Abstract
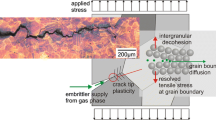
The microstructural basis of cyclic fatigue-crack propagation in monolithic alumina has been investigated experimentally and theoretically. A true cyclic fatigue effect has been verified, distinct from environmentally assisted slow crack growth (static fatigue). Microstructures with smaller grain sizes were found to promote faster crack-growth rates; growth rates were also increased at higher load ratios (i.e. ratio of minimum to maximum applied loads). Using in situ crack-path analysis performed on a tensile loading stage mounted in the scanning electron microscope, grain bridging was observed to be the primary source of toughening by crack-tip shielding. In fact, crack advance under cyclic fatigue appeared to result from a decrease in the shielding capacity of these bridges commensurate with oscillatory loading. It is proposed that the primary source of this degradation is frictional wear at the boundaries of the bridging grains, consistent with recently proposed bridging/degradation models, and as seen via fractographic and in situ analyses; specifically, load versus crack-openingdisplacement hysteresis loops can be measured and related to the irreversible energy losses corresponding to this phenomenon.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. M. Wiederhorn, B. J. Hockey and D. E. Roberts, Philos. Mag. 28 (1973) 783.
L. S. Williams, Trans. Br. Ceram. Soc. 55 (5) (1956) 287.
B.K. Sarkar and T. G. T. Glinn, ibid. 69 (5) (1970) 199.
D. A. Krohn and D. P. H. Hasselman, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 55 (1972) 208.
F. Guiu, J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 13 (1978) 1357.
E. B. Shand, Am. Ceram. Soc. Bull. 38 (1959) 653.
A. G. Evans and E. R. Fuller, Metall. Trans. 5 (1974) 27.
R. O. Ritchie and R. H. Dauskardt, J. Ceram. Soc. Jpn 99 (1991) 1047.
S. Horibe and R. Hirahara, Acta Metall. Mater. 39 (1991) 1309.
T. Hoshide, T. Ohara and T. Yamada, Int. J. Fract. 37 (1988) 47.
F. Guiu, M. J. Reece and D. A. J. Vaughan, J. Mater. Sci. 26 (1991) 3275.
H. Kishimoto, JSME Int. J. 34 (1991) 393.
S. Suresh, J. Hard Mater. 2 (1991) 29.
F. Guiu, M. Li and M. Reece, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 75 (1992) 2976.
S. Lathabai, Y. Mai and B. Lawn, ibid. 72 (1989) 1760.
T. Kawakubo and K. Komeya, ibid. 70 (1987) 400.
R. Knehans and R. Steinbrech, J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1 (1982) 327.
P. Becher, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 74 (1991) 255.
S. J. Bennison and B. R. Lawn, Acta Metall. Mater. 37 (1989) 2659.
A. G. Evans and K. T. Faber, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 67 (1984) 255.
R. M. McMeeking and A. G. Evans, ibid. 65 (1982) 242.
J. Rödel, J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 9 (1992) 323.
R. H. Dauskardt, Acta Metall. Mater. 41 (1993) 2765.
S. Lathabai, J. Rödel and B. Lawn, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 74 (1991) 1360.
P. L. Swanson, C. J. Fairbanks, B. R. Lawn, Y-W. Mai and B. J. Hockey, ibid. 70 (1987) 279.
J. Rödel, J. Kelly and B. Lawn, ibid. 73 (1990) 3313.
G. Vekinis, M. F. Ashby and P. W. R. Beaumont, Acta Metall. Mater. 38 (1990) 1151.
H. E. Lutz, X. Z. Hu and M. V. Swain, J Eur. Ceram. Soc. 9 (1992) 133.
Y. Maniette, M. Inagaki and M. Sakai, ibid. 7 (1991) 255.
D. C. Salmon and D. W. Hoeppner, in “Second Symposium on Cyclic Deformation, Fracture, and Nondestructive Evaluation of Advanced Materials,” Miami, November 1992, edited by M. R. Mitchell and O. Buck, STP 1184 (American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, PA, 1994).
C.-W. Li, D.-J. Lee and S.-C. Lui, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 75 (1992) 1777.
A. G. Evans, Mater. Sci. Eng. A143 (1991) 63.
H. Cai, K. T. Faber and E. R. Fuller, Jr, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 75 (1992) 3111.
J. C. Hay and K. W. White, ibid. 76 (1993) 1849.
T. Tanaka, N. Okabe and Y. Ishimaru, J. Soc. Mater. Sci. Jpn 38 (1989) 137.
D. Rouby and P. Reynaud, Compos. Sci. Technol. 48 (1993) 109.
R. H. Dauskardt and R. O. Ritchie, Closed Loop 17 (1989) 7.
R. O. Ritchie and W. Yu, in “Small Fatigue Cracks”, edited by R. O. Ritchie and J. Lankford (The Metallurgical Society of the American Institute of Mining, Metallurgical and Petroleum Engineers, Warrendale, PA, 1986) p. 167.
H. N. Ko, J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 5 (1986) 464.
Idem, ibid. 8 (1989) 1438.
P. C. Paris and F. Erdogan, J. Bas. Eng. Trans. ASME 85 (1963) 528.
Y. W. Mai and B. R. Lawn, J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 70 (1987) 289.
A. G. Evans and R. M. McMeeking, Acta Metall. Mater. 34 (12) (1986) 2435.
T. E. Fischer, M. P. Anderson, S. Jahanmir and R. Salher, in “Wear of Materials 1987”, Vol. 1, edited by K. C. Ludema (Asme, New York, 1987) p. 257.
N. Wallbridge, D. Dowson and E. W. Roberts, in “Wear of Materials 1983”, edited by K. C. Ludema (ASME, New York, 1983) p. 202.
R. H. VanStone, Mater. Sci. Eng. A103 (1988) 49.
B. N. Cox and D. B. Marshall, Acta Metall. 39 (1991) 579.
H. Tada, P. C. Paris and G. R. Irwin, “The Stress Analysis of Cracks Handbook”, Part III (Paris Productions, St Louis, 1985).
W. Elber, Eng. Fract. Mech. 2 (1970) 37.
S. Suresh and R. O. Ritchie, in “Fatigue Crack Growth Threshold Concepts”, edited by S. Suresh and D. L. Davidson (The Metallurgical Society of the American Institute of Mining, Metallurgical and Petroleum Engineers, Warrendale, PA, 1984) p. 227.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gilbert, C.J., Petrany, R.N., Ritchie, R.O. et al. Cyclic fatigue in monolithic alumina: mechanisms for crack advance promoted by frictional wear of grain bridges. JOURNAL OF MATERIALS SCIENCE 30, 643–654 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00356324
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00356324