Abstract
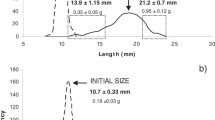
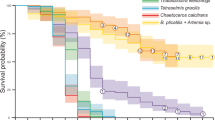
A feeding experiment was conducted on the pelagic stages of the tropical goatfish Upeneus tragula (family Mullidae) to examine how food quantity affects growth characteristics and potential success at settlement. Pelagic goatfish were collected from aggregation rafts 3 nautical miles west of Lizard Island on the northern Great Barrier Reef during December 1990. Three tanks in each of four feeding regimes were stocked with 25 pelagic goatfish between 20 and 23 mm standard length (SL). The four feeding regimes were: fed ad lib. (fed): fed once per day (f1pd); starved every second day (stld); starved for 3 d and re-fed (st3d). Fishes were fed 36 to 48 h old Artemia sp. nauplii (Ocean Star strain). Fish were removed from tanks when they underwent metamorphosis, changed pigmentation and settled to the bottom of the tanks. Morphology, muscle development, time taken to settle and biochemical condition were examined. Growth attributes of the treated fish were compared to fish which settled within 24 h of capture (field). All attributes examined were significantly influenced by the feeding treatments. Fish within the fed and st3d treatments were significantly larger and heavier than fish in the less well-fed treatments (f1pd, st1d). Similarly, concentrations of total lipid, carbohydrate and protein in the settled fish were significantly higher in the fed and st3d treatments compared with the st1d and f1pd treatments. For all these morphological and biochemical attributes the st1d and f1pd fish did not significantly differ from the field fishes, but did differ from the fed and st3d fishes. Water content was significantly higher in the f1pd, st1d and field fishes compared with the fed and st3d fish. Furthermore, the average time taken to settle followed the pattern: fed (14d)<st3d (16d)<st1d (22d)<f1pd (24d). Muscle development mirrored the patterns in fish length between treatments, being more developed in the fed treatment and least well developed in the st1d treatment. Feeding rate differed significantly between treatments and changed through the experiment for all but the fed treatment. Feeding rate decreased slightly for the f1pd and st1d treatments over the experimental period, but increased rapidly for the st3d treatment. The experiment suggests that U. tragula are physiologically well suited to exploiting a patchy food source, and that food availability within the pelagic stages can have a major influence on the growth characteristics of this reef fish at settlement. The ramifications of this finding are discussed in relation to survival and success once fish have recruited to the reef population.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Ahlström, E. H., Amaoka, K., Hensley, D. A., Moser, H. G., Sumida, B. Y. (1984). Pleuronectiformes: development. Spec. Publ. Am. Soc. Ichthyol. Herpetol. 1:640–670
Blaxter, J. H. S. (1970). Sensory depreviation and sensory input in rearing experiments. Helgoländer wiss. Meeresunters. 20:642–654
Blaxter, J. H. S. (1988). Pattern and variety in development. In: Hoar, W. S., Randall, D. J. (eds.) Fish physiology. Academic Press, New York, p. 1–58
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analyt. Biochem. 72:248–254
Browman, H. I. (1989). Embryology, ethology and ecology of ontogenetic critical periods in fish. Brain Behav. Evolut. 34:5–12
Buckley, L. J. (1984). RNA-DNA ratio: an index of larval fish growth in the sea. Mar. Biol. 80:291–298
Davis, C. S., Flieri, G. R., Wiebe, P. H., Franks, P. J. S. (1991). Micropatchiness, turbulence and recruitment in plankton. J. mar. Res. 49:109–151
Fukuhara, O. (1986). Morphological and functional development of Japanese flounder in early life stage. Bull. Jap. Soc. scient. Fish. 52:81–91
Fukuhara, O. (1988). Morphological and functional development of larval and juvenile Limanda yokohamae (Pisces: Pleuronectidae) reared in the laboratory. Mar. Biol. 99:271–281
Goldspink, G. (1980). Physiological factors influencing protein turnover and muscle growth in mammals. In: Development and specialization of skeletal muscle. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p. 65–89
Hixon, M. A. (1991). Predation as a process structuring coral-reef fish communities. In: Sale, P. F. (ed.) The ecology of fishes on coral reefs. Academic Press, New York, London 475–500
Hopkins, C. C. E., Seiring, J. V., Nyholmen, O., Hermannsen, A. (1984). Ecological energetics from total lipid and total proteins: fact and artifact using gravimetric method for lipid and biuret method for protein. Oceanogr. mar. Biol. A. Rev 22:211–261
Houde, E. D. (1989). Subtleties and episodes in the early life of fishes. J. Fish Biol. 35 (Suppl.):29–38
Jones, G. P. (1987). Competitive interactions among adults and juveniles in a coral reef fish. Ecology 68:1534–1547
Kingsford, M. J. (1990). Linear oceanographic features: a focus for research on recruitment processes. Aust. J. Ecol. 15:10–20
Kingsford, M. J., Choat, J. H. (1986). Influence of surface slicks on the distribution and onshore movement of small fish. Mar. Biol. 91:161–171
Kingsford, M. J., Wolanski, E., Choat, J. H. (1991). Influence of tidally induced fronts and Langmuir circulations on distribution and movements of presettlement fishes around a coral reef. Mar. Biol. 109:167–180
Laurence, G. C. (1975). Laboratory growth and metabolism of the winter flounder Pseudopleuronectes americanus from hatching through metamorphosis at three temperatures. Mar. Biol. 32: 223–229
Leis, J. M. (1991). The pelagic stage of reef fishes: the larval biology of coral reef fishes. In: Sale, P. F. (ed.) The ecology of fishes on coral reefs Academic Press, New York, London 183–227
Mann, K., Gallagher, B. M. (1985). Physiological and biochemical energetics of larvae of Teredo navalis L. and Bankia gouldi (Bartsch) (Bivalvia: Teredinidae). J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 85: 211–228
McCormick, M. I. (1989). Reproductive ecology of the large temperate reef fish Cheilodactylus spectabilis (Pisces: Cheilodactylidae). Mar. Ecol. Progr. Ser. 55:113–120
Miller, T. J., Crowder, L. B., Rice, J. A., Marschall, E. A. (1988). Larval size and recruitment mechanisms in fishes: toward a conceptual framework. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sciences 45:1657–1670
Munro, H. N., Fleck, A. (1966). The determination of nucleic acids. Meth. biochem. Analysis 14:113–176
Neilson, J. D., Perry, R. I., Valerio, P., Waiwood, K. G. (1986). Condition of Atlantic cod Gadus morhua larvae after transition to exogenous feeding: morphometrics, buoyancy and predator avoidance. Mar Ecol. Prog. Ser. 32:229–235
Ochi, H. (1986). Growth of the anemonefish Amphiprion clarkii in temperate waters, with special reference to the influence of settling time on the growth of 0-year olds. Mar. Biol. 92:223–229
Oliver, J. K., Willis, B. L. (1987). Coral-spawn slicks in the Great Barrier Reef: preliminary observations. Mar. Biol. 94:521–529
Pepin, P. (1991). Effect of temperature and size on development, mortality, and survival rates of the pelagic early life history stages of marine fish. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sciences 48:503–518
Pepin, P., Pearre, S., Koslow, J. A. (1987). Predation on larval fish by Atlantic mackerel, Scomber scombrus, with a comparison of predation by zooplankton. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sciences 44: 2012–2018
Peters, R. H. (1983). The ecological implications of body size. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Pfeiler, E. (1986). Towards an explanation of the developmental strategy in leptocephalous larvae of marine teleost fishes. Envir. Biol. Fish. 15:3–13
Pfeiler, E., Luna, A. (1984). Changes in biochemical composition and energy utilization during metamorphosis of leptocephalous larvae of the benefish (Albula). Envir. Biol. Fish. 10:243–251
Policansky, D. (1982). Influence of age, size and temperature on metamorphosis in the starry flounder, Platichthys stellatus. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sciences 39:514–517
Policansky, D. (1983). Size, age and demography of metamorphosis and sexual maturation in fishes. Am. Zool. 23:57–63
SAS Institute, Inc. (1987). SAS/STAT guide for personal computers. Version 6 ed. SAS Institute Inc. Cary, North Carolina
Sweatman, H. (1985). The timing of settlement by larval Dascyllus aruanus: some consequences of larval habitat selection. Proc. 5th int. coral Reef Congr. 5:367–371. [Gabrié, C. etal. (eds.) Antenne-Museum-EPHE, Moorea, French Polynesia]
Talbot, C. (1985). Laboratory methods in fish feeding and nutritional studies. In: Tytler, P., Calow, P. (eds.) Fish energetics: new perspective. Croom Helm, London, Sydney
Weatherley, A. H., Gill, H. S. (1981). Recovery growth following periods of restricted rations and starvation in rainbow trout Salmo gairdneri Richardson. J. Fish Biol. 18:195–208
Weatherley, A. H., Gill, H. S. (1985). Dynamics of increase in muscle fibres in fishes in relation to size and growth. Experientia 41:353–354
Weatherley, A. H., Gill, H. S. (1987). The biology of fish growth. Academic Press, London, New York
Weatherley, A. H., Gill, H. S., Lobo, A. F. (1988). Recruitment and maximal diameter of axial muscle fibres in teleosts and their relationship to somatic growth and ultimate size. J. Fish Biol. 33: 851–859
Werner, E. E., Gilliam, J. F. (1984). The ontogenic niche and species interactions in size-structured populations. A. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 15:393–425
Yin, M. C., Blaxter, J. H. S. (1987). Escape speeds of marine fish larvae during early development and starvation. Mar. Biol. 96: 459–468
Youson, J. H. (1988). First metamorphosis. In: Hoar, W. S., Randall, D. J. (eds.) Fish physiology. Vol. XI. The physiology of developing fish. Part B. Viviparity and posthatching juveniles. Academic Press, New York, London, p. 135–196
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. F. Humphrey, Sydney
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCormick, M.I., Molony, B.W. Effects of feeding history on the growth characteristics of a reef fish at settlement. Marine Biology 114, 165–173 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00350866
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00350866