Abstract
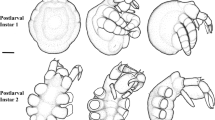
The life history of the dorvilleid polychaete Stauronereis rudolphi (Delle Chiaje) was studied through the F2 generation under laboratory conditions. The species released its gametes into the water where fertilization occurred. The pelagic larvae swam for one week before settling. Segments were added successively and sexual maturity was reached in one year of laboratory culture. Spawned adults recovered and began feeding a few days after spawning. The culture techniques and foods used to rear developing eggs, larvae, juveniles, and adults were described. Comparisons were made with other developmental studies in the superfamily Eunicea.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Aiyar, R. G.: An account of the development and breeding habits of a brackish water polychaete worm of the genus Marphysa. Linn. Soc. J. 37, 398–404 (1931).
—, and M. K. Panikkar: Observations on the swarming habits and lunar periodicity of Platynereis sp. from the Madras harbour. Indian Acad. Sci. Proc. 10, 113–140 (1937).
Allen, M. J.: Observations on living developmental stages of the polychaete, Diopatra cuprea (Bosc). Anat. Rec. 111, 550 (1951).
—: An example of parasitism among polychaetes. Nature 199, 197 (1952).
—: Development of the polychaete, Diopatra cuprea (Bosc). Anat. Rec. 117, 572–573 (1953).
—: The breeding of polychaetous annelids near Parguera, Puerto Rico. Biol. Bull. 113, 49–57 (1957).
—: Embryological development of the polychaetous annelid, Diopatra cuprea (Bosc). Biol. Bull. 116, 339–361 (1959).
—: A cytolochemical study of the developing oocytes and attached nurse cells of the polychaetous annelid Diopatra cuprea (Bosc). Acta. Embry. Morph. Exp. 4, 219–238 (1961).
Andrews, E. A.: Report upon the annelida polychaeta of Beaufort, North Carolina. Proc. U. S. Nat. Mus. 14, 277–302 (1891 a).
—: Reproductive organs of Diopatra. J. Morph. 5, 113–124 (1891 b)
Bacci, G.: Existence of true males and females in a hermaphrodite population of Ophryotrocha puerilis. Experientia 7, 222–224 (1951).
—, and O. Bortesi: Existence of multiple sex genotypes in the hermaphrodite polychaete worm Ophryotrocha puerilis siberti. Nature 190, 838 (1961).
—, and M. La Greca: Genetic and morphological evidence for subspecific differences between Naples and Plymouth populations of Ophryotrocha puerilis. Nature 171, 1115 (1953).
Banse, K.: Polychaetous annelids from Puget Sound and the San Juan Archipelago, Washington. Proc. Biol. Soc. Washington 76, 197–208 (1963).
Bonnier, J.: Notes sur les annélides du Boulonnais l'Ophryotrocha puerilis Clap. et Metsch., et son appareil maxillarie. Bull. scient. Fr. Belg. 25, 198–226 (1893).
Borradaile, L. A.: On the spawn and young of a polychaete worm of the genus Marphysa. Proc. Zool. Soc. London 2, 714–720 (1901).
Braem, F.: Zur Entwicklungsgeschichte von Ophryotrocha puerilis Clap. Metsch. Z. wiss. Zool. Leipzig 57, 187–223 (1893).
Burrows, W.: Periodic spawning of “palolo” worm in Pacific waters. Nature 155, 47–48 (1945).
Caspers, H.: Beobachtungen über Lebensraum und Schwarmperiodizität des Palolowurmes Eunice viridis (Polychaeta, Eunicidae). Int. Revue ges. Hydrobiol. 46, 175–183 (1961).
Choe, S.: On the life history of the polychaete worm Diopatra neapolitana Delle Chiaje. Bull. Japanese Soc. Sci. Fish 26, 430–437 (1960).
Claparède, E.: Les annélides chétopodes du golfe de Naples. Soc. Phys. Geneve, Mém. 19, 313–584 (1868).
—, and E. Metschnikoff: Beitrag zur Kenntnis der Entwicklungsgeschichte der Chaetopoden. Z. wiss. Zool. Leipzig 19, 163–205 (1869).
Clark, L., and W. Hess: The spawning of the Atlantic palolo, Leodice fucata (Ehlers). Tortugas Lab. Carnegie Inst. Pap. 33, 21–70 (1940a).
—, and W. Hess: The reaction of the Atlantic palolo, Leodice fucata to light. Tortugas Lab. Carnegie Inst. Pap. 33, 71–81 (1940b).
Coe, W. R.: Divergent pathways in sexual development. Science. 91, 175–182 (1940).
Fage, L., and R. Legendre: Pêches planctoniques à la lumière effectuées à Banyuls-sur-Mer et à Concarneau. Annélides polychètes. Arch. Zool. Exp. gén. Paris 67, 23–222 (1927).
Fauvel, P.: Polychètes errantes. Faune de France, Paris 5, 1–488 (1923).
Fewkes, J. N.: On the development of certain worm larvae. Mus. Comp. Zool. Bull. 11, 167–208 (1883).
Franzén, A.: On spermiogensis, morphology of the spermatozoan and of fertilization among invertebrates. Zool. Bidrag, Uppsala 31, 356–482 (1956).
Gilpin-Brown, J. B.: The reproduction and larval development of Nereis fucata (Savigny). J. Mar. Biol. Assoc. 38, 65–80 (1959).
Geavier, C.: La ponte et l'incubation chez les annélides polychètes. Ann. Sci. Nat. Zool. Paris 10, 153–247 (1923).
Geavier, C., and J. L. Dantan: Pêches nocturnes à la lumière dans la Baie d'Alger. Annélides polychètes. Inst. Oceanogr. Paris, Ann. n. s. 5, 1–187 (1928).
Hartman, O.: New species of polychaetous annelids from southern California. Allan Hancock Found. Pac. Exped. 7, 157–172 (1939).
—: Polychaetous annelids. Pt. 5. Eunicea. Allan Hancock Found. Pac. Exped. 10, 1–238 (1944).
—: The marine annelids of North Carolina. Duke Univ. Mar. Sta. Bull. 2, 1–54 (1945).
—: Catalogue of the polychaetous annelids of the world. Parts I, II, supplement 60–65 and index. Allan Hancock Found. Publ. Occ. Pap. 23, 1–628, suppl. 197 pp (1959).
—: Deep-water benthic polychaetous annelids off New England to Bermuda and other north Atlantic areas. Allan Hancock Found. Publ. Occ. Pap. 28, 1–378 (1965).
Hartnoll, R. G.: Iphtime cuenoti Fauvel (Eunicidae), a polychete new to British waters. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. 5, 93–96 (1962).
Heider, K.: Über Zahnwechsel bei polychaeten Anneliden. Sber. Akad. Wiss. Berlin (Phys. Math. Kl.) pp. 488–491 (1922).
Herpin, R.: Recherches Biologiques sur la réproduction et le dévelopement de quelques annélides polychaètes. Soc. Sci. Nat. l'Ouest France, Nantes, Bull. 4, 1–250 (1926).
Horst, R.: Wowo and palolo worms. Nature 69, 582 (1904).
Keishnan, G.: The development of Diopatra variabilis (Southern). Z. wiss. Zool. Leipzig 147, 513–525 (1926).
Krishnamoorthi, B.: Studies on the osmotic properties of the eggs and larvae of a brackish-water polychaete, Marphysa gravelyi Southern. Proc. Indian, Acad. Sci. 34, 199–209 (1951).
Mayer, A. G.: An Atlantic palolo, Staurocephalus gregaricus. Bull. Mus. Comp. Zool. 36, 1–14 (1900).
—: The Atlantic palolo (Eunice fucata). Brooklyn Mus. Bull. 1, 93–103 (1902).
—: The annual breeding-swarm of the Atlantic palolo. Tortugas Lab. Carnegie Inst. Pap. 102, 105–112 (1908).
—: The annual swarming of the Atlantic palolo (Eunice fucata). Int. Zool. Cong. Cambridge Proc. 7, 147–151 (1912).
Monro, C. C. A.: On the post-larval stage in Diopatra cuprea Bosc. Ann. Mag. Nat. Hist. 9, 193–199 (1924).
Moore, J. P.: Additional new species of polychaete from the North Pacific. Acad. Nat. Sci. Philadelphia Proc. 58, 217–260 (1906).
Okuda, S.: Studies on the development of annelida polychaeta. Fac. Sci. Hokkaido Imp. Univ. J. 9, 115–219 (1946).
Parenti, U.: Self-fertilization in Ophryotrocha labronica. Experentia 16, 413–414 (1960).
Pettibone, M. H.: Endoparasitic polychaetous annelids of the family Arabellidae with a description of new species. Biol. Bull. 113, 170–187 (1957).
—: Marine polychaete worms of the New England region. I. Aphroditidae through Trochaetidae. U. S. Nat. Mus. Bull. 227, 1–356 (1963).
Pillai, T. G.: Studies on a brackish-water polychaetous annelid, Marphysa borradailei sp. n. from Ceylon. Ceylon J. Sci. Biol. 1, 94–106 (1958).
Reish, D. J.: The life history of the polychaetous annelid Neanthes caudata (Delle Chiaje) including a summary of development in the family Nereidae. Pac. Sci. 11, 216–228 (1957).
—: The use of the sediment bottle, collector for monitoring polluted marine waters. California Fish Game 47, 261–272 (1961).
—, and T. L. Richards: A culture method for maintaining large populations of polychaetous annelids in the laboratory. Turtox News 44, 16–17 (1966).
Society of Photozologists, Committee on Cultures: A catalogue of laboratory strains of free-living and parasitic protozoa. J. Protozool. 5, 1–38 (1958).
Southern, R.: Polychaeta of the Chilka Lake and also of fresh and brackish waters in other parts of India. Mem. Indian Mus. Calcutta 5, 563–659 (1921).
Webster, H. E., and J. E. Benedict: The annelida chaetopoda from Provincetown and Wellfleet, Massachusetts. Rep. U. S. Fish Comm. for 1881. pp. 699–747 (1884).
Wilson, E. B.: Observations on the early developmental stages of some polychaetous annelids. Stud. Biol. Lab. Hopkins Univ. 2, 271–299 (1882).
Åkesson, B.: The embryology of polychaete Eunice kobiensis. Acta zool., Stockh. 48, 141–192 (1967).
—: On the biology and larval morphology of Ophryotrocha puerilis Claparède & Metschnikov (Polychaeta). Ophelia 4, 111–119 (1967).
Hartman, O.: Larval development of benthic invertebrates in Antarctic sea: early development of Nothria notialis (Monro) and Paronuphis antarctica (Monro) in Bransfield strait, Antaretic peninsula. Symp. Pacific-Antaretic Sci. Polar Res. Proc. Tokyo, pp. 154–157 (1967).
—: Polychaetous annelids collected by the USNS Eltanin and Staten Island cruises, chiefly from Antarctic seas. Allan Hancock Monogr. mar. Biol. 2, 1–387 (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. L. Voss, Miami
This study was a portion of a thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Arts in the Department of Biology, California State College at Long Beach. It was in part supported by research grant WP-00531-02 from the National Institute of Health, U. S. Public Health Service, under supervision of Dr. Donald J. Reish. Contribution No. 1 of the Ira C. Darling Center for Research, Teaching and Service, University of Maine, Maine 04573, U.S.A.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Richards, T.L. Reproduction and development of the polychaete Stauronereis rudolphi, including a summary of development in the superfamily Eunicea. Marine Biol. 1, 124–133 (1967). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00386517
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00386517