Abstract
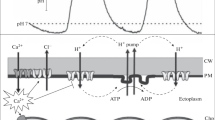
In order to investigate the role of the ionic relations in buoyancy of marine phytoplankton, voltage recordings have been made on the planktonic diatom Coscinodiscus radiatus using conventional glass microelectrode techniques. The most negative Nernst equilibrium voltage in C. radiatus is E K, the potassium equilibrium voltage of around-85 mV. Accordingly, stable voltages of-40 to-80 mV were recorded from C. radiatus which conforms to the general theory of electro-diffusion of ions through membranes (voltage range V d). In addition, membrane voltages much more negative, e.g. up to-140 mV (voltage range V p), have been recorded in C. radiatus; these voltages demonstrate the operation of an electrogenic pump. Within the voltage range V d, light-on and-off (microscope illumination) caused weak hyper- and depolarizations by about 2 mV with a time constant of about 10 s. Also within V d, spontaneous oscillations could be observed with a frequency of about 0.03 Hz and irregular amplitudes up to 30 mV. These phenomena are simulated by a model for electrocoupling of the major ion transporters in plants, as worked out for guard cells with their subtle osmoregulatory system. Equivalent mechanisms are suggested to operate in planktonic diatoms for adjustment of buoyancy by appropriate uptake and release of ions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blatt MR (1987) Electrical characteristics of stomatal guard cells: the ionic basis of the membrane potential and the consequence of potassium chloride leakage from microelectrodes. Planta 170: 272–287
Gradmann D (1970) Einfluss von Licht, Temperatur und Aussenmedium auf das elektrische Verhalten von Acetabularia. Planta 93: 323–353
Gradmann D, Blatt MR, Thiel G (1993) Electrocoupling of ion transporters in plants. J Membrane Biol 136: 327–332
Gross F, Zeuthen E (1948) The buoyancy of plankton diatoms: a problem of cell physiology. Proc R Soc Edinb 135: 382–389
Guillard RRL, Ryther JH (1962) Studies of marine planktonic diatoms. I. Cyclotella nana Hustedt and Detonula confervacea Cleve. Can J Microbiol 8: 229–239
Gutknecht J, Dainty J (1968) Ionic relations of marine algae. Oceanogr mar Biol A Rev 6: 163–200
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch ges Physiol 391: 85–100
Saddler HDW (1970) The membrane potential of Acetabularia mediterranea. J gen Physiol 55: 802–821
Slaymann CL (1965) Electrical properties of Neurospora crassa, effects of external cations on intracellular potential. J gen Physiol 49: 69–92
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by O. Kinne, Oldendorf/Luhe
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gradmann, D., Boyd, C.M. Membrane voltage of marine phytoplankton, measured in the diatom Coscinodiscus radiatus . Marine Biology 123, 645–650 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00349107
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00349107