Abstract
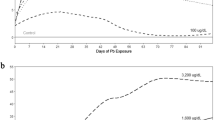
Sublethal behavioural responses including avoidance and burial rate were compared with 10 d acute morbidity and mortality in bioassays using juvenile Macomona liliana 1 to 3 mm long. The bivalves showed significant movement away from all copper-dosed sediments, with maximal movement after 96 h at 25 mg Cu kg (dry wt)-1. Increasing copper concentrations slowed the rate of burial, and above 15 mg Cu kg (dry wt)-1, most shellfish failed to bury after 90 min. After 10 d exposure, morbidity (defined as inability to rebury) occurred at 15 mg Cu kg (dry wt)-1 and mortality at 30 mg Cu kg (dry wt)-1. In avoidance trials, chlordane had a significant effect on overall movement from 20 μg kg (dry wt)-1, but increasing concentrations reduced movement away from dosed sediment. Chlordance appeared to have no effect on burial rate. Survival was affected by 10 d exposure to 400 μg chlordane kg (dry wt)-1, with increased morbidity and death. The relative sensitivities of the responses shown by M. liliana to copper were avoidance > burial/morbidity > mortality, with a 6-fold difference in the response threshold between avoidance and mortality. With chlordance, an avoidance response was detected at a concentration ∼20-fold lower than that causing morbidity. Behavioural responses of M. liliana have the potential to provide a sensitive bioassay.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA (1989). Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater. 17th edn. American Public Health Association, Washington
Chapman, P. M. (1988). Marine sediment toxicity tests. In: Lichtenberg, J. J., Winter, F. A., Weber, C. I., Fradkin, L. (eds.) Chemical and biological characterization of sludges, sediments, dredge spoils, and drilling muds. American Society for Testing and Materials. Philadelphia, p. 391–402 (ASTM STP 976)
Cummings, V. J., Pridmore, R. D., Thrush, S. F., Hewitt, J. E. (1994). Emergence and floating behaviour of post-settlement juveniles of Macomona liliana (Bivalvia: Tellinacea). Mar. Behav. Physiol. (in press)
Dearth, M. A., Hites, R. A. (1991). Complete analysis of technical chlordane using negative ionization mass spectrometry. Envir. Sci. Technol. 25: 245–254
Finney, D. J. (1981). Probit analysis. 3rd end. Cambridge University Press, Massachusetts
Fox, M. E., Roper, D. S., Thrush, S. F. (1988). Organochlorine contaminants in surficial sediments of Manukau Harbour, New Zealand. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 13: 217–218
Gaudette, H. E., Flight, W. R., Toner, L., Folger, D. W. (1974). An inexpensive titration method for the determination of organic carbon in recent sediments. J. sedim. Petrol. 44: 249–253
Glasby, G. P., Stoffers, P., Walter, P., Davis, K. R., Renner, R. M. (1988). Heavy-metal pollution in Manukau and Waitemata Harbours, New Zealand. N.Z. Jl mar. Freshwat. Res. 22: 595–611
Hughes, J. M., Chapman, H. F., Kitching, R. L. (1987). Effects of sublethal concentrations of copper and freshwater on behaviour in an estuarine gastropod Polinices sordidus. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 18: 127–131
Kitching, R. L., Chapman, H. F., Hughes, J. M. (1987). Levels of activity as indicators of sublethal impacts of copper contamination and salinity reduction in the intertidal gastropod, Polinices incei Philippi. Mar. envirl Res. 23: 79–87
McGreer, E. R. (1979). Sublethal effects of heavy metal contaminated sediments on the bivalve Macoma balthica (L.). Mar. Pollut. Bull. 10: 259–262
McLeese, D. W., Burridge, L. E., Van Dinter, J. (1982). Toxicities of five organochlorine compounds in water and sediment to Nereis virens. Bull. envir. Contam. Toxic. 28: 216–220
McLeese, D. W., Metcalfe, C. D. (1980). Toxicities of eight organochlorine compounds in sediment and seawater to Crangon septemspinosa. Bull. envir. Contam. Toxic. 25: 921–928
Miller, D. C. (1980). Some applications of locomotor responses in pollution monitoring. Rapp. P.-v. Réun. Cons. perm. int. Explor. Mer 179: 154–161
Morton, J., Miller, M. (1968). The New Zealand seashore. Collins, Auckland
Oakden, J. M., Oliver, J. S., Flegal, A. R. (1984). Behavioral responses of a phoxocephalid amphipod to organic enrichment and trace metals in sediment. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 14: 253–257
Olla, B. L., Pearson, W. H., Studholme, A. L. (1980). Applicability of behavioural measures in environmental stress assessment. Rapp. P.-v. Réun. Cons. perm. int. Explor. Mer 179: 162–173
Parrish, P. S., Schimmel, S. C., Hansen, D. J., Patrick, J. M., Forester, J. (1976). Chlordane: effect on several estuarine organisms. J. Toxic envirl Hlth 1: 485–494
Pearson, W. H., Woodruff, D. L., Sugarman, P. C. (1981). Effects of oiled sediment on predation on the littleneck clam, Protothaca staminea, by the Dungeness crab, Cancer magister. Estuar. cstl Shelf Sci. 13: 445–454
Phelps, H. L., Hardy, J. T., Pearson, W. H., Apts, C. W. (1983). Clam burrowing behaviour: inhibition by copper-enriched sediment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 14: 452–455
Phelps, H. L., Pearson, W. H., Hardy, J. T. (1985). Clam burrowing behaviour and mortality related to sediment copper. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 16: 309–313
Phillips, D. J. H., Spies, R. B. (1988). Chlorinated hydrocarbons in the San Francisco estuarine ecosystem. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 19: 445–453
Pridmore, R. D., Thrush, S. F., Cummings, V. J., Hewitt, J. E. (1992). Effect of the organochlorine pesticide technical chlordane on intertidal macrofauna. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 24: 98–102
Pridmore, R. D., Thrush, S. F., Hewitt, J. E., Reper, D. S. (1990). Macrobenthic community composition of six intertidal sandflats in Manukau Harbour, New Zealand. N.Z. Jl mar. Freshwat. Res. 24: 81–96
Pridmore, R. D., Thrush, S. F., Wilcock, R. J., Smith, T. J., Hewitt, J. E., Cummings, V. J. (1991). Effect of the organochlorine pesticide technical chlordane on the population structure of suspension and deposit feeding bivalves. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 76: 261–271
Roper, D. S., Pridmore, R. D., Thrush, S. F. (1992). Recruitment to the macrobenthos of Macomona liliana (Bivalvia: Tellinidae) in Manukau Harbour, New Zealand. N.Z. Jl mar. Freshwat. Res. 26: 405–412
Rosales, M. T. L., Botello, A. V., Bravo, H., Mandelli, E. F. (1979). PCBs and organochlorine insecticides in oysters from coastal lagoons of the Gulf of Mexico. Bull. envir. Contam. Toxic. 21: 652–656
Shigenaka, G. (1990). Chlordane in the marine environment of the United States: review and results from the National Status and Trends Program. National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, Seattle (NOAA natn. mar. Fish. Serv. tech. Memo. NOS OMA 55)
Smith, T. J., Wilcock, R. J., Pridmore, R. D., Thrush, S. F., Langdon, A. G., Wilkins, A. L., Northcott, G. L. (1992). Persistence of chlordane applied to an intertidal sandflat. Bull. envir. Contam. Toxic. 49: 129–136
Sovocool, G. W., Lewis, R. G., Harless, R. L., Wilson, N. K., Zehr, R. D. (1977). Analysis of technical chlordane by gas chromatography/mass spectrometry. Analyt. Chem. 49: 734–740
Stirling, E. A. (1975). Some effects of pollutants on the behavior of the bivalve Tellina tenuis. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 6: 122–124
Stumm, W., Morgan, J. J. (1981). Aquatic chemistry. An introduction emphasizing chemical equilibria in natural waters. Wiley-Interscience, New York
Swartz, R. C. (1987). Toxicological methods for determining the effects of contaminated sediment on marine organisms. In: Dickson, K. L., Maki, A. W., Brungs, W. A. (eds.) Fate and effects of sediment-bound chemicals in aquatic systems. Pergamon, New York, p. 183–198
Tanita, R., Johnson, J. M., Chun, M., Maciolek, J. (1976). Organochlorine pesticides in the Hawaii Kai marina. Pestic. Monit. J. 10: 24–29
Zar, J. H. (1984). Biostatistical analysis. 2nd edn. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs, N.J.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. F. Humphrey, Sydney
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roper, D.S., Hickey, C.W. Behavioural responses of the marine bivalve Macomona liliana exposed to copper- and chlordane-dosed sediments. Marine Biology 118, 673–680 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00347515
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00347515