Abstract
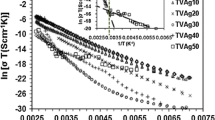
Ionic mobility, conductivity, number of charge carriers and transference number are reported for annealed and rapidly quenched [xAgl∶(1−x)AgCl] mixed systems, these results are compared with Agl. Of these three materials the quenched mixed-system had the highest Ag+ ion conductivity. Further, preliminary studies are reported where the high conductivity system (i.e. quenched 0.75 Agl∶0.25 AgCl) has been used as host material for the preparation of Ag+ ion conducting glasses and composites. Detailed thermal/phase diagram studies have also been carried out on the quenched composition. The conductivity enhancement in the quenched system is attributed to the formation of new disordered phases and the introduction of amorphisity, the simple space-charge model applicable to the annealed system failed to explain these results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
A. L. Laskar and S. Chandra (eds) “Superionic solids and solid electrolytes — recent trends” (Academic Press, NY, 1989).
P. S. Nicholson, M. S. Whittingham, G. C. Farrington, W. W. Smeltzer and J. Thomas (eds) “Solid state ionics — 91” (North Holland. Amsterdam, 1992).
B. V. R. Chowdari, S. Chandra, S. Singh and P. C. Srivastava (eds) “Solid state ionics — materials and applications” (World Scientific, Singapore, 1992).
T. Minami and N. Machida, in “Solid state ionics international conference on advanced materials — 91”, edited by M. Balakanski, T. Takahashi and H. L. Tuller (Elsevier, Amsterdam, 1992) p. 91.
C. A. Angell, Solid State Ionics 18/19 (1986) 72.
M. D. Ingram, Phys. Chem. Glasses 28 (1987) 215.
K. Shahi and J. B. Wagner jr, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 43 (1982) 713.
J. Maier, in “Superionics solids and solid electrolytes — recent trends”, edited by A. L. Laskar and S. Chandra (Academic Press, NY, 1989) p. 137.
A. K. Shukla and V. Sharma, in “Solid state ionics — materials and applications”, edited by B. V. R. Chowdari, S. Chandra, S. Singh and P. C. Srivastava (World Scientific, Singapore, 1992) p. 91.
U. Lauer and J. Maier, Solid State Ionics 51 (1992) 209.
M. Watanabe, K. Sanui, N. Ogata, T. Kobayashi and Z. Ontaki, J. Appl. Phys. 57 (1985) 123.
S. Chandra, S. K. Tolpadi and S. A. Hashimi, Solid State Ionics 28/30 (1988) 651.
R. C. Agrawal, K. Kathal, R. Chandola and R. K. Gupta, in “Solid state ionics — materials and applications”, edited by B. V. R. Chowdari, S. Chandra, S. Singh and P. C. Srivastava (World Scientific, Singapore, 1992) p. 363.
E. A. Secco, ibid.in “ p.46.
R. C. Agrawal, K. Kathal and R. K. Gupta, Unpublished work.
R. Kumar and R. C. Agrawal, Unpublished work.
R. K. Gupta and R. C. Agrawal, Unpublished work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agrawal, R.C., Gupta, R.K., Kumar, R. et al. Ionic transport in the (Agl∶AgCl) mixed-system. JOURNAL OF MATERIALS SCIENCE 29, 3673–3677 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00357334
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00357334