Abstract
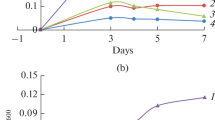
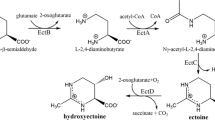
The moderate halophile Vibrio costicola, growing on a chemically-defined medium, transformed choline into glycine betaine (betaine) by the membrane-bound enzyme choline dehydrogenase and the cytoplasmic enzyme betainal (betaine aldehyde) dehydrogenase. Choline dehydrogenase was strongly induced and betainal dehydrogenase less strongly induced by choline. The formation of these enzymes was also regulated by the NaCl concentration of the growth medium, increasing with increasing NaCl concentrations. Intracellular betaine concentrations also increased with increasing choline and NaCl concentrations in the medium. This increase was almost completely blocked by chloramphenicol, which does not block the increase in salt-tolerant active transport on transfer from a low to a high salt concentration.
Choline dehydrogenase was inhibited by chloride salts of Na+, K+, and NH su+inf4 , the inhibition being due to the Cl- ions. Betainal dehydrogenase was stimulated by 0.5 M salts and could function in up to 2.0 M salts.
Cells grew as well in the presence as in the absence of choline in 0.5 M and 1.0 M NaCl, but formed no intracellular betaine. Choline stimulated growth in 2.0 M NaCl and was essential for growth in 3.0 M NaCl. Thus, while betaine is important for some of the adaptations to high salt concentration by V. costicola, it by no means accounts for all of them.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CDMM:
-
chemically-defined minimal medium
- PPT:
-
proteose-peptone tryptone medium
- SDS:
-
sodium dodecyl sulfate
References
Bengis-GarberC, Gromet-ElhananZ (1979) Purification of the energy transducing adenosine triphosphatase complex from Rhodospirillum rubrum. Biochemistry 18:3577–3581
Bengis-GarberC, KushnerDJ (1981) Purification and properties of 5′-nucleotidase from the membrane of Vibrio costicola, a moderately halophilic bacterium. J Bacteriol 146:24–32
BorowitzkaLJ, BrownAD (1974) The salt relations of marine and halophilic species of the unicellular green alga, Dunaliella. The role of glycerol as a compatible solute. Arch Microbiol 96:37–52
BouillardL, LeRudulierD (1983) Nitrogen fixation under osmotic stress: enhancement of nitrogenase biosynthesis in Klebsiella pneumoniae by glycine betaine. Physiol Veg 21:447–457
BrownAD (1976) Microbial water stress. Bacteriol Rev 40:803–846
ChoquetCG, KamekuraM, KushnerDJ (1989) In vitro protein synthesis by the moderate halophile Vibrio costicola: site of action of Cl- ions. J Bacteriol 171:880–886
ChoquetCG, KushnerDJ (1990) Use of natural mRNAs in the cell-free protein-synthesising systems of the moderate halophile Vibrio costicola. J Bacteriol 172:3462–3468
FlanneryWL, DoetschRN, HansenPA (1952) Salt desideratum of Vibrio costicolus, an obligate halophilic bacterium. I. Ionic replacement of sodium chloride requirement. J Bacteriol 64:713–717
ForsythMP, KushnerDJ (1970) Nutrition and distribution of salt response in populations of moderately halophilic bacteria. Can J Microbiol 16:253–261
GalinskyEA, PfeifferHP, TrüperHG (1985) 1,4,5,5-tetrahydro-2-methyl-4-pyrimidinecarboxylic acid. A novel cyclic amino acid from halophilic phototrophic bacteria of the genus Ectothiorhodospira. Eur J Biochem 149:135–140
IkutaS, MatuuraK, ImamuraS, MisakiH, HoriutiY (1977) Oxidative pathway of choline to betaine in the soluble fraction prepared from Arthrobacter globiformis. J Biochem 82:157–163
ImhoffJF (1986) Osmoregulation and compatible solutes in eubacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 39:57–66
ImhoffJF, Rodriguez-ValeraF (1984) Betaine is the main compatible solute of halophilic eubacteria. J Bacteriol 160:478–479
KamekuraM, KushnerDJ (1984) Effect of chloride and glutamate ions on in vitro protein synthesis by the moderate halophile, Vibrio costicola. J Bacteriol 160:385–390
KamekuraM, WallaceR, HipkissAR, KushnerDJ (1985) Growth of Vibrio costicola and other moderate halophiles in a chemically defined minimal medium. Can J Microbiol 31:870–872
KushnerDJ (1978) Life in high salt and solute concentrations: halophilic bacteria. In: KushnerDJ (ed) Microbial life in extreme environments. Academic Press, London, pp 317–368
KushnerDJ (1988) What is the “true” internal environment of halophilic and other bacteria? Can J Microbiol 34:482–486
KushnerDJ, KamekuraM (1988) Physiology of halophilic eubacteria. In: Rodriguez-ValeraF (ed) Halophilic bacteria. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, USA, pp 109–140
KushnerDJ, HamaideF, MacLeodRA (1983) Development of saltresistant active transport in a moderately halophilic bacterium. J Bacteriol 153:1163–1171
LandfaldB, StromAR (1986) Choline-glycine betaine pathway confers high level of osmotic tolerance in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol 165:849–855
LeRudulierD, BernardT (1986) Salt tolerance in Rhizobium: a possible role for betaines. FEMS Microbiol Rev 39:67–72
LowryOH, RosebroughNJ, FarrAL, RandallRJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Mol Biol 193:265–275
MeuryJ (1988) Glycine betaine reverses the effects of osmotic stress on DNA replication and cellular division in Escherichia coli. Arch Microbiol 149:232–239
NagasawaT, KawabataY, TaniY, OgataK (1975) Choline dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas aeruginosa A-16. Agric Biol Chem 7:1513–1514
NagasawaT, KawabataY, TaniY, OgataK (1976) Purification and characterization of betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa A-16. Agric Biol Chem 9:1743–1749
Ohte-FukuyamaM, MiyakeY, EmiS, YamanoT (1980) Identification and properties of the prosthetic group of choline oxidase from Alcaligenes sp. J Biochem 88:197–203
PavlicekKA, YoppJH (1982) Betaine as a compatible solute in the complete relief of salt inhibition of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase from a halophilic blue-green alga. Plant Physiol (Suppl) 69:58
PollardA, Wyn JonesRG (1979) Enzyme activities in concentrated solutions of glycinebetaine and other solutes. Plant 144:291–298
Rafaeli-EshkolD, Avi-DorY (1968) Studies on halotolerance in a moderately halophilic bacterium. Effect of betaine on salt resistance of the respiratory system. Biochem J 109:687–691
ShindlerDB, WydroRM, KushnerDJ (1977) Cell-bound cations of the moderately halophilic bacterium Vibrio costicola. J Bacteriol 130:698–703
SibleyMH, YoppJH (1987) Regulation of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase in the halophilic cyanobacterium Aphanothece halophytica: a possible role in glycinebetaine biosynthesis. Arch Microbiol 149:43–46
SmithLT, PocardJA, BernardT, LeRudulierD (1988) Osmotic control of glycine betaine biosynthesis and degradation in Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol 170:3142–3149
Trüper HG (1990) Halophily, taxonomy, phylogeny and nomenclature. Workshop on General and Applied Aspects of Halophilic Microorganisms, Alicante, Spain; In proceedings of this workshop (in press)
WallJS, ChristiansonRJ, DimlerRJ, SentiFR (1960) Spectrophotometric determination of betaines and other quaternary nitrogen compounds as their periodides. Anal Chem 32:870–874
WarrSRC, ReedRH, StewartWDP (1984) Osmotic adjustment of cyanobacteria: the effects of NaCl, KCl, sucrose and glycine betaine on glutamine synthetase activity in a marine and a halotolerant strain. J Gen Microbiol 130:2169–2175
WohlfarthA, SeverinJ, GalinskiEA (1990) The spectrum of compatible solutes in heterotrophic halophilic eubacteria of the family Halomonadaceae. J Gen Microbiol 136:705–712
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Deceased, 1987
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choquet, C.G., Ahonkhai, I., Klein, M. et al. Formation and role of glycine betaine in the moderate halophile Vibrio costicola . Arch. Microbiol. 155, 153–158 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00248610
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00248610