Summary
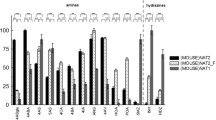
Batracylin (NSC-320846) is a quinalzolineone recently evaluated as a potential antitumor agent by the National Cancer Institute. The analog was active against a number of murine tumors, including colon adenocarcinoma 38 and multidrug resistant sublines of P-388 leukemia. Preclinical toxicity studies revealed that batracylin was much more toxic when administered orally to rats than to mice. The combined sex LD10 in mice was 5,655 mg/m2 while 576 mg/m2 was lethal to all rats treated at that dose. We determined that following oral administration of batracylin, systemic exposure of parent drug to the rat was only 14.9% of that to the mouse. It was subsequently noted that systemic exposure of a relatively non-polar metabolite was approximately 9 times greater in the rat than in the mouse. The metabolite was identified as N-acetylbatracylin by TLC, HPLC and mass spectral analyses. Observations by the National Cancer Institute that N-acetylbatracylin was not toxic following oral administration to mice or rats prompted evaluation of systemic exposure following oral administration to rats. Following oral administration of N-acetylbatracylin to rats, systemic exposure was almost nil. Indeed, exposure of rats to N-acetylbatracylin was several orders of magnitude greater following oral administration of six-fold lower doses of the parent drug, batracylin. Thus, N-acetylation may play a role in the toxicity of batracylin despite the lack of toxicity observed following oral administration of N-acetylbatracylin. In addition, further metabolism of the N-acetyl conjugate, analogous to that of other aromataic amines, may be involved in the pharmacology of batracylin and similar analogs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Plowman J, Paul KD, Atassi G, Harrison SD, Dykes DJ, Kabbe HJ, Narayanan VL, Yoder OC: Preclinical antitumor activity of batracylin (NSC 320846). Invest New Drugs 6: 147–153, 1988
El-Hawari M, Stoltz ML, Pallas F: Species differences in the toxic responses to batracylin (NSC-320846). Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 30: 626, 1989
Ames MM, Mathiesen DA: High-performance liquid Chromatographic assay and preclinical pharmacologic studies with the experimental antitumor agent batracylin. J Chromatog 491: 488–494, 1989
Reddy V, El-hawari M: Acute toxicity of N-acetyl-batracylin in mice and rats. Pilot Study Report to NCI for Contract N01-CM-87202, July 1989
Weber WW, Hein DW: N-acetylation pharmacogenetics. Pharmacol Rev 37: 25–79, 1985
Collins JM, Zaharko DS, Dedrick RL, Chabner BA: Potential roles for preclinical pharmacology in Phase I clinical trials. Cancer Treat Rep 70: 73–80, 1986
Ratain MJ, Propert K, Costanza M, Allen S, Berezin F, Schilsky RL, Van Echo DA: Population pharmacodynamic study of amonifides: CALGB 8862. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 31: 181, 1990
Grever MR, Staubus AE, Malspeis L: Correlation of N-acetylation phenotype with plasma levels of the N-acetyl metabolite of amonifide (NSC 308847). Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res 31: 178, 1990
Hanna PE, Banks RB: Arylhydroxylamines and arylhydroxamic acids: Conjugation reactions. In: Anders MW (ed) Bioactivation of Foreign Compounds. Academic Press, New York, 1985, Chapter 13, pp 375–402
Nelson SD: Metabolic activation and drug toxicity. J Med Chem 25: 753–765, 1982
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ames, M.M., Mathiesen, D.A. & Reid, J.M. Differences in N-acetylation of the experimental antitumor agent batracylin in the mouse and the rat. Invest New Drugs 9, 219–225 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00176974
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00176974