Abstract
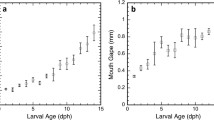
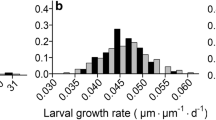
We examined feeding by larval weakfish, Cynoscion regalis (Bloch and Schneider), in laboratory experiments conducted during the 1991 spawning season. under natural conditions weakfish larval development is ca. 3 wk, and we ran separate experiments with larvae of five different ages (5, 8, 11, 14, and 17 d post-hatching). We used two different size classes of rotifers (Brachionus plicatilis) and brine shrimp nauplii (Artemia sp.) as prey organisms. Contrary to results of previous research, weakfish larvae did not select prey based on size alone. When prey abundance was above 100 itemsl-1 weakfish, larvae always chose large rotifers (length = 216 μm) over small rotifers (length = 160 μm). At 11 d post-hatching, larvae switched their diet from large rotifers to small brine shrimp nauplii (length = 449 μm); however, when fed small rotifers and small brine shrimp nauplii the change in diet occurred at 14 d post-hatching. This pattern of selectivity was maintained in each larval age class. Early-stage larvae (5 and 8 d post-hatching) did not feed selectively when prey abundance was less than 100 itemsl-1. Late-stage larvae (17 d post-hatching) fed selectively at abundances ranging from 10 to 10000 items-1. Lwimming speeds of prey items, which ranged from 1 to 6 mms-1, had no consistent effect on prey selection. These results suggest that weakfish larvae are able to feed selectively, that selectivity changes as larvae age, and that selectivity is also influenced by prey abundance.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Bartell, S. M. (1982). Influence of prey abundance on size-selective predation by bluegills. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 111: 453–461
Blaxter, J. H. S., Batty, R. S. (1985). The development of startle responses in herring larvae. J. mar. biol. Ass. U.K. 65: 737–750
Boisclair, D., Leggett, W. C. (1989). Among-population variability of fish growth: II. Influence of prey type. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sciences 46: 468–482
Bookhout, C. G., Costlow, Jr., J. D. (1970). Nutritional effects of Artemia from different locations on larval development of crabs. Helgoländer wiss. Meeresunters. 20: 435–442
Clement, P. (1987). Movements in rotifers: correlations of ultrastructure and behavior. Hydrobiologia 147: 339–359
Cohen, R. E., Lough, R. G. (1983). Prey field of larval herring Clupea harengus on a continental shelf spawning area. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 10: 211–222
Cope, J. S. (1991). Effects of prey density on growth and survival of larval weakfish (Cynoscion regalis) in field-deployed enclosures and in laboratory aquaria. Master's thesis. University of Delaware, College of Marine Studies, Lewes, Delaware
Detwyler, R., Houde, E. D. (1970). Food selection by laboratory-reared larvae of the scaled sardine Harengula pensacolae (Pisces, Clupeidae) and the bay anchovy Anchoa mitchilli (Pisces, Engraulidae). Mar. Biol. 7: 214–222
Durst, F., Melling, A., Whitelaw, J. H. (1981).Principles and practice of laser-doppler anemometry, 2nd Edn. Academic Press, London
Epp, R. W., Lewis, Jr. W. M. (1979). Sexual dimorphism in Brachionus plicatilis (Rotifera): evolutionary and adaptive significance. Ecology 33: 919–928
Gauld, D. T. (1959). Swimming and feeding in crustacean larvae: the nauplius larva. Proc. Zool. Soc., Lond 132: 31–50
Gibson, R. N., Ezzi, I. A. (1990). Relative importance of prey size and concentration in determining the feeding behaviour of the herring Clupea harengus. Mar. Biol. 107: 357–362
Goshorn, D. M. (1990). Distribution of larval weakfish (Cynoscion regalis) in Delaware Bay and the relationship of field prey concentration to laboratory determined growth and mortality rates. Ph. D. Diss., Univ. of Delaware, College of Marine Studies, Lewes, Delaware
Goshorn, D. M., Epifanio, C. E. (1991a). Diet of larval weakfish and prey abundance in Delaware Bay. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 120: 684–692
Goshorn, D. M., Epifanio, C. E. (1991b). Development, survival, and growth of larval weakfish at different prey abundances. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 120: 693–700
Govoni, J. J., Hoss, D. E., Chester, A. J. (1983). Comparative feeding of three species of larval fishes in the northern Gulf of Mexico: Brevoortia patronus, Leiostomus xanthurus, and Micropogonias undulatus. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 13: 189–199
Govoni, J. J., Ortner, P. B., Al-Yamani, F., Hill, L. C. (1986). Selective feeding of spot, Leiostomus xanthurus, and Atlantic croaker, Micropogonias undulatus, larvae in the northern Gulf of Mexico. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 28: 175–183
Hunter, J. R. (1980). The feeding behavior and ecology of marine fish larvae. In: Bardach, J. E., Magnuson, J. J., May, R. C., Reinhart, J. M. (eds.) Fish behavior and its use in the capture and culture of fishes. ICLARM Conf. Proc. 5 Internat'l. Center for the Living Aquatic Resources Mgmt, Manila, Philippines, p. 287–330
Johns, D. M., Peters, M. E., Beck, A. D. (1980). International study on Artemia VI. Nutritional value of geographical and temporal strains of Artemia: effects on survival and growth of two species of Brachyuran larvae. In: Persoone, G., Sorgeloos, P., Roels, O., Jaspers, E. (eds.) The brine shrimp Artemia, Vol. 3. Ecology, culturing, use in aquaculture. Universa Press, Wetteren, Belgium, p. 291–304
Khadka, R. B., Ramakrishna-Rao, T. (1986). Prey size selection by common carp (Cyprinus carpio var. communis) larvae in relation to age and prey density. Aquaculture, Amsterdam 54: 89–96
Kislalioglu, M., Gibson, R. N. (1976). Some factors governing prey selection by the 15-spined stickleback, Spinachia spinachia (L.). J. exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 25: 159–169
Klein-MacPhee, G., Howell, W. H., Beck, A. D. (1980). International study on Artemia VII. Nutritional value of five geographical strains of Artemia to winter flounder Pseudopleuronectes americanus larvae. In: Persoone, G., Sorgeloos, P., Roels, O., Jaspers, E. (eds.) The brine shrimp Artemia, Vol. 3. Ecology, culturing, use in aquaculture. Universa Press, Wetteren, Belgium, p. 305–312
Leggett, W. C. (1986). The dependence of fish larval survival on food and predator densities. In: Skreslet, S. (ed.) The role of freshwater outflow in coastal marine ecosystems. NATO ASI ser, Vol. G7. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, p. 117–137
Mercer, L. P. (1983). The biological and fisheries profile of the weakfish, Cynoscion regalis. Spec. Scientific Rept. No. 39. North Carolina Dept. of Natural Resources and Community Development. State-Federal Fish. Mgmt. Prog., Project SF-13, Morehead City, North Carolina
Munk, P., Kiorboe, T. (1985). Feeding behavior and swimming activity of larval herring (Clupea harengus) in relation to density of copepod nauplii. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 24: 15–24
Olney, C. E., Schauer, P. S., McLean, S., Lu, Y., Simpson, K. L. (1980). International study on Artemia VIII. Comparison of the chlorinated hydrocarbons and heavy metals in five different strains of newly hatched Artemia and laboratory-reared marine fish. In: Persoone, G., Sorgeloos, P., Roels, O., Jaspers, E. (eds.) The brine shrimp Artemia, Vol. 3. Ecology, culturing, use in aquaculture. Universa Press, Wetteren, Belgium, p. 343–352
Peterson, D. E. (1990). Investigations of the trophic relationships, feeding ecology and feeding behavior of larval spot, Leiostomus xanthurus Lacepede, and Atlantic croaker, Micropogonias undulatus (Linnaeus) (Pisces: Sciaenidae). Ph. D. Diss., Old Dominion Univ., Norfolk, Virginia
Polo, A., Yufera, M., Pascual, E. (1992) Feeding and growth of gilthead seabream (Sparus aurata L.) larvae in relation to the size of the rotifer strain used as food. Aquaculture, Amsterdam 103: 45–54
Pyke, G. H., Pulliam, H. R., Charnov, E. L. (1977). Optimal foraging: a selective review of theories and tests. Q. Rev. Biol. 52: 137–154
Rice, W. R. (1990). A consensus combined p-value test and the family-wide significance of component tests. Biometrics 46: 303–308
Schael, D. M., Rudstam, L. G., Post, J. R. (1991). Gape limitation and prey selection in larval yellow perch (Perca flavescens), freshwater drum (Aplodinotus grunniens), and black crappie (Pomoxis nigromaculatus). Can. J. Fish aquat. Sciences 48: 1919–1925
Stoecker, D. K., Govoni, J. J. (1984). Food selection by young larval gulf menhaden (Brevoortia patronus). Mar. Biol. 80: 299–306
Turner, J. T. (ed.) (1990). Laser anemometry advances and applications. Proc. 3rd International Conf. BHRA/Springer-Verlag, London
Werner, R. G., Blaxter, J. H. S. (1980). The effect of prey density on mortality, growth, and food consumption of larval herring (Clupea harengus L.). Rapp. P.-v. Réun. Cons. int. Explor. Mer. 178: 405–408
Wickins, J. G. (1972). The food value of brine shrimp. Artemia salina L., to larvae of the prawn Palaemon serratus Pennant. J exp. mar. Biol. Ecol. 10: 151–170
Zar, J. H. (1984). Biostatistical analysis, 2nd Edn. Prentice-Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey
Zaret, T. M., Kerfoot, W. C. (1975). Fish predation on Bosmina longirostris: body-size selection versus visibility selection. Ecology 56: 232–237
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. Grassle, New Brunswick
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pryor, V.K., Epifanio, C.E. Prey selection by larval weakfish (Cynoscion regalis): the effects of prey size, speed, and abundance. Marine Biology 116, 31–37 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00350728
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00350728