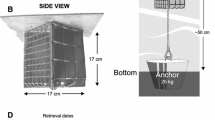
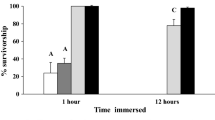
Abstract
The importance of predators in controlling the densities of infaunal (>0.5 mm) organisms was investigated in the mesohaline region of the Upper Chesapeake Bay (USA) using field experiments. The role of predators in controlling infaunal density and community characteristics varied with habitat type, season (i.e., predator abundance) and developmental or successional stage of the community. Few infaunal species were adversely affected by predator exclusion. Species that increased greatly in abundance in the absence of predators (e.g. Eteone heteropoda, Streblospio benedicti, Nereis succinea, and juvenile Macoma balthica and Mya arenaria) lived near the sediment-water interface and had major population pulses from fall through spring. Species whose abundances increased moderately or were not affected by predator exclusion were deeper burrowing organisms (e.g. Heteromastus filiformis and adult Mya arenaria), or were relatively small organisms (e.g. Paraprionospio pinnata, Scolecolepides viridis and Peloscolex gabriellae) whose principal predators could be other members of the infauna. Competition did not appear to be an important factor controlling infaunal density in these experiments.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Abbe, G. R.: Blue crab studies. In: Non-radiological environmental monitoring report, Calvert Cliffs nuclear power plant, pp 9-1 to 9-24. Prepared by Baltimore Gas and Electricity Company and the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia for the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission 1978. (Copies available from: The Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, Division of Limnology and Ecology, 19th Street and the Parkway, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19103, USA)
Arntz, W. E.: Results and problems of an “unsuccessful” benthos cage experiment (western Baltic). In: Biology of benthic organisms, pp 31–44. Ed. by B. F. Keegan, P. O. Ceidigh and P. J. S. Boaden. New York: Pergamon Press 1977
Boesch, D. F.: Classification and community structure of macrobenthos in the Hampton Roads area, Virginia. Mar. Biol. 21, 226–244 (1973)
Boesch, D. F.: A new look at the distribution of benthos along the estuarine gadient. In: Ecology of marine benthos, pp 245–266. Ed. by B. C. Coull. Columbia, South Carolina: University of South Carolina Press 1977
Boesch, D. F., M. L. Wass and R. W. Virnstein: The dynamics of estuarine benthic communities. In: Estuarine processes, Vol. 1. Uses, stresses, and adaptation to the estuary, pp 177–196. Ed. by M. L. Wiley. New York: Academic Press 1976
Brownlee, K. A.: Statistical theory and methodology in science and engineering, 590 pp. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc. 1965
Buchanan, J. B. and J. M. Kain: Measurement of the physical and chemical environment. In: Methods for the study of marine benthos, pp 30–58. Ed. by N. A. Holme and A. D. McIntyre. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications 1971
Buchanan, J. B., P. F. Kingston and M. Sheader: Long-term population trends of benthic macrofauna in the offshore mud of the Northumberland coast. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 54, 785–795 (1974)
Buttleman, K. P.: Aquatic chemistry and bacteriological studies. In: Non-radiological environmental monitoring report, Calvert Cliffs nuclear power plant, January–December 1977, pp 5.1-1 to 5.1-128. Prepared by Baltimore Gas and Electricity Company and the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia for the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission 1978. (Copies available from: The Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, Division of Limnology and Ecology, 19th Street and the Parkway, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19103, USA)
Carriker, M. R.: Ecology of estuarine benthic invertebrates: a perspective. In: Estuaries, pp 442–487. Ed. by G. H. Lauff. Washington, D. C.: American Association for the Advancement of Science 1967. (Publs Am. Ass. Advmt Sci. No. 83)
Chao, L. N. and J. A. Musick: Life history, feeding habits and functional morphology of juvenile sciaenid fishes in the York River estuary, Virginia. Fish. Bull. U.S. 75, 657–702 (1977)
Connell, J. H.: The influence of interspecific competition and other factors on the distribution of the barnacle Chthamalus stellatus. Ecology 42, 710–723 (1961a)
Connell, J. H.: Effects of competition, predation by Thais lapillus and other factors on natural populations of the barnacle Balanus balanoides. Ecol. Monogr. 31, 61–104 (1961b)
Dayton, P. K.: Competition, disturbance and community organization: the provision and subsequent utilization of space in a rocky intertidal community. Ecol. Monogr. 41, 351–389 (1971)
Diaz, R. J.: Asiatic clam, Corbicula manilensis (Philippi), in the tidal James River, Virginia. Chesapeake Sci. 15, 118–119 (1974)
Frankenberg, D.: The dynamics of benthic communities off Georgia, U.S.A. Thalassia jugosl. 7, 49–55 (1971)
Hamilton, D. H. and R. S. LaPlante: Cove Point benthic study, 66 pp. Solomons, Md.: Chesapeake Biological Laboratory 1972 (Rep. Chesapeake Biol. Lab., Natural Resources Institute Ref. No. 72-36)
Hixon, J. H. III: Fish bottom trawling. In: Semi-annual environmental monitoring report, Calvert Cliffs nuclear power plant, pp 8-1 to 8-54. Prepared by Baltimore Gas and Electric Company and the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia for the Nuclear Regulatory Commission 1977. (Copies available from: The Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, Division of Limnology and Ecology, 19th Street and the Parkway, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19103, USA)
Holland, A. F., N. K. Mountford and J. A. Mihursky: Temporal variation in upper bay mesohaline benthic communities: I. the 9-m mud habitat. Chesapeake Sci. 18, 370–378 (1977)
Jackson, J. B. C.: The ecology of molluscs of Thalassia communities. I. Distribution, environmental physiology, and ecology of shallow water species. Bull. mar. Sci. 23, 313–350 (1973)
Jackson, J. B. C.: Biogeographic consequences of eurytopy and stenotopy among marine bivalves and their evolutionary significance. Am. Nat. 108, 54–56 (1974)
Jacobs, F.: Zooplankton distribution, biomass, biochemical composition and seasonal community structure in lower Chesapeake Bay, 104 pp. Ph.D. dissertion, University of Virginia, Virginia, Institute of Marine Science, Gloucester Point, Virginia 1978
Kinne, O.: Salinity: animals-invertebrates. In: Marine ecology, Vol. I. Part 2. pp 821–995. Ed. by O. Kinne. London: Wiley-Interscience 1971
Lie, U. and R. A. Evans: Long-term variability in the structure of subtidal benthic communities in Puget Sound, Washington, USA. Mar. Biol. 21, 122–126 (1973)
Lippson, A. J.: The Chesapeake Bay in Maryland, 55 pp. Baltimore, Md: Johns Hopkins University Press 1973
Lippson, A. J., M. S. Haire, A. F. Polgar and W. A. Richkus: Environmental atlas of the Potomac estuary, 288 pp. Baltimore, Md.: Martin Marietta Corporation (1450 South Rolling Rd) 1979
McCall, P. L.: Community patterns and adaptive strategies of the infaunal benthos of Long Island Sound. J. mar. Res. 35, 221–266 (1977)
McCarthy, J. J., W. Rowland Taylor and M. E. Loftus: Significance of nanoplankton in the Chesapeake Bay estuary and problems associated with the measurement of nanoplankton productivity. Mar. Biol. 24, 7–16 (1974)
Menge, B. A.: Organization of the New England rocky intertidal community: role of predation, competition and environmental heterogeneity. Ecol. Monogr. 46, 355–393 (1976)
Menge, B. A. and J. P. Sutherland: Species diversity gradients: synthesis of the roles of predation, competition and temporal heterogeneity. Am. Nat. 110, 351–369 (1976)
Mountford, N. K., A. F. Holland and J. A. Mihursky: Identification and description of macrobenthic communities in the Calvert Cliffs region of the Chesapeake Bay. Chesapeake Sci. 18, 360–369 (1977)
Mountford, N. K., D. K. Phillips and J. A. Mihursky: Benthic animal-sediment investigations. In: Ecological effects of nuclear steam electric station operations on estuarine systems. Second Progress Report to Atomic Energy Commission, pp 192–344. Ed. by J. A. Mihursky. Solomons, Md.: Chesapeake Biological Laboratory 1973. (Natural Resources Institute Ref. No. 73-83)
Naiman, R. J., J. H. Hixon, III and T. Capizzi: Fish bottom trawling. In: Non-radiological environmental monitoring report, Calvert Cliffs nuclear power plant, January–December 1977, pp 8-1 to 8-37. Prepared by Baltimore Gas and Electric Company and the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia for the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission 1978. (Copies available from: The Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, Division of Limnology and Ecology, 19th Street and the Parkway, Philadelphia, Pennsyvania, USA)
Naqvi, S. M. Z.: Effects of predation on infaunal invertebrates of Alligator Harbor, Florida. Gulf Res. Rep. 2, 313–321 (1968)
Orth, R. J.: The importance of sediment stability in seagrass communities. In: Ecology of marine benthos, pp 281–300. Ed. by B. C. Coull. Columbia, South Carolina: University of South Carolina Press 1977
Paine, R. T.: Food web complexity and species diversity. Am. Nat. 100, 65–75 (1966)
Paine, R. T.: A note on trophic complexity and community stability. Am. Nat. 103, 91–93 (1969)
Paine, R. T.: Intertidal community structure. Experimental studies on the relationship between a dominant competitor and its principal predator. Oecologia 15, 93–120 (1974)
Peterson, C. H.: Competitive organization of the soft-bottom macrobenthic communities of Southern California lagoons. Mar. Biol. 43, 343–359 (1977)
Pfitzenmeyer, H. T.: Periods of spawning and settling of the soft-shelled clam, Mya arenaria at Solomons, Maryland. Chesapeake Sci. 3, 114–120 (1962)
Pfitzenmeyer, H. T.: Benthos of Maryland waters in and near C and D canal, 41 pp. Solomons, Md.: Chesapeake Biological Laboratory 1973. (Rep. Chesapeake Biol. Lab., Natural Resources Institute Ref. No. 73-113)
Pfitzenmeyer, H. T. and K. G. Drobeck: The occurrence of the brackish water clam, Rangia cuneata, in the Potomac River, Maryland. Chesapeake Sci. 5, 209–212 (1964)
Polgar, T. T.: Characterization of benthic community responses to environmental variations by multiple discriminant analysis. In: Fisheries and energy production, pp 267–292. Ed. by S. B. Salia. Lexington, Mass.: Lexington Books, D. C. Heath & Co. 1975
Rasmussen, E.: Systematics and ecology of the Isefjord marine fauna (Denmark) Ophelia 11, 1–495 (1973)
Reish, D. J. and H. A. Winter: The ecology of Alamitos Bay, California, with special reference to pollution. Calif. Fish Game 40, 105–121 (1954)
Rosenberg, R.: Benthic faunal recovery in a Swedish fjord following closure of a sulphite pulp mill. Oikos 23, 93–108 (1972)
Rowe, G. T.: The effects of pollution on the dynamics of the benthos of New York Bight. Thalassia jugosl. 7, 353–359 (1971)
Sage, L. E. and A. G. Bacheler: Zooplankton entrainment. In: Non-radiological environmental monitoring report, Calvert Cliffs nuclear power plant, January–December 1977, pp 12.2-1 to 12.2-54. Prepared by Baltimore Gas and Electric Company and the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia for the Nuclear Regulatory Commission 1978. (Copies available from: The Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, Division of Limnology and Ecology, 19th Street and the Parkway, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19103, USA)
Sage, L. E. and M. M. Olsen: Zooplankton entrainment. In: Semi-annual environmental monitoring report, Calvert Cliffs nuclear power plant, pp 13.2-1 to 13.2-71. Prepared by Baltimore Gas and Electric Company and the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia for the Nuclear Regulatory Commission 1977. (Copies available from: The Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, Division of Limnology and Ecology, 19th Street and the Parkway, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19103, USA)
Shaw, W. N.: Seasonal setting patterns of five species of bivalves in the Tred Avon River, Maryland. Chesapeake Sci. 6, 33–37 (1965)
Simons, W. I.: Water chemistry and bacteriological studies. In: Semi-annual environmental monitoring report, Calvert Cliffs nuclear power plant, pp 5.1-1 to 5.1-133. Prepared by Baltimore Gas and Electric Company and the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia for the Nuclear Regulatory Commission 1977. (Copies available from: The Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, Division of Limnology and Ecology, 19th Street and the Parkway, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19103, USA)
Sulkin, S. D.: Blue crab study in Chesapeake Bay, Maryland, 66 pp. Solomons, Md.: Chesapeake Biological Laboratory 1973. (Rep. Chesapeake Biol. Lab., Natural Resources Institute Ref. No 73-94)
Van Engel, W. A.: The blue crab and its fishery in Chesapeake Bay. Part. 1. Reproduction, early development, growth and migration. Comml Fish. Rev. 20, 6–17 (1958)
Van Valkenburg, S. D. and D. A. Flemer: The distribution and productivity of nannoplankton in a temperate esuarine area. Estuar. cstl mar. Sci. 2, 311–322 (1974)
Virnstein, R. W.: The importance of predation by crabs and fishes on benthic infauna in Chesapeake Bay. Ecology 58, 1199–1217 (1977)
Virnstein, R. W.: Predator caging experiments in soft sediments: caution advised. In: Estuarine interactions, pp 261–273. Ed. by M. L. Wiley, New York: Academic Press 1978
Virnstein, R. W.: Predation on estuarine infauna: response patterns of component species. Estuaries, Solomons, Md 2, 69–86 (1979)
Walkley, A. and I. A. Black: An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Sci. 37, 29–38 (1934)
Woodin, S. A.: Polychaete abundance patterns in a marine soft-sediment environment: the importance of biological interactions. Ecol. Monogr. 44, 171–187 (1974)
Woodin, S. A.: Adult-larval interactions in dense infaunal assemblages: patterns of abundance. J. mar. Res. 34, 25–41 (1976)
Young, D. K. and M. W. Young: Community structure of the benthos associated with seagrass of the Indian River estuary, Florida. In: Ecology of marine benthos, pp 359–382. Ed. by B. C. Coull. Columbia, South Carolina: University of South Carolina Press 1977
Young, D. K. and M. W. Young: Regulation of species densities of seagrass-associated macrobenthos: evidence from field experiments in the Indian River estuary, Florida. J. mar. Res. 36, 569–593 (1978)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by I. Morris, West Boothbay Harbor
This work is Contribution No. 973 of the Center for Environmental and Estuarine Studies of the University of Maryland
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holland, A.F., Mountford, N.K., Hiegel, M.H. et al. Influence of predation on infaunal abundance in Upper Chesapeake Bay, USA. Mar. Biol. 57, 221–235 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00390739
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00390739