Abstract
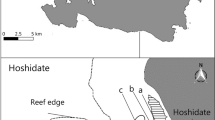
Little is known about the fish fauna of deep Posidonia australis seagrass beds in Australia. We investigated associated with the deep and shallow margins of P. australis during two surveys in Jervis Bay, New South Wales. Fish associated with deep and shallow seagrass at each of two areas within a large bed of P. australis were compared over a period of 3 mo (November 1986 to January 1987). This was followed by a larger scale survey in which we compared fish found at the two depths within three large beds of P. australis in Jervis Bay over 2 yr (September 1988 to June 1990). In the smaller scale survey there were marked dissimilarities in relative abhundance and composition of species between samples from deep and shallow P. australis. There were also significant differences in abundance between deep and shallow seagrass on most occasions for the majority of the dominant fish species. As a result of the small-scale survey, we concluded that differences in species composition of fish associated with deep and shallow P. australis may have been due to the presence of species from nearby bare substrate among the sparser leaves of the deep seagrass. The results of the smaller scale survey were not confirmed by the larger survey. The relative abundances of species in samples from deep and shallow P. australis were not dissimilar for all beds. In addition, it was rare for any of the dominant species to have significantly different abundances in deep and shallow seagrass. There was little evidence that the species composition of fish associated with deep P. australis was strongly influenced by the fauna of deep bare substrate. Rather, samples from deep P. australis were far more similar to those from shallow P. australis than to a comparable set of samples collected from deep bare substrata. This study demonstrates how the results and conclusions of small-scale survey work, a feature of many environmental impact asseesments, can be misleading when applied to larger spatial and temporal scales, even within the same bay.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Andrew, N. L., Mapstone, B. D. (1987). Sampling and the description of spatial pattern in marine ecology. Oceanogr. mar. Biol. A. Rev. 25: 39–90
Bay, D. (1984). A field study of the growth dynamics and productivity of Posidonia oceanica (L.) in Calvi Bay, Corsica. Aquat. Bot. 20: 43–64
Bell, J. D., Harmelin-Vivien, M. L. (1982). Fish fauna of French Mediterranean Posidonia oceanica seagrass meadows. I. Community structure. Tethys 10: 337–347
Bell, J. D., Pollard, D. A. (1989). Ecology of fish assemblages and fisheries associated with seagrasses. In: Larkum, A. W. D., McComb, A. J., Shepherd, S. A. (eds.) Biology of seagrasses. Aquatic plant studies. II. Elsevier, Amsterdam, p. 565–609
Bell, J. D., Westoby, M. (1986). Importance of local changes in leaf height and density to fish and decapods associated with seagrasses. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 104: 249–274
Burchmore, J. J., Bell, J. D., Pollard, D. A. (1984). Community structure and trophic relationships of the fish fauna of an estuarine Posidonia australis seagrass habitat in Port Hacking, New South Wales. Aquat. Bot. 18: 71–87
Clifford, H. T., Stephenson, W. (1975). An introduction to numerical classification. Academic Press, New York
Eckert, G. J. (1985). Settlement of coral reef fishes to different natural substrata and at different depths. Proc. 5th int. coral Reef Symp. 5: 385–390. [Gabrié, C. et al. (eds.) Antenne Museum-EPHE, Moorea, French Polynesia]
Gray, C. A., Bell, J. D. (1986). Consequences of two common techniques for sampling vagile macrofauna associated with the seagrass Zostera capricorni. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 28: 43–48
Harmelin-Vivien, M. L. (1983). Etude comparative de l'ichtyofauna des herbiers de phanerogames marines en milieux tropical et tempere. Revue Ecol. (Terre Vie) 38: 179–210
Holt, S. A., Kitting, C. L., Arnold, C. R. (1983). Distribution of young red drums among different sea-grass meadows. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 112: 267–271
Larkum, A. W. D., McComb, A. J., Shepherd, S. A., (eds.) (1989). Biology of seagrasses. Aquatic plant studies. II. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Larkum, A. W. D., West, R. J. (1990). Long term changes of seagrass meadows in Botany Bay, Australia. Aquat. Bot. 37: 55–70
Leber, K. M., Greening, M. S. (1986). Community studies in seagrass meadows: a comparison of two methods for sampling macroinvertebrates and fishes. Fish. Bull. U.S. 84: 443–450
Lincoln Smith, M. (1985). The development and application of visual survey procedures for fish communities on shallow rocky reefs. M. Sc. thesis. University of Sydney
Lincoln Smith, M. (1991). Environmental impact assessment: the roles of predicting and monitoring the extent of impacts. Aust. J. mar. Freshwat. Res. 42: 603–614
Martin, F. D., Cooper, M. (1981). A comparison of fish fauna found in pure stands of two tropical Atlantic seagrasses, Thalassia testudinum and Syringodium filiforme. NE Gulf Sci. 5: 31–37
McNeill, S. E., Bell, J. D. (1992). Comparison of beam trawls for sampling macro-fauna of Posidonia seagrass. Estuaries (in press)
Middleton, M. J., Bell, J. D., Burchmore, J. J., Pollard, D. A., Pease, B. C. (1984). Structural differences in the fish communities of Zostera capricorni and Posidonia australis seagrass meadows in Botany Bay, New South Wales. Aquat. Bot. 18: 89–109
Ross, D., Daie, M., Shields, K., Huleh, C. (1986). Taxon users manuai. Edition P4. CSIRONET Reference Manual 6. CSIRO, Melbourne
Scott, J. K. (1981). The seagrass fish fauna of Geographe Bay, Western Australia. J. Proc. R. Soc. West. Aust. 63: 97–102
Shepherd, S. A., McComb, A. J., Bulthuis, D. A., Neverauskas, V., Steffensen, D. A., West, R. J. (1989). Decline of seagrasses. In: Larkum, A. W. D., McComb, A. J., Shepherd, S. A. (eds.) Biology of seagrasses. Aquatic plant studies. II. Elsevier, Amsterdam, p. 346–393
Steffe, A. S., Westoby, M., Bell, J. D. (1989). Habitat selection and diet in two species of pipefish from seagrass: sex differences. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 55: 23–30
Underwood, A. J. (1981). Techniques of analysis of variance in experimental marine biology and ecology. Oceanogr. mar. Biol. A. Rev. 19: 513–605
Weins, J. A. (1989). Spatial scaling in ecology. Funct. Ecol. 3: 385–397
West, R. J. (1990). Depth-related structural and morphological variations in an Australian Posidonia seagrass bed. Aquat. Bot. 36: 153–166
Young, P. C. (1981). Temporal changes in the vagile epibenthic fauna of two seagrass meadows (Zostera capricorni and Posidonia australis). Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 5: 91–102
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. F. Humphrey, Sydney
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bell, J.D., Ferrell, D.J., McNeill, S.E. et al. Variation in assemblages of fish associated with deep and shallow margins of the seagrass Posidonia australis . Marine Biology 114, 667–676 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00357264
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00357264