Abstract
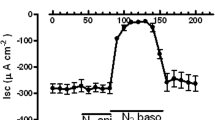
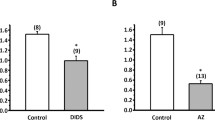
Single split lamella preparations of posterior gills of low-salt adapted shore crabs Carcinus maenas (collected from the Kiel Bay, Baltic Sea in 1991) were mounted in a micro Ussing-chamber. With NaCl salines on both sides we found an outside positive potential difference (PD) of 6.6±1.3 mV, a short-circuit current (Isc) of-240±65 μAcm-2 and a resistance (Rt) of 25±3 Ωcm2 (n=8). Substitution of Cl- (gluconate) on both sides of the preparation resulted in a decrease of Isc by more than 90% at constant Rt. Isc disappeared and Rt increased after substitution of Na+ (choline). When ouabain (2 mmol l-1) was applied to the internal NaCl-saline, Isc decreased and Rt remained unchanged. Internal addition of 0.1 mmol l-1 acetazolamide left Isc and Rt unaffected. Application of amiloride to the external NaCl saline resulted in a increase of both inward negative Isc and Rt. The dose dependence of the diuretic showed a maximal effect between 50 and 200 μmol l-1 with a half-maximal blocker concentration (KAMI) of ca. 10 μmol l-1. The results show that the split lamella preparation of posterior gills of C. maenas is a low resistance epithelium which is able to effect a massive, electrogenic and coupled absorption of Na+ and Cl-.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Benos, D.J. (1982). Amiloride: a molecular probe of sodium transport in tissues and cells. Am. J. Physiol. 242: C131-C145
Böttcher, K., Siebers, D., Becker, W., Petrausch, G. (1991). Physiological role of branchial carbonic anhydrase in the shore crab Carcinus maenas. Mar. Biol. 110: 337–342
Dannenmaier, B., Heinke, B., Weber, W.-M., Clauss, W. (1991). Amiloride-sensitive Na+-channels in the dorsal skin of Hirudo medicinalis. Verh. dt. zool. Ges. 84: 402–403
Drews, G. (1985). Elektrophysiologische und biochemische Untersuchungen zur osmoregulatorischen Fähigkeit und zur Salzaufnahme über das Kiemenepithel von Uca tangeri (Eydoux 1835). Ph.D. thesis, Freie Universität Berlin, Germany
Drews, G., Graszynski, K. (1987). The transepithelial potential difference in the gills of the fiddler crab, Uca tangeri: influence of some inhibitors. J. comp. Physiol. 157: 345–353
Erlij, D., Ussing, H. H. (1978). Transport across amphibian skin. In: Giebisch, G., Tosteson, D. C. Ussing, H. H. (eds) Membrane transport in biology, Vol. III. Springer Verlag, Berlin, p. 178–208
Graszynski, K., Bigalke, T. (1986). Osmoregulation and ion transport in the extremely euryhaline fiddler crabs Uca pugilator and Uca tangeri (Ocypodidae). Zool. Beitr. 30: 339–358
Greger, R. (1985). Ion transport in thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of mammalian nephron. Physiol. Rev. 65(3): 760–797
Lignon, J. M. (1987). Ionic permeabilities of the isolated gill cuticle of the shore crab Carcinus maenas. J. exp. Biol. 131: 159–174
Lignon, J. M., Pequeux, A. (1990). Permeability properties of the cuticle and gill ion exchangers in decapod crustaceans. In: Truchot, J.P., Lahlou, B. (eds.) Animal nutrition and transport processes. 2. Transport, respiration and excretion: comparative and environmental aspects. Comp. Physiol. Vol. 6. Karger, Basel, p. 14–27
Lucu, C. (1989). Evidence for Cl--exchangers in perfused Carcinus gills. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 92A: 415–420
Lucu, C. (1990). Ionic regulatory mechanisms in crustacean gill epithelia. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 97A: 297–306
Lucu, C, Siebers, D. (1986). Amiloride-sensitive Na+-flux and potentials in perfused Carcinus gill preparations. J. exp. Biol. 122: 25–35
Lucu, C., Siebers, D. (1987). Linkage of Cl- fluxes with ouabain sensitive Na/K exchange through Carcinus gill epithelia. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 87A: 807–811
Maren, T. (1967). Carbonic anhydrase: chemistry, physiology, and inhibition. Physiol. Rev. 47: 595–781
Onken, H., Graszynski, K., Zeiske, W. (1991). Na+-independent, electrogenic Cl--uptake across the posterior gills of the Chinese crab (Eriocheir sinensis): voltage-clamp and microelectrode studies. J. comp. Physiol. 161: 293–301
Pequeux, A., Gilles, R., Marshall, W. S. (1988). NaCl transport in gills and related structures. In: Greger, R. (ed.) Advances in comparative and environmental physiology, Vol. 1. Springer, Berlin, p 1–73
Schwarz, H. -J. (1990). Elektrophysiologische Untersuchungen des transepithelialen Natrium-Transportes isolierter, halbierter Kiemenplättchen posteriorer Kiemen der Wollhandkrabbe Eriocheir sinensis und der Winkerkrabbe Uca tangeri. Ph.D. thesis, Freie Universität Berlin, Germany
Schwarz, H.-J., Graszynski, K. (1989). Ion transport in crab gills: a new method using isolated half platelets of Eriocheir gills in an Ussing-type chamber. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 92A: 601–604
Schwarz, H.-J., Graszynski, K. (1990). Characterization of the Na+-transport from posterior gills of the Chinese crab Eriocheir sinensis using voltage-clamp-technique. Verh. dt. zool. Ges. 83: 555–556
Shetlar, R. E., Towle, D. W. (1989). Electrogenic sodium-proton exchange in membrane vesicles from crab (Carcinus maenas) gill. Am. J. Physiol. 257: R924-R931
Siebers, D., Böttcher, K., Petrausch, G., Hamann, A. (1990). Effects of some chloride channel blockers on potential differences and ion fluxes in isolated perfused gills of shore crabs Carcinus maenas. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 97a: 9–15
Siebers, D., Lucu, C., Winkler, A. (1987a). Active influx of ions across the gills of osmoregulating shore crabs Carcinus maenas. Zool. Beitr. 30: 315–338
Siebers, D., Lucu, C., Winkler, A., Dalla Venezia, L., Wille, H. (1986). Active uptake of sodium in the gills of the hyperregulating shore crab Carcinus maenas. Helgoländer Meersunters. 40: 151–160
Siebers, D., Lucu, C., Winkler, A., Grammerstorf, U., Wille, H. (1987 b). Effects of amiloride on sodium chloride transport across isolated perfused gills of shore crabs Carcinus maenas acclimated to brackish water. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 87A: 333–340
Siebers, D., Wille, H., Lucu, C., Dalla Venezia, L. (1989). Conductive sodium entry in gill cells of the shore crab, Carcinus maenas. Mar. Biol. 101: 61–68
Siebers, D., Winkler, A., Lucu, C., Thedens, G., Weichart, D. (1985). Na-K-ATPase generates an active transport potential in the gills of the hyperregulating shore crab Carcinus maenas. Mar. Biol. 87: 186–192
Skou, J. C. (1965). Enzymatic basis for active transport of Na+ and K+ across cell membrane. Physiol. Rev. 45: 596–617
Zeiske, W., Onken, H., Schwarz, H.-J., Graszynski, K. (1992). Invertebrate epithelial Na+ channels: amiloride-induced currentnoise in crab gill. Biochim. biophys. Acta 1105: 245–252
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by O. Kinne, Oldendorf/Luhe
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Onken, H., Siebers, D. Voltage-clamp measurements on single split lamellae of posterior gills of the shore crab Carcinus maenas . Marine Biology 114, 385–390 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00350028
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00350028