Abstract
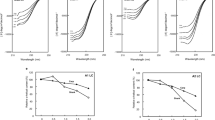
Kinetic properties such as the Michaelis-Menten constant and the activation energy of the flexor muscle myosin ATPase were investigated in the estuarine crab Scylla serrata. These properties varied at different salinities, but the extractability of the enzyme remained unaltered. The qualitative changes upon salinity adaptation are discussed with reference to estuarine conditions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Barany, M. and K. Barany: Myosin from the striated adductor muscle of the scallop (Pecten arradians). Biochem. Z. 345, 37–56 (1966).
—, T. E. Conover, H. Schliselfeld, D. Gaetjens and M. Goffart: Relation of properties of isolated myosin to those of intact muscle of the cat and sloth. Eur. J. Biochem. 2, 156–164 (1967).
Brahms, J. and C. M. Kay: Molecular and enzymatic properties of cardiac myosin A as compared with those of skeletal muscle myosin A. J. Biol. Chem. 238, 198–205 (1963).
Das, A. B. and R. V. Krishnamoorthy: Thermal acclimation in adenosine triphosphatase of myosin obtained from goldfish skeletal muscle. Indian Biologist 1 (2), 30–33 (1969).
Dixon, M. and E. C. Webb: Enzymes, 2nd ed. 950 pp. New York: Academic Press 1964.
Fiske, C. H. and Y. Subbarow: The colorimetric determination of phosphorus. J. biol. Chem. 66, 375–400 (1925).
Giese, A. C.: Temperature as a factor in the cell environment. In: Cell physiology pp 235–251. 3rd ed. International Students' edition. Japan: Toppan Co. 1968.
Hasselbach, W. and G. Schneider: Der L-Myosin-und Aktingehalt des Kaninchenmuskels. Biochem. Z. 321, 462–475 (1951).
Itzaki, R. F. and D. M. Gill: A micro-Biuret method for estimating proteins. Analyt. Biochem. 9, 401–410 (1964).
Kiely, B. and A. Martinosi: Kinetics and substrate binding of myosin adenosine triphosphatase. J. biol. Chem. 243, 2273–2278 (1968).
Kinne, O.: Physiological aspects of animal life in estuaries with special reference to salinity. Neth. J. Sea Res. 3, 222–244 (1966).
Kinne, O.: Non-genetic adaptation in crustacea. In: Proceedings of Symposium on Crustacea. Pt 3. Symp. Ser. mar. [Biol. ass. India. 2, 999–1007 (1967)].
Krishnamoorthy, R. V. and A. Venkataramiah: Myosin ATPase activity in an estuarine decapod crustacean, Scylla serrata, as a function of salinity adaptation. Mar. Biol. 4, 345–348 (1969).
— and V. Venkata Reddy: Hepatopancreatic amylase activity as a function of warm-adaptation in a fresh water field crab. Experientia 24, 1019–1020 (1968).
Leenders, H. J.: Catch, peak tension and ATPase activity in glycerinated oyster adductor. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 31, 187–196 (1969).
Mahler, H. R. and E. H. Cordes: Biological chemistry, 872 pp. New York: Harper & Row 1966.
McCarl, R. L., S. S. Margossian, I. M. Jackman and R. L. Webb: Characterization of rat heart myosin. II Enzymatic properties. Biochemistry 8, 3659–3664 (1969).
Nanninga, L. B. and W. F. H. M. Mommaerts: Kinetic constants of the interaction between myosin and adenosine triphosphate. Proc. Natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 46, 1166–1173 (1960).
Ouellet, L., K. J. Laidler and M. F. Morales: Molecular kinetics of muscle adenosine triphosphatase. Archs Biochem. Biophys. 39, 37–50 (1952).
Perry, S. V.: Myosin adenosine triphosphatase. In: Methods in enzymology, Vol. 2, pp 582–583. Ed. by S. P. Colowick and N. O. Kalpan, New York: Academic Press 1955.
— The structure and interaction of myosin. In: Progress in biophysics and molecular biology, Vol. 17, pp 327–381. Ed. by J. A. V. Butler and D. Noble. Oxford: Pergamon Press 1967.
Prosser, C. L.: The nature of physiological adaptation. In: Physiological adaptation, pp 167–180. Ed. by C. L. Prosser. Washington: American Physiological Society 1958.
Szent-Gyorgyl, A. G.: The role of actin-myosin interaction in contraction. In: Aspects of cell motility. Symposia of the society for Experimental Biology. No. 22, pp 87–100. Ed. by P. L. Miller. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1968.
Venkatramiah, A.: Studies on the hydrobiology of the Krishna estuary: salinity, adaptive physiology of selected estuarine species. Doct. diss. Sri Venkateswara University, Tirupati, A. P. India 1966.
Young, M.: The molecular basis of muscle contraction. A. Rev. Biochem. 38, 913–950 (1969).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by N. K. Panikkar, Panaji
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishnamoorthy, R.V., Venkatramiah, A. Kinetic changes in flexor myosin ATPase of Scylla serrata adapted to different salinities. Marine Biology 8, 30–34 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00349342
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00349342