Abstract
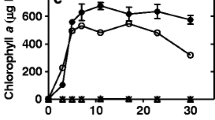
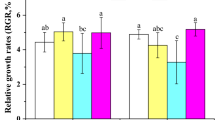
Marine phytoplankton forms are frequently exposed to sudden biological changes such as rapid rise in water temperature and chlorine content of their environment, resulting from the use of sea water for cooling purposes by electric generators. The direct influence of these effluents, i.e. inhibitory effects of high temperature and residual chlorine on growth and photosynthesis of Chlamydomonas sp. and Skeletonema costatum, were investigated experimentally. Chlamydomonas sp. and S. costatum exposed to high temperatures were affected in their growth from 43° and 35°C, respectively, by immersion of the respective cultures in a warm bath for 10 min. Treatment at high temperatures of 40 °C and 30° ∼ 35°C for 10 min, influenced their photosynthetic activities, which were completely inhibited immediately after 10 min exposure at 42° and 37 °C, respectively. S. costatum was killed by chlorine at a concentration of 1.5 ∼ 2.3 ppm when exposed for exactly 5 or 10 min, while Chlamydomonas sp. was not irreversibly damaged even at 20 ppm chlorine or more with the same exposure period. These results lead to the conclusion that the high temperature of, and residual chlorine in, effuents from a power plant discharging into the open sea, should not cause great damage to marine phytoplankton in that area.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Hirayama, K. and R. Hirano: Influences of high temperature and residual chlorine on the marine planktonic larvae [Jap., Engl. Abstr.]. Bull. Fac. Fish. Nagasaki Univ. 29, (1970). (In press).
Naylor, E.: Effects of heated effluents upon marine and estuarine organisms. In: Advances in marine biology, Vol. 3, pp 63–103. Ed. by F. S. Russell. New York: Academic Press 1965.
Yamada, N.: Effects of free chlorine on the respiration of seaweeds. [Jap.]. The aquiculture 7, 3, pp 24–28 (1960).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by M. Anraku, Nagasaki
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hirayama, K., Hirano, r. Influence of high temperature and residual chlorine on marine phytoplankton. Marine Biology 7, 205–213 (1970). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00367490
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00367490