Abstract
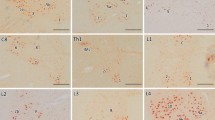
Expression of LeY, a difucosylated type 2 chain determinant, has been previously identified as a characteristic of cells undergoing apoptosis. Immunohistochemistry using an antibody for LeY, as well as nick-end labeling for the detection of DNA breaks, was done on cervical spinal cord sections from ten patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and nine patients who had died from other causes. LeY-positive immunoreactivity was seen in the motor neurons of seven ALS cases, but in none of the other cases. Nickend labeling was also positive in four ALS cases. Double staining of motor neurons by anti-LeY antibody and nick-end labeling was shwon in these cases. Other LeY-positive structures, such as reactive astrocytes and fatladen microglia/macrophages in the lateral and anterior columns, were negative for nick-end labeling. These results suggest that the mechanism of cell death in the spinal motor neurons of ALS may be apoptosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe K, McKibbin JM, Hakomori S (1983) The monoclonal antibody directed to difucosylated type 2 chain (Fuca12Galß1→4[Fuca1→3]GlcNAc; Y determinant). J Biol Chem 258: 11793–11797
Ansari B, Coates PJ, Greenstein BD, Hall PA (1993) In situ end-labeling detects DNA strand breaks in apoptosis and other physiological and pathological states. J Pathol 170: 1–8
Edwards SN, Buckmaster AE, Tolkovsky AM (1991) The death programme in cultured sympathetic neurons can be suppressed at the posttranslational level by nerve growth factor, cyclic AMP, and depolarization. J Neurochem 57: 2140–2143
Forloni G, Angeretti N, Chiesa R, Monzani E, Salmona M, Bugiani O, Tagliavini F (1993) Neurotoxity of a prion protein fragment. Nature 362: 543–546
Forloni G, Chiesa R, Smiroldo S, Verga L, Salmona M, Tagliavini F, Angeretti N (1993) Apoptosis mediated neurotoxity induced by chronic application of β amyloid fragment 25–35. NeuroReport 4: 523–526
Gavrieli Y, Sherman Y, Ben-Sasson SA (1992) Identification of programmed cell death in situ via specific labeling of nuclear DNA fragmentation. J Cell Biol 119: 493–501
Gold R, Schmied M, Rothe G, Zischler H, Breitschope H, Wekerle H, Lassmann H (1993) Detection of DNA fragmentation in apoptosis: application of in situ nick translation to cell culture systems and tissue sections. J Histochem Cytochem 41: 1023–1030
Hiraishi K, Suzuki K, Hakomori S, Adachi M (1993) LeY antigen expression is correlated with apoptosis (programmed cell death). Glycobiology 3: 381–390
Kerr JFR, Wyllie AH, Currie AR (1972) Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implication in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer 26: 239–257
Kerr JFR, Searle J, Harmon BV, Bishop CJ (1987) Apoptosis. In: Potton CS (ed) Perspectives on mammalian cell death, Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 93–128
Kiernan JA, Hudson AJ (1993) Changes in shapes of surviving motor neurons in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Brain 116: 203–215
Masu Y, Wolf E, Holtmann B, Sendtner M, Brem G, Thoenen H (1993) Disruption of the CNTF gene results in motor neuron degeneration. Nature 365: 27–32
Mourelatos Z, Yachnis A, Rorke L, Mikol J, Gonatas NK (1993) The Golgi apparatus of motor neurons in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol 33: 608–615
Wyllie AH (1980) Glucocorticoid-induced thymocyte apoptosis is associated with endogenous endonuclease activation. Nature 284: 555–556
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by grants from the Ministry of Education in Japan
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshiyama, Y., Yamada, T., Asanuma, K. et al. Apoptosis related antigen, LeY and nick-end labeling are positive in spinal motor neurons in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol 88, 207–211 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00293395
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00293395