Abstract
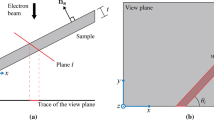
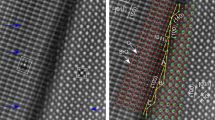
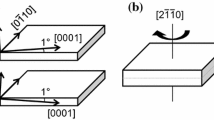
Dislocations in K-feldspars were studied by high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HRTEM) and HRTEM images were further submitted to a filtering in order to improve their interpretation. (010)[101] dislocations appear to be dissociated with (001)[001]/2 planar defect, whereas (001)[110]/2 dislocations are perfect. Structural models of planar defects in (010) and (001) planes were investigated. The energy estimation of these models was performed using the Keating potential. The structural analysis agreed with the experimental result in that dislocations can be dissociated in the (010) plane, whereas they cannot be dissociated in the (001) plane.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Friedel J (1972) On the splitting of dislocations in the diamond cubic lattice. J Less-Common Met 28:241–248
Gandais M, Willaime C (1984) Mechanical properties of feldspars. In: Brown WL (ed) Feldspars and feldspathoids, NATO ASI series. D. Reidel, Dordrecht
Heggie M, Zheng Y (1987) Planar defects and dissociation of dislocations in a K-feldspar. Phil Mag A 56:681–688
Hirth JP, Lothe J (1968) Theory of dislocations. Materials science and engineering series. McGraw-Hill, New York
Kovacs MP, Gandais M (1980) Transmission electron microscope study of experimentally deformed K-feldspar single crystals. Phys Chem Minerals 6:61–76
Marshall DB, McLaren AC (1977b) The direct observation and analysis of dislocations in experimentally deformed plagioclase feldspars. J Mater Sci 12:893–903
Montardi Y, Mainprice C (1987) A transmission electron microscopy study of the natural plastic deformation of calcic plagioclase (An68–70). Bull Minéral 110:1–14
Olsen TS, Kohlstedt DL (1984) Analysis of dislocations in some naturally deformed plagioclase feldspars. Phys Chem Minerals 11:153–160
Sacerdoti M, Labernardière H, Gandais M (1980) Transmission electron microscope (TEM) study of geologically deformed potassic feldspars. Bull Minéral 103:148–155
Scandale E, Gandais M, Willaime C (1983) Transmission electron microscopic study of experimentally deformed K-feldspar single crystals. Phys Chem Minerals 9:182–187
Tullis J (1982) Deformation of feldspars. In: Ribbe PH (ed) Feldspar mineralogy. Reviews in Mineralogy, Mineralogical Soc. of America
Willaime C, Christie JM, Kovacs MP (1979) Experimental deformation of K-feldspar single crystals. Bull Minéral 102:168–177
Willaime C, Gandais M (1977) Electron microscope study of plastic defects in experimentally deformed alkali feldspar. Bull Soc fr Minéral Cristallogr 100:263–271
Zheng Y, Gandais M (1987a) Fine structure of (010)[001] dislocations in K-feldspars. Phil Mag A 55:329–338
Zheng Y, Gandais M (1987b) Modèles de structure des dislocations (010)[001] dans les feldspaths alcalins. Bull Minéral 110:15–24
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Y., Gandais, M. & Heggie, M. Study of (010)[101] and (001)[110]/2 dislocations in K-feldspars by HRTEM and modelling. Phys Chem Minerals 15, 349–354 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00311039
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00311039