Abstract
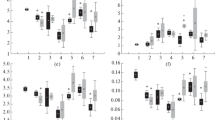
Changes in the biochemical composition of the digestive gland and in the proteins of the mantle muscle of Sepia officinalis L, collected in September 1989 from the Ria de Vigo (northwest Spain), were measured during periods of 2, 4, 10 and >53 d starvation. The digestive gland lost weight faster than the rest of the body throughout the whole period of starvation. In the digestive gland, carbohydrate and protein contents did not change during starvation; however, lipid levels decreased significantly after 53 d. Phospholipid content increased during longterm starvation. The content of free fatty acids rose after 16 d. Sterols, diacylglycerylethers, triacylglycerols and carotenoids contents did not change significantly. Of the total fatty acids, 18:0, 20:2n6, 20:4n6 and the monounsaturated moieties were preferentially consumed; others, such as 22:5n3, 22:6n3 and 16:4n1, were selectively retained. In the mantle muscle, water content increased and total protein content decreased. The myofibrillar proteins decreased after 53 d starvation, whereas the sarcoplasmic fraction did not change and the stromatic proteins increased. No changes were observed in the electrophoretic patterns of sarcoplasmic and myofibrillar proteins. The digestive gland of S. officinalis does not seem to be an important reserve organ during long-term starvation, but does seem to be important during shortterm starvation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Allen, W. V. (1976). Biochemical aspects of lipid storage and utilization in animals. Am. Zool. 16: 631–647
Ballantyne, J. S., Hochachka, P. W., Mommser, T. P. (1981). Studies on the metabolism of the migratory squid, Loligo opalescens, enzymes of tissues and heart mitochondria. Mar. Biol. Lett. 2: 75–85
Beardall, C. H., Johnston, I. A. (1983). Muscle atrophy during starvation in a marine teleost. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 29: 209–217
Black, D., Love, R. M. (1986). The sequential mobilisation and restoration of energy reserves in tissues of Atlantic cod during starvation and refeeding. J. comp. Physiol. (Sect. B) 156: 469–479
Blanchier, B., Boucaud-Camou, E. (1982). Contenu lipidique de la glande digestive de Sepia officinalis L. a maturité sexuelle. Malacologia 22: 691–696
Blanchier, B., Boucaud-Camou, E. (1984). Lipids in the digestive gland and the gonad of immature and mature Sepia officinalis (Mollusca: Cephalopoda). Mar. Biol. 80: 39–43
Boucaud-Camou, E., Boucher-Rodoni, R. (1983). Feeding and digestion in cephalopods. In: Salenddin, A. S. M., Wilbur, K. M. (eds.) The Mollusca. Vol. 5. Academic Press, London, p. 149–188
Boucaud-Camou, E., Yim, M. (1980). Fine structure and function of the digestive cell of Sepia officinalis (Mollusca: Cephalopoda). J. Zool., Lond. 191: 89–105
Boucher-Rodoni, R. (1982a). La glande digestive des céphalopodes, organe de synthése et de sécretion d'enzymes digestives. Cah. Biol. mar. 23: 299–318
Boucher-Rodoni, R. (1982b). Etude cytologique de la glande digestive de deux céphalopodes Eledone cirrosa et Sepia officinalis. Cah. Biol. mar. 23: 393–413
Boucher-Rodoni, R. (1989). Consommation d'oxygéne et excrétion ammonicale de Nautilus macrophalus. C. r. hebd. Séanc. Acad. Sci., Paris 309 (Sér. III): 173–179
Boucher-Rodoni, R., Boucaud-Camou, E., Mangold, K. (1987). Feeding and digestion. In: Boyle, P. R. (ed.) Cephalopods life cycles. Vol. 2. Academic Press, London, p. 85–108
Boucher-Rodoni, R., Mangold, K. (1988). Comparative aspects of ammonia excretion in cephalopods. Malacologia 29: 145–151
Christie, W. W. (1989). Gas chromatography and lipids: a practical guide. The Oily Press, Ayr, Scotland
Chu Fulin, E. (1984). Polyunsaturated fatty acids and neutral lipids in developing larvae of the oyster, Crassostrea virginica. Lipids 19: 815–820
Clarke, A. (1977). Lipids class and fatty acids composition of Chorismus antarcticus (Pfetter) (Crustacea: Decapoda) at South Georgia. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol 28: 279–314
Clarke, A., Rodhouse, P. G., Holmes, L. J., Pascoe, P. L. (1989). Growth rate and nucleic acid ratio in cultured cuttlefish Sepia officinalis (Mollusca: Cephalopoda). J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 133: 229–240
Cuzon, G., Cahu, J., Aldrin, J. F., Messager, J. L., Stéphan, G., Mével, M. (1980). Starvation effect on metabolism of Penaus japonicus. Proc. Wld Maricult. Soc. 11: 410–423
Dave, G., Johansson-Sjöbeckm M.-L., Larsson Å., Lewander, K., Lidman, U. (1976). Metabolic and hematological effects of starvation in the European eel, Anguilla anguilla L. III Fatty acid composition. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 53 (B): 509–515
Davies, B. H. (1976). Carotenoids. In: Goodwin, T. W. (ed). Chemistry and biochemistry of plant pigments. Vol 2. Academic Press, London, p. 38–165
Filliben, J. J. (1975). The probability plot correlation coefficient test for normality. Technometrics 17: 111–117
Fisher, L. R., Kon, S. K., Thompson S. Y. (1956). Vitamin A and carotenoids in certain invertebrates. V. Mollusca: Cephalopoda. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 35: 63–80
Fraser, A. J. (1989). Triacylglycerol content as a condition index for fish, bivalve, and crustacean larvae. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sciences 49: 1868–1873
Gas, N. (1972). Structural alterations in the white muscle of carp (Cyprinus carpio L.) during prolonged starvation. C. r. hebd. Séanc. Acad. Sci., Paris 275 (Sér. D): 1403–1406
Gehron, M. J., White, D. C. (1982). Quantitative determination of the nutritional status of detrital microbiota and the grazing fauna by triglyceride glycerol analysis. J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 64: 145–158
Hames, D. B. (1981). An introduction to polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. In: Hames, B. D., Rickwod, D. (eds.) Gel electrophoresis of proteins. A practical approach. IRL Press, Oxford, Washington, p. 1–86
Hammond, E. W. (1986). Packed column gas-chromatography. In: Hamilton, R. J., Rossell, J. B. (eds.) Analysis of oils and fats. Elsevier Applied Science, Barking, p. 113–136
Hashimoto, K., Watabe, S., Kono, M., Shiro, K. (1979). Muscle protein composition of sardine and mackerel. Bull. Jap. Soc. scient. Fish. 45: 1435–1441
Hayashi, K., Takagi, T. (1977). Lipid metabolism in fish. II. Changes of lipids and fatty acids in the liver of puffer, Fugu vermiculare porphyreum, during starvation. Bull. Fac. Fish. Hokkaido Univ. 28: 193–201
Herbes, S. E., Allen, C. P. (1983). Lipid quantification of freshwater invertebrates: method modification for microquantitation. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sciences 40: 1315–1317
Huang, T. C., Chen, C. P., Wefler, V., Raftery, A. (1961). A stable reagent for the Libermann-Buchard reaction. Application to rapid serum cholesterol determination. Analyt. Chem. 33: 1405–1407
Jezierska, B., Hazel, J. R., Gerking, S. D. (1982). Lipid mobilization during starvation in the rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri Richardson, with attention to fatty acids. J. Fish Biol. 21: 681–692
Johansen, K., Brix, O., Kornerup, S., Lykkeboe, G. (1982). Factors affecting O2-uptake in the cuttlefish Sepia officinalis. J. mar biol. Ass. U.K. 62: 187–191
Johnston, I. A. (1981). Quantitative analysis of muscle breakdown during starvation in the marine flatfish Pleuronectes platessa. Cell Tissue Res. 214: 369–386
Johnston, I. A., Goldspink, G. (1973). Some effects of prolonged starvation on the metabolism of the red and white myotomal muscles of the plaice Pleuronectes platessa. Mar. Biol. 19: 348–353
Joseph, J. (1982). Lipid composition of marine and estuarine invertebrates. Part II: Mollusca. Prog. Lipid Res. 21: 109–153
Kanazawa, A., Teshima, S., Kazuo, O. (1979). Relationship between essential fatty acid requirements of aquatic animals and the capacity for bioconversion of linolenic acid to highly unsaturated fatty acids. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 63 B: 295–298
Kreuzer, R. (1984). Cephalopods: handling, processing and products. F.A.O. Fish. tech. Pap. 254: 1–108
Laemmli, U. K. (1970). Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature, Lond. 227: 680–685
Love, R. M. (1970). The chemical biology of fishes. Vol 1. Academic Press, New York and London
Love, R. M. (1980). The chemical biology of fishes. Vol 2. Academic Press, New York and London
Lowry, O. H., Rosebrough, N. J., Farr, A. L., Randall, R. J. (1951). Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J. biol. Chem. 193: 265–275
Lowry, R. R., Tinsley, I. J. (1976). Rapid colorimetric determination of free fatty acids. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 53: 470–472
Mangold, K. (1983). Food, feeding and growth in cephalopods. Mem. natn. Mus. Vict. 44: 81–83
Mangold, K., Bidder, A. M. (1989). L'appareil digestif et la digestion. In: Traité de zoologie. Anatomie systématique, biologie: céphalopodes. Tomo V. Fascicule 4. Masson, Paris, p. 321–373
Mather, J. A. (1986). A female-dominated feeding hierarchy in juvenile Sepia officinalis in the laboratory. Mar. Behav. Physiol. 12: 223–244
Millward, D. J. (1970). Protein turnover in skeletal muscle. II. The effect of starvation and a protein free diet on the synthesis and catabolism of skeletal muscle proteins in comparison to liver. Clin. Sci. 39: 591–603
Mommsen, T. P., Hochachka, P. W. (1981). Respiratory and enzymatic properties of squid heart mitochondria. Eur. J. Biochem. 120: 345–350
Nakamura, K., Handa, S. (1984). Coomassie brilliant blue staining of lipids on thin-layer plates. Analyt. Biochem. 142: 406–410
O'Dor, R. K., Mangold, K., Boucher-Rodoni, R., Wells, M. J., Wells, J. (1984). Nutrient absorption, storage and remobilization in Octopus vulgaris. Mar. behav. Physiol. 11: 239–258
O'Dor, R. K., Weber, D. M. (1986). The constraints on cephalopods: why squid aren't fish. Can. J. Zool. 64: 1591–1605
O'Dor, R. K., Wells, M. J. (1987). Energy and nutrient flow. In: Boyle, P. R. (ed.) Cephalopod life cycles. Vol 2. Academic Press, London, p. 109–133
Packard, A. (1972). Cephalopods and fish: limits of convergence. Biol. Rev. 47: 241–307
Pollero, R. J., Iribarne, O. O. (1988). Biochemical changes during the reproductive cycle of the small Patagonian octopus, Octopus tehuelchus, D'Orb. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 90 (B): 317–320
Raheja, R. K., Knaur, C., Singh, A., Bathia, I. S. (1973). New colorimetric method for the quantitative estimation of phospholipids without acid digestion. J. Lipid Res. 14: 695–697
Reinard, T., Jacobsen, H.-J. (1989). An inexpensive small volume equilibrium dialysis system for protein-ligand binding assays. Analyt. Biochem. 176: 157–160
Sargent, J. R. (1975). The structure, metabolism and function of lipids in marine organisms. In: Malins, D. C., Sargent, J. R. (eds.) Biochemical and biophysical perspectives in marine biology. Vol 2. Academic Press, New York and London, p. 149–212
Sargent, J. R., Whittle, K. J. (1981). Lipids and hydrocarbons in the marine food web. In: Longhurst, A. R. (ed.) Analysis of marine ecosystems. Academic Press, London, p. 491–533
Satho, S., Takeuchi, T., Watanabe, T. (1984). Effects of starvation and environmental temperature on proximate and fatty acid compositions of Tilapia nilotica. Bull. Jap. Soc. scient. Fish. 50: 79–84
Segawa, S., Hanlon, R. T. (1988). Oxygen consumption and ammonia excretion rates in Octopus maya, Loligo forbesi and Lolliguncula brevis (Mollusca: Cephalopoda). Mar. Behav. Physiol. 13: 389–400
Siegel, S., Castellan, N. J. (1988). Nonparametric statistics for the behavioral sciences. McGraw-Hill Book Co., New York
Sikorski, Z. E., Kolodzieiska, I. (1986). The composition and properties of squid meat. Fd Chem. 20: 213–224
Sokal, R. R., Rohlf, F. J. (1981). Biometry. The principles and practice of statistics in biological research. 2nd ed. W.H. Freeman & Co., New York.
Steel, G. D., Torrie, J. H. (1985). Bioestadística. McGraw-Hill, Bogotá
Storey, K. B., Storey, J. B. (1983). Carbohydrate metabolism in cephalopod molluscs. In: Hochachka, P. W. (ed) The Mollusca. Vol. 1. Academic Press, New York and London, p. 91–136
Strancari, M. T., Lozano, F. (1987) Determinación de los contenidos en humedad, grasos y cenizas, en especies de sepiáridos (Cephalopoda: Sepioidea) del Banco Sahariano. Alimentaria 182: 57–62
Strickland, J. D. H., Parsons, T. R. (1968). A practical handbook of seawater analysis. Bull. Fish. Res. Bd Can. 167: 1–311
Suryanarayanan, H., Alexander, K. M. (1971). Fuel reserves of molluscan muscle. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 40 (A):55–60
Tait, R. W. (1986) Aspects physiologiques de la sénescence post-reproductive chez Octopus vulgaris. Thése de Doctorat. L'Université Paris VI
Takahashi, T. S. (1960). Studies on the utilization of cuttlefish, Ommastrephes sloani pacificus. III. The seasonal variations in the gravimetric constitution and the chemical composition of the various parts of the body. Bull. Jap. Soc. scient. Fish. 26: 95–98
Takeuchi, T., Watanabe, T. (1982). The effects of starvation and environmental temperature on proximate and fatty acid composition of carp and rainbow trout. Bull. Jap. Soc. scient. Fish. 48: 1307–1316
Wells, M. (1990). The dilemma of the jet set. New Scient. 125: 44–49
Woo, N., Murat, Y. S. (1981). Studies on the biology of the red sea bream Chrysophrys major. III. Metabolic response to starvation in different salinities. Mar. Biol. 61: 255–260
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. M. Pérès, Marseille
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castro, B.G., Garrido, J.L. & Sotelo, C.G. Changes in composition of digestive gland and mantle muscle of the cuttlefish Sepia officinalis during starvation. Marine Biology 114, 11–20 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00350851
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00350851