Abstract
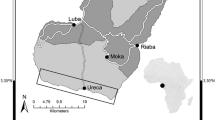
The location of spawning grounds of the squid Loligo vulgaris reynaudii (D'Orbigny) was investigated in the years 1988–1990. At least 39 spawning sites were found during this period along the inshore areas of the Eastern Cape coastline between Algoa Bay and Plettenberg Bay. The substrate chosen for egg laying was mostly fine sand or flat reef, frequently in large and relatively shettered bays. Spawning was found to occur sporadically throughout the year, and some spawning sites were used repeatedly within a particular year and in subsequent years. Squid migrate in discrete schools separated by sex in the vicinity of the spawning sites; these schools mix during spawning. Mating and egg deposition behaviour is described from observations made on the spawning grounds. Cannibalism was seen on a number of occasions, but no post-spawning mortality was recorded. Egg beds consisted mostly of large concentrations of egg strands (>3 m in diameter), with smaller aggregations of one to ten egg strands surrounding these, with single strands in the immediate vicinity. Three basic patterns of echotraces were identified and interpreted according to diving observations. These patterns were classified as loose patches, dense patches, and complex patterns. The first two represent non-spawning schooling patterns and the third, mating and egg laying behaviour. This observation led to the general classification of squid aggregations: schools (non-spawning mode) and concentrations (spawning mode). Concentrations as far as Loligo vulgaris reynaudii was concerned were further divided into two patterns: suprabenthic and benthic (spawning) squid.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Amos, D., DeMello, R. (1982). Application of multifrequency echo sounders to squid detection. In: Proc. int. Squid Symp., August 9–12, 1981, Boston, Massachusetts. UNIPUB, New York, p. 45–53
Arnold, J. M. (1962). Mating behavior and social structure in Loligo pealii. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 123: 53–57
Arnold, J. M. (1990). Squid mating behavior. In: Gilbert, D. L., Adelman, Jr., W. J., Arnold, J. M. (eds.) Squid as experimental animals. Plenum Press, New York, p. 65–75
Arnold, J. M., Williams-Arnold, L. D. (1977). Cephalopoda: Decapoda. In: Giese, A. G., Pearse, J. S. (eds.) Reproduction of marine invertebrates, Vol 4. Academic Press, New York, p. 243–290
Augustyn, C. J. (1989). Systematics, life cycle and fisheries potential of the chokker squid Loligo vulgaris reynaudii. PhD Thesis, University of Port Elizabeth, Port Elizabeth, South Africa
Augustyn, C. J. (1990). Biological studies on the chokker squid Loligo vulgaris reynaudii (Cephalopoda; Myopsida) on spawning grounds off the South-East coast of South Africa. S. Afr. J. mar. Sci. 9: 11–26
Augustyn, C. J., Grant, W. S. (1988). Biochemical and morphological systematics of Loligo vulgaris vulgaris Lamarck and Loligo vulgaris reynaudii D'Orbigny nov. comb. (Cehphalopoda: Myopsida). Malacalogia 29 (1): 215–233
Cailliet, G. M., Vaughan, D. L. (1983). A review of the methods and problems of quantitative assessment of Loligo opalescens. Biol. Oceanogr. (N.Y) 2 (2/3/4): 379–400
Christensen, M. S. (1980). Sea-surface temperature charts for Southern Africa, south of 26°S. S. Afr. J. Sci. 76: 541–546
Fields, W. G. (1965). The structure, development, food relations, reproduction and life history of the squid, Loligo opalescens Berry. Calif. Dep. Fish Game Fish Bull. 131: 1–108
Hanlon, R. T. (1982). The functional organization of chromatophores and iridescent cells in the body patterning of Loligo plei (Cephalopoda: Myopsida). Malacologia 23: 89–119
Hixon, R. F. (1983). Loligo opalescens. In: Boyle, P. R. (ed.) Cephalopod life cycles, Vol. 1. Academic Press, London, p. 95–114
Hurley, A. C. (1977). Mating behavior of the squid Loligo opalescens. Mar. Behav. Physiol. 4: 195–203
Hurley, A. C. (1978). School structure of the squid Loligo opalescens. Fish. Bull. US 76 (2): 433–442
Jefferts, K., Burczynski, J., Pearcy, W. G. (1987). Acoustical assessment of squid (Loligo opalescens) off the central Oregon coast. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sciences 44: 1261–1267
Lipinski, M. R. (1978). Stock assessment of Illex illecebrosus (Lesueur, 1821) in ICNAF Div. 4W determined by area-density method. Int. Comm NW Atlant. Fish Res Doc. 78/II/10, Ser. No. 5162
Lipinski, M. R. (1979). Universal maturity scale for the commercially important squids (Cephalopoda: Teuthoidea). The results of maturity classification of the Illex illecebrosus (LeSueur, 1821) populations for the years 1973–1977. Int. Commn NW Atlant. Fish Res. Doc. 79/II/38, Ser. No. 5364
Lipinski, M. R. (1985). Laboratory survival of Allotheuthis subulata (Cehphalopoda: Loliginidae) from the Plymouth area. J. mar. biol. Assoc. U. K. 65: 845–855
Lipinski, M. R. (1987). Food and feeding of Loligo vulgaris reynaudii from St. Francis Bay, South Africa. In: Payne, A. I. L., Gulland, J. A., Brink, K. H., (eds.) The Benguela and comparable ecosystems. S. Afr. J. mar. Sci. 5: 557–564
Lipinski, M. R., Wrzesinski, O. (1982). Some observations on the behavior of squid (Cephalopoda: Ommastrephidae) during jigging operations. Proc. int. Squid Symp., August 9–12, 1981, Boston, Massachusetts. UNIPUB, New York: 137–144
Mangold, K. (1987). Reproduction. In: Boyle, P. R. (ed.) Cephalopod life cycles, Vol. 2. Comparative reviews. Academic Press, London, p. 157–200
Mangold-Wirz, K. (1963). Biologie des Cephalopodes benthiques et nectoniques de la Mer Catalane. Vie Milieu (Suppl.) 13: 1–285
McGowan, J. A. (1954). Observations on the sexual behavior and spawning of the squid, Loligo opalescens, at La Jolla, California. Calif. Fish Game 40: 47–54
Movnihan, M., Rodaniche, A. F. (1982). The behavior and natural history of the Caribbean Reef squid Sepioteuthis sepioidea. Fortschr. Verhaltensforsch. 25: 1–150
Natsukari, Y. (1978). Scuba diving observations on the spawning ground of the squid, Doryteuthis kensaki (Wakiya et Ishikawa, 1921) (Cephalopoda, Loliginidae). Venus, Jpn J. Malacol. (Kairuigaku Zasshi) 45 (4): 206–208
Nesis, K. N. (1985). Okeanyceske Gocovonogye Molluski (Oceanic Cephalopod Molluses). Nauka Press, Moscow (in Russian)
O'Dor, R. K. (1983). Illex illecebrosus. In: Boyle, P. R. (ed.) Cephalopod life cycles, Vol. 1. Species accounts. Academic Press, London, p. 175–199
Pond, S., Packard, G. L. (1986). Introductory dynamical oceanography. Pergamon Press, Oxford
Porteiro, F. M., Martins, M. R., Hanlon, R. T. (1990). Some observations on the behaviour of adult squids, Loligo forbesi, in captivity. J. mar. biol. Assoc. U.K. 70(2): 459–472
Roper, C. F. E., Young, R. E. (1975). Vertical distribution of pelagic cephalopods. Smithson. Contr. Zool. 209: 1–51
Sauer, W. H. H. (1991). Aspects of the ecology of the chokka squid Loligo vulgaris reynaudii (D'Orbigny) in Algoa Bay and St. Francis Bay. M. Sc. Thesis, University of Port Elizabeth, Port Elizabeth, South Africa
Sauer, W. H. H., Lipinski, M. R. (1990). Histological validation of morphological stages of sexual maturity in chokker squid Loligo vulgaris reynaudii D'Orbigny (Cephalopoda: Loliginidae). S. Afr. J. mar. Sci. 9: 189–200
Sauer, W. H. H., Lipinski, M. R. (1991). Food of squid Loligo vulgaris reynaudii (Cephalopoda: Loliginidae) on their spawning grounds off the eastern Cape, South Africa. S. Afr. J. mar. Biol. 10: 193–201
Summers, W. C. (1983). Loligo pealei. In: Boyle, P. R. (ed.) Cephalopod life cycles, Vol. 1. Species accounts. Academic Press, London, p. 115–142
Suzuki, T. (1976). Echosounding for squid Todarodes pacificus (Steenstrup) in offshore waters of the sea of Japan and estimation of its abundance. In: Expert consultation on fishing for squid and other cephalopods. F.A.O. Fish. Rep. 170 (Suppl. 1): 89–92
Suzuki, T., Tashiro, M., Yamagishi, Y. (1974). Studies on the swimming layer of squid Todarodes pacificus Steenstrup as observed by a fish finder in the offshore region of the northern part of the Japan Sea. Bull. Fac. Fish. Hokkaido Univ. 25: 238–246 (in Japanese with English summary)
Vaughan, D. L., Recksiek, C. W. (1978a). An acoustic investigation of market squid, Loligo opalescens. Calif. Dep. Fish Game Fish. Bull. 169: 135–147
Vaughan, D. L., Recksiek, C. W. (1978b). Detection of market squid, Loligo opalescens, with echosounders. Calif. coop. ocean. Fish. Invest. Rep. 20: 40–50
Voss, G. L. (1983). A review of cephalopod fisheries biology. Mem. natn. Mus. Vict. 44: 229–241
Worms, J. (1983). Loligo vulgaris. In: Boyle, P. R. (ed.) Cephalopod life cycles, Vol. 1. Species accounts. Academic Press, London, 143–157
Zuev, G. V., Nigmatulin, C. M., Nikolsky, V. N. (1985). Nektonnye Okeanyceskye Kalmary (nectonic oceanic squids). Agropromyzdat, Moscow (in Russian)
Zuev, G. V., Nikolsky, V. N. (1991). Ecological mechanisms forming intra-specific structure of nectonic squids: Sthenoteuthis pteropus (Seenstrup) taken as an example. Int. Symp. Recent Adv. Ceph. Fish. Biol., Shimizu, Japan July 1991: 29
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by O. Kinne, Oldendorf/Luhe
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sauer, W.H.H., Smale, M.J. & Lipinski, M.R. The location of spawning grounds, spawning and schooling behaviour of the squid Loligo vulgaris reynaudii (Cephalopoda: Myopsida) off the Eastern Cape Coast, South Africa. Marine Biology 114, 97–107 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00350859
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00350859