Abstract
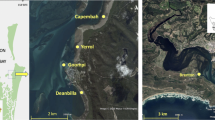
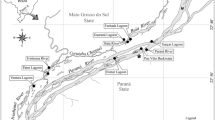
Large-scale patchiness in the distribution of the benthic fauna was investigated in Loch Etive (Scottish west coast) by two series of van Veen grab hauls. Each series was taken along a traverse across the width of the loch, with sampling points about 100 m apart. One sample series was taken on sandy mud and the other, at a greater depth, on soft mud. Two approaches in data processing were applied: (1) The variance: mean ratio and the Morisita I δ tests for significant aggregation were applied to the species abundances in the sample series; (2) 3 measures of sample homogeneity, each involving the calculation of an index of faunal similarity, were applied to the separate samples. The results, however, could not show significant differences between the two series of samples. These findings were compared to results obtained from (a) a previous study, where differences in patchiness between areas were shown for a smaller scale of sampling design in Loch Etive and neighbouring areas, and to which the I δ method is also applied here; and (b) the results of applying the variance: mean ratio and I δ tests to data published by Holme (1953). The present results indicate greater aggregation at the present scale of sampling than for the previous, smaller scale of sampling, or for the comparable scale of Holme's sampling. The degree of concordance shown by the values of I δ for the circular-design sampling to the values of the 3 measures of patchiness applied previously, and to the means of the species abundances, was measured by Spearman's rank correlation coefficient. The results clearly demonstrated the I δ values, unlike the others measured, to be almost completely independent of the mean. It was concluded that, for comparing the pattern from benthic samples using standard-size bottom samplers, where the mean may vary widely between each set of samples, the I δ method is probably most useful.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature Cited
Angel, H. H. and M. V. Angel: Distribution pattern analysis in a marine benthic community. Helgoländer wiss. Meeresunters. 15, 445–454 (1967).
Bateman, G. I.: The power of the χ2 index of dispersion test when Neyman's contagious distribution is the alternative hypothesis. Biometrika 37, 59–63 (1950).
Blackman, G. E.: Statistical and ecological studies in the distribution of species in plant communities I. Dispersion as a factor in the study of changes in plant populations. Ann. Bot. 6, 351–370 (1942).
Bray, J. R. and J. T. Curtis: An ordination of the upland forest communities of Southern Wisconsin. Ecol. Monogr. 27, 325–349 (1957).
Clarke, R. B. and A. Milne: The sublittoral fauna of two sandy bays on the Isle of Cumbrae, Firth of Clyde. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 34, 161–180 (1955).
Gage, J.: A preliminary survey of the benthic macrofauna and sediments in Lochs Etive and Creran, sea-lochs along the west coast of Scotland. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 52, 237–276 (1972a).
—: Community structure of the benthos in Scottish sea-lochs. I. Introduction and species diversity. Mar. Biol. 14, 281–297 (1972b),
— and A. D. Geekie: Community structure of the benthos in Scottish sea-lochs. II. Spatial pattern. Mar. Biol. 19, 41–53 (1973).
Holme, N. A.: The biomass of the bottom fauna in the English Channel off Plymouth. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 32, 1–49 (1953).
Jones, M. L.: A quantitative evaluation of the benthic fauna off Point Richmond, California. Univ. Calif. Publs Zool. 67, 219–320 (1961).
Morisita, M.: Measuring of the dispersion of individuals and analysis of the distributional patterns. Mem. Fac. Sci. Kyushu Univ. (Ser. E) 2, 215–235 (1959a).
— Measuring of interspecific association and similarity between communities. Mem. Fac. Sci. Kyushu Univ. (Ser. E) 3, 65–80 (1959b).
Mountford, M. D.: An index of similarity and its application to classifactory problems. In: Progress in soil zoology, pp 43–50. Ed. by P. W. Murphy. London: Butterworths 1962.
Simpson, E. H.: Measurement of diversity. Nature, Lond. 163, p. 688 (1949).
Sørensen, T.: A method establishing groups of equal amplitude in plant sociology based on similarity of species content and its application to analyses of the vegetation of Danish Commons. Biol. Skr. 5, 1–34 (1948).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. H. S. Blaxter, Oban
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gage, J., Geekie, A.D. Community structure of the benthos in Scottish sea-lochs. III. Further studies on patchiness. Marine Biology 20, 89–100 (1973). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00351448
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00351448