Abstract
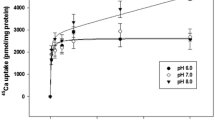
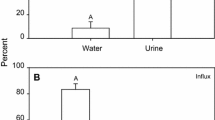
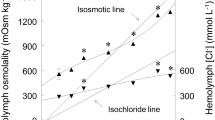
Transbranchial potentials (TP) and sodium or chloride fluxes were measured in an apparatus designed for the simultaneous perfusion of eight isolated gills of Uca rapax. In anterior gills perfused with U. rapax−saline (US) the TP varied almost linearly from-7.5 to +10 mV inside, and in posterior gills from +2 to-8.5 mV (inside), on exposure to salinities ranging from 8.7 through 52‰, i.e. 25 to 150% seawater (100%=34.6‰ S). Sodium influx and efflux in anterior gills exposed to US, 8.7 or 43.3‰ S (0.7 to 4.0 mmol h−1 g−1 dry wt) were always greater than in posterior gills (0.5 mmol h−1). The chloride fluxes were slightly smaller than sodium fluxes in anterior gills, while in the posterior gills the chloride influx (2.8 to 4.6 mmol h−1) was always larger than chloride efflux (0.6 to 1.1 mmol h−1) or the sodium fluxes. At least three ion-transport mechanisms may be present in these gills: (1) an internal ( = basolateral), ouabain-sensitive Na+, K+ pump, restricted to anterior gills; (2) a furosemide-sensitive Na+, K+, 2Cl− (plus water) transporter, apparently restricted to posterior gills, and (3) a Na+ exchanger (and possibly other as yet unidentified ion transporters, as suggested by large increases of the chloride influxes caused by amiloride), probably located on the apical membranes of the epithelial cells of both gill types. The differential selectivity of the gills of U. rapax for sodium or chloride may limit the transbranchial movements of either ion, without a reduction of the overall permeability of these crabs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avella M, Bornancin M (1990) Ion fluxes in the gills of freshwater and seawater salmonid fish. In: Truchot JP, Lahlou B (eds) Animal nutrition and transport processes. Karger, Basel, Munich, New York, pp 1–13
Baldwin GF, Kirschner LB (1976a) Sodium and chloride regulation in Uca adapted to 175% sea water. Physiol Zoöl 49: 158–171
Baldwin GF, Kirschner LB (1976b) Sodium and chloride regulation in Uca adapted to 10% sea water. Physiol Zoöl 49: 172–180
Bayliss D, Harris RR (1988) Chloride ion regulation in the freshwater amphipod Corophium curvispinum and acclimatory effects of external Cl−. J comp Physiol 158B: 81–90
Burnett LE, Towle DW (1990) Sodium ion uptake by perfused gills of the blue crab Callinectes sapidus: effects of ouabain and amiloride. J exp Biol 149: 293–305
Cameron JN (1979) Effects of inhibitors on ion fluxes, trans-gill potential and pH regulation in freshwater blue crabs, Callinectes sapidus (Rathbun). J comp Physiol B133: 219–225
Croghan PC, Curra RA, Lockwood APM (1965) The electrical potential difference across the gills of the crayfish Austropotamobius pallipes (Lereboullet). J exp Biol 42: 463–474
Díaz M, Lorenzo A (1991) Coexistence of absortive and secretory NaCl processes in the isolated lizard colon: effects of AMP. Zool Sci 8: 477–484
Drews G, Graszynski K (1987) The transephitelial potential difference in the gills of the fiddler crab, Uca tangeri: influence of some inhibitors. J comp Physiol B157: 345–353
Gilles R, Pèqueux A, Bianchini A (1988) Physiological aspects of NaCl movements in the gills of the euryhaline crab, Eriochiir sinensis, acclimated to fresh water. Comp Biochem Physiol 90A: 201–207
Graszynski K, Bigalke T (1986) Osmoregulation and ion transport in the extremely euryhaline fiddler crabs Uca pugilator and Uca tangeri (Ocypodidae). Zool Beitr (NF) 30: 339–358
Greger R (1985) Ion transport mechanisms in thick ascending limb of Henle's loop of mammalian nephron. Physiol Rev 65: 760–797
Kirschner LB (1982) Physical basis of solute and water transfer across gills. In: Houlihan DF, Rankin JC, Shuttleworth TJ (eds) Gills. University Press, Cambridge, pp 63–76
Krippeit-Drews P, Drews G, Graszynski K (1989) Effects of ion substitution on the transepithelial potential difference of the gills of the fiddler crab Uca tangeri: evidence for a H pump in the apical membrane. J comp Physiol B59: 43–49
Lee SH, Pritchard JB (1985) Bicarbonate-chloride exchange in gill plasma membranes of blue crab. Am J Physiol 249: R544-R550
Lignon JM, Pèqueux A (1990) Permeability properties of the cuticle and gill ion exchanges in decapod crustaceans. In: Truchot JP, Lahlou B (eds) Animal nutrition and transport processes. Karger, Basel, Munich, New York, pp 14–27
Lucu C (1977) Sodium kinetics in the shrimp, Palaemonetes pugio. II. Sodium fluxes and electrochemical potentials. J comp Physiol B115: 207–214
Lucu C (1990) Ionic regulatory mechanisms in crustacean gill epithelia. Comp Biochem Physiol 97A: 297–306
Lucu C, Siebers D (1986) Amiloride-sensitive sodium flux and potentials in perfused Carcinus gill preparations. J exp Biol 122: 25–35
Lucu C, Siebers D (1987) Linkage of Cl-fluxes with ouabain sensitive Na/K exchange through Carcinus gill epithelia. Comp Biochem Physiol 87A: 807–811
Lucu C, Siebers D, Newiskiene V, Skaramuca B, Spaargaten D (1992) Rubidium fluxes and ion permeability studies in isolated perfused Carcinus gills. Comp Biochem Physiol 102A: 307–310
Onken H, Graszynski K, Zeiske W (1991) Na+−independent, electrogenic Cl− uptake across the posterior gills of the Chinese crab (Eriocheir sinensis): voltage-clamp and microelectrode studies. J comp Physiol B161: 293–301
Parker RE (1981) Estadistica para biólogos. Omega, Barcelona
Pèqueux A, Gilles R (1981) Na+ fluxes across isolated perfused gills of the crab Eriocheir sinensis. J exp Biol 92: 173–186
Pèqueux A, Gilles R (1988) The transephitelial potential difference of isolated perfused gills of the Chinese crab Eriocheir sinensis acclimated to fresh water. Comp Biochem Physiol 89A: 163–172
Proverbio T, Zanders IP, Marín R, Rodríguez JM, Proverbio F (1990) Effects of Na+ and/or K+ on the Mg2+−dependent ATPase activities in shrimp (Macrobrachium amazonicum) gill homogenates. Comp Biochem Physiol 97B: 383–390
Rojas W, Zanders IP (1991) Un nuevo diseño para perfundir simultaneamente varias branquias aisladas de crustáceo y medir sus propiedades bioélectricas y flujos iónicos. IV Congreso Latinoamericano de Ciencias del Mar. Facultad de Ciencias del Mar, Universidad Católica del Norte, Coquimbo, Chile (Resumen p. 93)
Schwarz HJ, Graszynski K (1989) Ion transport in crab gills: a new method using isolated half platelets of Eriocheir sinensis gills in a Ussing chamber. Comp Biochem Physiol 92A: 601–604
Shetlar RE, Towle DW (1989) Electrogenic sodium/proton exchange in membrane vesicles from crab (Carcinus meanas) gill. Am J Physiol 257: R924-R931
Siebers D, Böttcher K, Petrausch G, Hamann A, Wille H (1990) Effects of some chloride channel blockers on potential differences and ion fluxes in isolated perfused gills of shore crabs Carcinus maenas. Comp Biochem Physiol 97A: 9–15
Siebers D, Lucu C, Winkler A, Grammerstorf U, Wille H (1987) Effects of amiloride on sodium chloride transport across isolated perfused gills of shore crabs Carcinus maenas acclimated to brackish water. Comp Biochem Physiol 87A: 333–340
Siebers D, Lucu C, Winkler A, Venezia LD, Wille H (1986) Active uptake of sodium in the gills of the hyperregulating crab Carcinus maenas. Helgoländer Meeresunters 40: 151–160
Siebers D, Wille H, Lucu C, Dalla Venezia L (1989) Conductive sodium entry in gill cells of the shore crab, Carcinus maenas. Mar Biol 101: 61–68
Siebers D, Winkler A, Lucu C, Thedens G, Weichart D (1985) Na-K-ATPase generates an active transport potential in the gills of the hyperregulating crab Carcinus maenas. Mar Biol 87: 185–192
Smith DS, Linton JR (1971) Potentiometric evidence for the active transport of sodium and chloride across the excised gill of Callinectes sapidus. Comp Biochem Physiol 39A: 367–378
Towle DW (1990) Sodium transport systems in gills. In: Kinne RK (ed) Comparative aspects of sodium cotransport systems. Karger, Basel, Munich, New York, pp 241–264
Ussing HH (1947) Interpretation of the exchange of radiosodium in isolated muscle. Nature, Lond 160: 262–263
Ussing HH (1949) The distinction by means of tracers between active transport and diffusion. Acta physiol scand 19: 43–56
Zanders IP (1978) Ionic regulation in the mangrove crab Goniopsis cruentata. Comp Biochem Physiol 60: 293–302
Zanders IP (1980) Regulation of blood ions in Carcinus maenas (L.). Comp Biochem Physiol 65A: 97–108
Zanders IP (1981) Control and dynamics of ionic balance in Carcinus maenas (L.). Comp Biochem Physiol 70A: 457–468
Zanders IP, Martelo MJ (1984) The influence of acclimation temperature on magnesium and sulphate regulation in two mangrove crabs. Comp Biochem Physiol 78A: 487–492
Zanders IP, Martelo MJ (1987) Contribution of Na/Na and Cl/Cl exchanges to sodium and chloride fluxes in the crab Goniopsis cruentata. J comp Physiol 157B: 599–606
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by N.H. Marcus, Tallahassee
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zanders, I.P., Rojas, W.E. Transbranchial potentials and ion fluxes across isolated, perfused gills of Uca rapax . Marine Biology 125, 307–314 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00346311
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00346311