Abstract
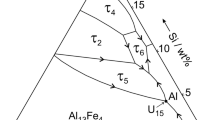
The microstructures of melt-spun Al-2.03 Fe-0.46 Ti-0.35 C (at %) superheated to 1523 K (ribbon I), and 1673 K (ribbon II), respectively, before quenching, have been characterized using analytical electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction. A duplex microstructure has been observed for ribbon I, consisting of a microcellular region, across a sharp transition, followed by a coarser cellular or dendritic structure. The intercellular phases consisted mostly of Al6Fe (few of Al3Fe) and the dispersed TiC particles distributed in the α-Al matrix with an exact orientation relationship. However, the microstructure of ribbon II comprised uniform, fine-scale dispersions of Al6Fe phase in α-Al grains, and larger size, elongated amorphous phase particles located along the grain boundaries, and approximately 0.46 at % Ti and 0.35 at % C dissolved in the α-Al matrix. During the annealing of ribbon II, the amorphous phase transformed to αT-AlFeSi phase, the Al6Fe dispersoids grew upwards and Al3Fe, TiC particles precipitated in the α-Al matrix. TiC phase formed both in ribbon I and in annealed ribbon II all had an atomic composition of TiC0.79 (the nominal atomic percent ratio for the alloy \(X_C /X_{T_{_j } } \) was 0.74) and a lattice parameter of 0.424 nm. Moreover, there is a cube-cube orientation relationship between TiC and α-Al matrix with a disregistry δ=0.049. In addition, the solidification characteristics of rapid solidification processing (RSP) Al-Fe-Ti-C alloy and mechanism of TiC formation have been discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
W. E. Quist and R. E. Lewis, in “Rapidly solidified powder aluminium alloy”, edited by M. E. Fine and E. A. Starke (American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, 1986) p. 7.
W. M. Griffith, R. E. Saders, Jr and G. L. Hildeman, in “High-strength powder metallurgy aluminium alloys”, edited by M. J. Koczak and G. J. Hildeman (The Metallurgical Society of AIME, Warrendale, PA, 1982) p. 209.
D. J. Skinner, K. Okazaki and C. M. Adams, “Rapidly solidified powder aluminum alloys”, edited by M. E. Fine and E. A. Starke (American Society for Testing and Materials, Philadelphia, 1986) p. 211.
M. H. Jacobs, A. G. Doggett and M. J. Stowell, J. Mater. Sci. 10 (1974) 1631.
W. J. Boettinger, L. A. Bendersky and J. G. Early, Metall. Trans. 17A (1986) 781.
M. G. Chu and D. A. Granger, Ibid. 21A (1990) 205.
M. DeSancis, A. P. Woodfield and M. H. Loreto, Inter. J. Rapid Solidification 4 (1988) 53.
L. F. Mondolfo, “Aluminium alloys: structure and properties” (Butterworths, New York 1976).
D. Shechtman and L. J. Swartzendruber, “Alloy phase diagrams”, edited by L. H. Bennett, T. B. Massalski and B. C. Giessen (Elsevier Science Publishing Co. Inc; New York, 1983) p. 265.
P. Skjerpe, Metall. Trans. 18A (1987) 189.
P. J. Black and J. A. Cundall, Acta Cryst. 20 (1966) 417.
J. L. Murray, “Alloy phase diagrams”, edited by L. H. Bennett, T. B. Massalski and B. C. Giessen (Elsevier Publishing Co., New York, 1983) p. 249.
“Smithells Metals Reference Book”, edited by E. A. Brandes (Butterworth & Co. Ltd. London & Boston 1983).
J. L. Murray, Metall. Trans. 19A (1988) 243.
A. Jarfors and H. Fredriksson, Microgravity Science and Technology, III 4 (1991) 216.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tong, X.C., Shen, N.F. & Liu, B.C. The structure of a rapidly solidified Al-Fe-Ti-C alloy. JOURNAL OF MATERIALS SCIENCE 30, 3680–3689 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00351885
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00351885