Abstract
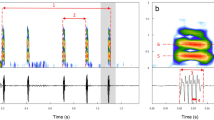
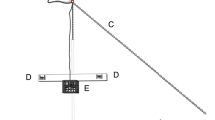
Linuparus trigonus V. Siebold were placed in a tank, with a hydrophone suspended in one corner, in order to investigate the mechanism of sound production and the under-water sounds released. Sounds were recorded by tape recorder and analyzed by means of sound spectrograph. L. trigonus emits creaky sounds by rubbing the protuberance of the antennal coxa against the white tubercle in front of its optic stalk. The protuberance of the coxa molds a hollow, with the opening covered by a thin membrane; this facilitates the production of under-water sounds. However, these sounds are produced only when the antenna is lifted. It is also possible to produce these sounds artificially using dead lobsters. When disturbed by external stimulus, L. trigonus flaps back and accelerates the repitition rate. The under-water sounds produced are a series of pulses, which can be divided into 2 groups: (1) The A type sound; this has a relatively slow repetition rate (10 to 80 times/sec) and is weak at the low frequency range below 3 kHz; the sounds, therefore, are manifested on the sonagram in a pattern consisting of some layers of frequencies which are almost constant. (2) The B type sound; this comprises a series of pulses which are powerful even at low frequency. The repetition rate is very high, and not recognizable on the sonagram.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature cited
Balss, H.: Über Stridulationsorgane bei dekapoden Crustaceen. Naturw. Wschr. 49, 697–701 (1921).
Dijkgraaf, S.: Lauterzeugung und Schallwahrnehmung bei der Languste (Palinurus vulgaris). Experientia 11, 330–331 (1955).
Everest, F. A., R. W. Young and M. W. Johnson: Acoustical characteristics of noise produced by snapping shrimp. J. acoust. Soc. Am. 20, 137–142 (1948).
Fish, M. P.: Biological sources of sustained ambient sea noise. In: Marine bio-acoustic I, pp 175–194. Ed. by W. N. Tavolga. New York: Pergamon Press 1964.
Hashimoto, T. and Y. Maniwa: Frequency analysis of marine sounds. In: Modern fishing gear of the world, II, pp 410–412. Ed. by the Technical Staff of Fishing News International and Fishing News. London: Fishing News Ltd. 1964.
Johnson, M. W., F. A. Everest and R. W. Young: The role of snapping shrimp (Crangon and Synalpheus) in the production of underwater noise in the sea. Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Woods Hole 93, 122–138 (1947).
Kubo, I.: Part of Crustacea. In: Encyclopaedia zoologica illustrated in colours, IV, pp 100–101. Ed. Y. Okada et al. Tokyo: Hokuryu-Kan Publishing Co. Ltd. 1961.
—: Part of Crustacea. In: New illustrated encyclopedia of fauna of Japan, II, pp 625–627. Ed. by Okada et al. Tokyo: Hokuryu-Kan Publishing Co. Ltd. 1965.
Moulton, J. M.: Sound production in the spiny lobster Panulirus argus (Latreille). Biol. Bull. mar. biol. Lab., Wood's Hole 113, 286–295 (1957).
Salmon, M. and J. F. Stout: Sexual discrimination and sound production in Uca pugilator Bosc. Zoologica, N.Y. 47, 15–20 (1962).
Takemura, A. and K. Mizue: Studies on the underwater sound, I. On the underwater sound of genus Alpheus Fabricus in the coastal waters of Japan. Bull. Fac. Fish. Nagasaki Univ. 26, 37–48 (1968).
—: Studies on the underwater sound, II. On the diurnal variation of the Tenpura noise in the coastal waters of Nagasaki Prefecture. Bull. Fac. Fish. Nagasaki Univ. 28, 31–41 (1969).
Tavolga, W. N.: Review of marine bio-acoustic, 100 pp. New York: U.S. Naval Training Device Center 1965.
Volt, P.: Studien über das “Knallen” der Alpheiden nach Untersuchungen an Alpheus dentipes Guérin und Synalpheus laevimanus (Heller). Z. Morph. Ökol. Tiere 34, 272–316 (1938).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by M. Anraku, Nagasaki
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takemura, A. Studies on underwater sounds III. On the mechanism of sound production and the underwater sounds produced by Linuparus trigonus . Marine Biology 9, 87–91 (1971). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00348247
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00348247