Summary
The haemodynamic effects of an i.v. infusion of 2 mg nitrendipine have been studied in six healthy volunteers.
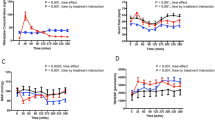
Nitrendipine significantly decreased the systolic (−8.3%) diastolic (−19.9%) and mean arterial (−11.6%) blood pressures and the peripheral vascular resistance (−57.8%), and significantly increased leg blood flow (+128%).
Stroke volume did not change. Due to the increase in heart rate (+28.5%), the cardiac output (2.8.2%) rose significantly. The haemodynamic effects were closely related to the serum nitrendipine concentration. The sigmoidal Emax-model was appropriate to describe the data.
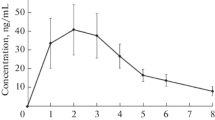
Pronounced interindividual differences in the serum nitrendipine concentrations required to elicit 50% of the maximum haemodynamic effect (EC50) were observed. The EC50 for the increase in leg blood flow ranged from 2.9 to 30.9 ng/ml and for the reduction in peripheral vascular resistance from 2.1 to 25.7 ng/ml. Interindividual differences in EC50 values were less pronounced if based on unbound serum nitrendipine levels.
The fraction of nitrendipine not bound to serum proteins showed a three-fold difference between subjects, with free fractions ranging from 0.011 to 0.036. The unbound EC50 values for the increase in leg blood flow varied between 0.06 and 0.44 ng/ml and for the reduction in peripheral vascular resistance from 0.07 to 0.35 ng/ml.
Based on the serum concentrations associated with comparable haemodynamic effects nitrendipine was at least three-times more potent than nifedipine.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Esper RJ, Esper RC, Cassola D, Spiritoso RA, Mosca H, Sami HH, Castro JM, Rohwedder RW (1984) Effectiveness of nitrendipine in the treatment of essential hypertension: a multi-center trial. In: Scriabine A, Vanov S, Deck K (eds) Nitrendipine. Urban and Schwarzenberg, Baltimore, pp 477–490
Fischer C, Heuer B, Heuck K, Eichelbaum M (1986) Quantification of nitrendipine by stable isotope dilution and elecron capture negative ion chemical ionization. Biomed Envirom Mass Spectrom 13: 645–650
Franz I-W, Wievel D (1985) Antihypertensive Wirkung von Nitrendipin, Nifedipin und Acebutolol und deren Kombination auf den Ruhe- und Balastungsblutdruck bei Hochdruckkranken. Z Kardiol 74: 111–116
Garthoff B, Kazda S, Knorr A, Luckhaus G, Stoepel K (1984) Pharmacology of a new antihypertensive calcium antagonist. In: Scriabine A, Vanov S, Deck K (eds) Nitrendipine. Urban and Schwarzenberg, Baltimore, pp 11–24
Holford NHG, Sheiner LB (1981) Understanding the dose-effect relationship: clinical application of pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic models. Clin Pharmacokinet 6: 429–453
Hulthen UL, Bolli P, Erne P, Kiowski W, Bühler FR (1984) Peripheral vasodilating effect of nitrendipine in man. In: Scriabine A, Vanov S, Deck K (eds) Nitrendipine. Urban and Schwarzenberg, Baltimore Munich, pp 463–468
Kazda S, Garthoff B, Knorr A (1983) Nitrendipine and other calcium entry blockers (calcium antagonists) in hypertension. Fed Proc 42: 196–200
Kazda S, Garthoff B, Luckhaus G (1984) Mode of antihypertensive action of nitrendipine. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 6: S956-S962
Kleinbloesem CH, van Brummelen P, van de Linde JA, Voogd PJO, Breimer DD (1984) Nifedipine: Kinetics and dynamics in healthy subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther 35: 742–749
Kleinbolesem CH, van Brummelen P, van Harten J, Danhof M, Breimer DD (1985) Kinetics and haemodynamics of nifedipine in patients with different degrees of impaired renal function. Clin Pharmacol Ther 37: 563–574
Kleinbloesem CH, van Harten J, Wilson JPH, Danhof M, van Brummelen P, Breimer DD (1986) Nifedipine: Kinetics and haemodynamic effects in patients with liver cirrhosis after intravenous and oral administration. Clin Pharmacol Ther 40: 21–28
Lehmann H-U, Hochrein H, Witt E, Mies HW (1983) Haemodynamic effects of calcium antagonists. Hypertension [Suppl II] 5: 66–73
Löllgen H (1983) Kardiopulmonale Funktionsdiagnostik. Ciba-Geigy GmbH, Wehr/Baden
Mikus G, Fischer C, Machleidt C, Kuhlmann U, Eichelbaum M (1991) Pharmacokinetics, bioavailability, metabolism and acute and chronic antihypertensive effects of nitrendipine in patients with chronic renal failure and moderate to severe hypertension. Br J Clin Pharmacol (31: 313–322)
Peck CC, Barrett BB (1979) Nonlinear least squares regression programs for microcomputers. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 5: 537–541
Ram CVS, Carnegie AL, Kaplan NM (1984) Effect of nitrendipine therapy on ambulatory blood pressures. In: Scriabine A, Vanov S, Deck K (eds) Nitrendipine. Urban and Schwarzenberg, Baltimore, pp 501–507
Walley TJ, Heagerty AM, Woods KL, Bing RF, Pohl JEF, Barnett DB (1987) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of nifedipine infusion in normal volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol 23: 693–701
Wezler K, Sinn W (1963) Das Strömungsgesetz des Blutkreislaufs. Editio Kantor, Aulendorf, Württemberg
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mikus, G., Zekorn, C., Brecht, T. et al. Acute haemodynamic effects of i.v. nitrendipine in healthy subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 41, 99–103 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00265899
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00265899