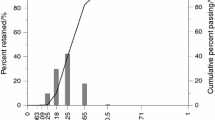
Abstract
The process of removing a multicomponent binder from a metal powder compact has been investigated. Model experiments of debinding were performed on compounds consisting of less than 40 vol% binders (low molecular weight polyethylene, paraffin and Carnauba waxes) and more than 60 vol% metal content. As typical representatives for injection moulding morphology and meeting all other requirements for optimal powder characteristics, elemental powders of the Fe-Al system were used. Viscosity results over a wide range of shear rates for various plastisols are presented as functions of binder system composition and metal powder content. Based on the rheological response, an optimization of plastisol formulation was performed. Results are reported on three series of debinding modes using heat and fluid wicking in air and in nitrogen. The time dependence of fractional debinding, x(t), during wicking has been estimated using a model. Direct observation by SEM of binder distribution and pore structure evolution at different stages of the debinding process was made. Wick-assisted thermal debinding in nitrogen proved to be an effective debinding method in terms of shape preservation and the absence of defects in the studied material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
P. Calvert and M. Cima, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 73 (1990) 575.
G. C. Stangle and I. A. Aksay, Chem. Eng. Sci. 45 (1990) 1719.
J. R. Gasperovich and R. C. Drewes, Int. J. Powder Metall. 27(2) (1991) 169.
S. T. Lin and R. M. German, Powder Metall Int. 21(5) (1989) 10.
C. W. Finn, Int. J. Powder Metall 27(2) (1991) 127.
K. S. Hwang and K. H. Lin, ibid. 28(4) (1992) 357.
H. H. Angermann, F. K. Yang and van der Biest, J. Mater. Sci. 27 (1992) 2534.
C. G. McKamey, J. H. DeVan, P. F. Tortorelli and V. K. Sikka, J. Mater. Res. 6 (1991) 1779.
R. M. German, “Powder Injection Molding” (Metal Powder Industries Federation, Princetown, NJ, 1990).
K. F. Hens, in “Proceedings of the Intensive course on MIM”, Technical University Delft, The Netherlands (1992) p. 3–1.
M. Vogel, “Nichtmetalle in Metallen” (D. Hischfeld, Munster, Deutche Gesellschaft fur Metallkunde, Oberursel, 1987) p. 197.
I. Majewska-Glabus, “Plastisol formulation with Fe3Al-X intermetallics for injection moulding”, Technical report, Delft University of Technology, Laboratory for Material Science. Delft, The Netherlands (1990).
I. Majewska-Glabus, L. Zhuang, R. Vetter and J. Duszczyk, in “Proceedings of High Temperature Intermetallics” (The Royal Society, London, 1991) p. 162.
H. Zhang, R. M. German and A. Bose, Int. J. Powder Metall 26(3) (1990) 217.
K. F. Hens, S. T. Lin, R. M. German and D. Lee, J. Metals 41(8) (1989) 17.
M. Sanders, Master Thesis, Delft University of Technology, Delft, The Netherlands (1991).
R. M. German, Int. J. Powder Metall 23(4) (1987) 237.
R. Vetter, M. Sanders, I. Majewska-Glabus, L. Z. Zhuang and J. Duszczyk, J. Powder Metall, in press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Majewska-Glabus, I., Zhuang, L., Vetter, R. et al. Thermal debinding of Fe3Al-X metal powder compacts. Journal of Materials Science 30, 6209–6217 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00369668
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00369668