Abstract
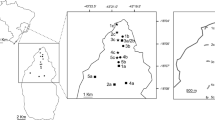
This study investigated the orchid-bee community in a conservation gradient of the high-altitude rocky fields in the state of Minas Gerais, Brazil. Sampling was performed at two sites with different anthropic influences: a disturbed area (DA), with exotic plant species, and a preserved area (PA). From September 2009 through February 2011, males of euglossine bees were sampled using aromatic bait-traps. We collected a total of 819 specimens belonging to 11 species and three genera: Euglossa Latreille, Eulaema Lepeletier, and Eufriesea Cockerell. Despite the proximity of DA and PA (about 1.2 km), differences in orchid-bee abundance and richness were observed. Higher abundance was observed in the PA (n = 485) compared with the DA (n = 334). Eight species were common to both sites, and only the DA showed exclusive species. The DA showed higher diversity and higher estimated species richness. Euglossa leucotricha Rebêlo & Moure was the most abundant species at both sites followed by Euglossa melanotricha Moure. Higher abundance and richness were found in the warm rainy season. This study contributes to the knowledge of the orchid-bee fauna in the rocky fields and suggests that the greater resource availability in the DA was responsible for the higher orchid-bee diversity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ackerman JD (1983) Diversity and seansonality of male euglossine bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae) in Central Panama. Ecology 63:274–283
Ackerman JD (1989) Geographic and seasonal variation in fragrance choices and preferences of male euglossine bees. Biotropica 21:340–347
Aguiar WM, Gaglianone MC (2008) Comunidades de abelhas Euglossina (Hymenoptera: Apidae) em remanescentes de mata estacional semidecidual sobre tabuleiro no estado do Rio de Janeiro. Neotrop Entomol 37:118–125
Alvarenga PEF, Freitas RF, Augusto SC (2007) Diversidade de Euglossini (Hymenoptera: Apidae) em áreas de cerrado do triângulo mineiro, MG. Biosci J 23:30–37
Andena SR, Nascimento FS, Bispo PC, Mechi MR, Mateus S, Bego LR (2009) Bee communities (Hymenoptera: Anthophila) of the "Cerrado" ecosystem in São Paulo State, Brazil. Genet Mol Res 8:766–774
Andrade-Silva ACR, Nemésio A, de Oliveira FF, Nascimento FS (2012) Spatial-temporal variation in orchid bee communities (Hymenoptera: Apidae) in remnants of arboreal Caatinga in the Chapada Diamantina region, state of Bahia, Brazil. Neotrop Entomol 41:296–305
Araújo VA, Araújo APA, Antonini Y (2010) Impact of resource availability on bee diversity. Sociobiology 55:1–13
Ayres M, Ayres Junior M, Ayres DL, Santos AA (2007) BIOESTAT—5.0. Aplicações estatísticas nas áreas das ciências bio-médicas. Sociedade Civil Mamirauá/MCT-CNPQ
Azevedo AA, Silveira FA, Aguiar CML, Pereira VS (2008) Fauna de abelhas (Hymenoptera, Apoidea) nos campos rupestres da Cadeia do Espinhaço-Minas Gerais e Bahia, Brasil: riqueza de espécies, padrões de distribuição e ameaças para conservação. Megadiversidade 4:126–157
Bezerra CP, Martins CF (2001) Diversidade de Euglossinae (Hymenoptera, Apidae) em dois fragmentos de Mata Atlântica localizados na região urbana de João Pessoa, Paraíba, Brasil. Rev Bras Zool 18:823–835
Cameron SA (2004) Phylogeny and biology of neotropical orchid bees (Euglossini). Ann Rev Entomol 49:377–404
Colwell RK (2006) EstimateS: Statistical estimation of species richness and shared species from samples Version 8. Persistent [online]. http://purl.oclc.org/estimates
Dodson CH, Dressler RL, Hills HG, Adams RM, Williams NH (1969) Biologically active compounds in orchid fragrances. Science 164:1243–1249
dos Anjos-Silva EJ, Camillo E, Garófalo CA (2006) Occurrence of Aglae caerulea Lepeletier & Serville (Hymenoptera: Apidae: Euglossini) in the Parque Nacional da Chapada dos Guimarães, Mato Grosso State, Brazil. Neotrop Entomol 35:868–870
Dressler RL (1982) Biology of the orchid bees (Euglossini). Ann Rev Ecol Syst 13:373–394
Drummond GM, Martins CS, Machado ABM, Sebaio FA, Antonini Y (2005) Biodiversidade em Minas Gerais-um atlas para sua conservação, 2ath edn. Fundação Biodiversitas, Belo Horizonte, Brasil
Eltz T, Roubik DW, Lunau K (2005) Experience dependent choices ensure species-specific fragrance accumulation in male orchid bees. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 59:146–156
Faria LRR, Silveira FA (2011) The orchid bee fauna (Hymenoptera, Apidae) of a core area of the Cerrado, Brazil: the role of riparian forests as corridors for forest-associated bees. Biota Neotrop 11:87–94
Ferreira MG, Pinho OC, Balestieri JBP, Faccenda O (2011) Fauna and stratification of male orchid bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae) and their preference for odor baits in a forest fragment. Neotrop Entomol 40:639–646
Giangarelli DC, Freiria GA, Colatreli OP, Suzuki KM, Sofia SH (2009) Eufriesea violacea (Blanchard) (Hymenoptera: Apidae): an orchid bee apparently sensitive to size reduction in forest patches. Neotrop Entomol 38:610–615
Hammer Ø, Harper DAT, Ryan PD (2001) PAST: paleontological statistics software package for education and data analysis. Palaeontol Electron 4:1–9
Janzen DH, De Vries PJ, Higgins ML, Kimsey LS (1982) Seasonal and site variation in Costa Rican euglossine bees at chemical baits in lowland deciduous and evergreen forests. Ecology 63:6–74
Justino DG, Augusto SC (2010) Avaliação da eficiência de coleta utilizando armadilhas aromáticas e riqueza de Euglossini Hymenoptera, Apidae) em áreas de Cerrado do Triângulo Mineiro. Rev Bras Zool 12: 227–239
Klink CA, Machado RB (2005) A conservação do Cerrado brasileiro. Megadiversidade 1:147–155
Knoll FRN, Penatti NC (2012) Habitat fragmentation effects on the orchid bee communities in remnant forests of southeastern Brazil. Neotrop Entomol 41:355–365
Krug C, Alves-dos-Santos I (2008) O uso de diferentes métodos para amostragem da fauna de abelhas (Hymenoptera: Apoidea), um estudo em Floresta Ombrófila Mista em Santa Catarina. Neotrop Entomol 37:265–278
Martins CF, Souza AKP (2005) Estratificação vertical de abelhas Euglossina (Hymenoptera: Apidae) em uma área de Mata Atlântica, Paraíba, Brasil. Rev Bras Zool 22:913–918
Mattozo VC, Faria LRR, Melo GAR (2011) Orchid bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae) in the coastal forests of southern Brazil: diversity, efficiency of sampling methods and comparison with other Atlantic forest surveys. Pap Avulsos Zool 51:505–515
Mendes FN, Rêgo M, Carvalho CC (2008) Abelhas Euglossina (Hymenoptera, Apidae) coletadas em uma monocultura de eucalipto circundada por Cerrado em Urbano Santos, Maranhão, Brasil. Iheringia Ser Zool 98:285–290
Myers N, Mittermeier RA, Mittermeier CG (2000) Biodiversity hotspots for conservation priorities. Nature 403:853–858
Nemésio A (2005) Description of the male Eufriesea nigrohirta (Friese, 1899) (Hymenoptera: Apidae: Euglossina) with comments on the holotype, species biology and distribution. Lundiana 6:41–45
Nemésio A (2008) Orchid bee community (Hymenoptera, Apidae) at an altitudinal gradient in a large forest fragment in southeastern Brazil. Rev Bras Zooc 10:249–256
Nemésio A (2009) Orchid bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae) of the Brazilian Atlantic Forest. Zootaxa 2041:1–242
Nemésio A (2012a) The western limits of the “Hileia Baiana” for orchid bees, including seven new records for the state of Minas Gerais, eastern Brazil (Hymenoptera, Apidae, Euglossina). Spixiana 35:109–116
Nemésio A (2012b) Methodological concerns and challenges in ecological studies with orchid bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae: Euglossina). Biosci J 28:118–134
Nemésio A, Engel M (2012) Three new cryptic species of Euglossa from Brazil (Hymenoptera, Apidae). ZooKeys 222:47–68
Nemésio A, Faria LRR Jr (2004) First assessment of the orchid-bee fauna (Hymenoptera: Apidae) at Parque Estadual do Rio Preto, a cerrado area in southeastern Brazil. Lundiana 5:113–117
Nemésio A, Morato EF (2004) Euglossina (Hymenoptera: Apidae: Apini) of the Humaitá Reserve, Acre state, Brazilian Amazon, with comments on bait trap efficiency. Rev Tecnol Ambient 10:71–80
Nemésio A, Morato EF (2006) The orchid-bee fauna (Hymenoptera: Apidae) of Acre state (northwestern Brazil) and a re-evaluation of euglossine bait-trapping. Lundiana 7:59–64
Nemésio A, Rasmussem C (2011) Nomenclatural issues in the orchid bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae: Euglossina) and an updated catalogue. Zootaxa 3006:1–42
Nemésio A, Silveira FA (2007) Orchid bee fauna (Hymenoptera: Apidade: Euglossina) of Atlantic Forest fragments inside an urban area in southeastern Brazil. Neotrop Entomol 36:186–191
Nemésio A, Silveira FA (2010) Forest fragments with larger core areas better sustain diverse orchid bee faunas (Hymenoptera: Apidae: Euglossina). Neotrop Entomol 39:555–561
Neves EL, Viana BF (1997) Inventário da fauna de Euglossinae (Hymenoptera, Apidae) do baixo sul da Bahia, Brasil. Rev Bras Zool 14:831–837
Neves EL, Viana BF (2003) A fauna de abelhas da subtribo Euglossina (Hymenoptera, Apidae) do Estado da Bahia, Brasil, p. 223–229. In: Melo GAR, Santos IA (eds) Apoidea Neotropica: Homenagem aos 90 anos de Jesus Santiago Moure. UNESC, Criciúma, 320 p
Neves SC, Abreu PAA, Fraga LMS (2005) Fisiografia, p.47-58. In Silva AC, Pereira LCVSF, Abreu PAA (eds) Serra do Espinhaço Meridional: Paisagens e Ambientes. O Lutador, Belo Horizonte, 272 p
Peruquetti RC, Campos LAO (1997) Aspectos da Biologia de Euplusia violacea (Blanchard) (Hymenoptera, Apidae, Euglossini). Rev Bras Zool 14:91–97
Peruquetti RC, Campos LAO, Coelho CDP, Abrantes CVM, Lisboa LCO (1999) Abelhas Euglossini (Apidae) de áreas de Mata Atlântica: abundância, riqueza e aspectos biológicos. Rev Bras Zool 16:101–118
Pielou EC (1977) Ecological diversity. John Wiley & Sons, New York, 165p
Poole RW (1974) An introduction to quantitative ecology. McGraw-Hill, New York, 532 p
Ramalho AV, Gaglianone MC, Oliveira ML (2009) Comunidades de abelhas Euglossina (Hymenoptera, Apidae) em fragmentos de Mata Atlântica no Sudeste do Brasil. Rev Bras Entomol 53:95–101
Rapini A, Ribeio PL, Lambert S, Pirani JR (2008) A flora dos campos rupestres da Cadeia do Espinhaço. Megadiversidade 4:16–24
Ratter JA, Riveiro JF, Bridgewater S (1997) The Brazilian cerrado vegetation and threats to its biodiversity. Ann Bot 80:223–230
Rebêlo JMM, Cabral AJM (1997) Abelhas Euglossinae de Barreirinhas, zona do litoral da baixada oriental maranhense. Acta Amazonica 27:145–152
Rebêlo JMM, Garófalo CA (1991) Diversidade e sazonalidade de machos de Euglossini (Hymenoptera, Apidae) e preferências por iscas-odores em um fragmento de floresta no Sudeste do Brasil. Rev Bras Biol 51:787–799
Rebêlo JMM, Garófalo CA (1997) Comunidades de machos de Euglossini (Hymenoptera: Apidae) em matas semidecíduas do Noroeste do estado de São Paulo. An Soc Entomol Brasil 26:243–255
Roubik DW (1989) Ecology and natural history of tropical bees. Cambridge University Press, New York, 514 p
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O, Baliga NS, Wang JT, Ramage D, Amin N, Schwikowski B, Ideker T (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13:2498–2504
Silveira FA, Cure JR (1993) High altitude bee fauna of southeastern Brazil: implications for biogeographic patterns (Hymenoptera: Apoidea). Stud Neotrop Fauna Environ 28:47–55
Silveira GD, Nascimento AM, Sofia SH, Augusto SC (2011) Diversity of the euglossine bee community (Hymenoptera, Apidae) of an Atlantic Forest remnant in southeastern Brazil. Rev Bras Entomol 55:109–115
Sofia SH, Santos AL, Silva CRM (2004) Euglossine bees (Hymenoptera, Apidae) in a remnant of Atlantic Forest in Paraná State, Brazil. Iheringia Ser Zool 94:217–222
Storck-Tonon D, Silva MV, Morato EF (2011) Checklist of orchid bees (Hymenoptera: Apidae) of “Lago do Silêncio” Area, Boca do Acre, Amazonas, Brazil. Check List 7:648–651
Tonhasca JRA, Blackmer JL, Albuquerque GS (2002) Abundance and diversity of euglossine bees in the fragmented landscape of the Brazilian Atlantic Forest. Biotropica 34:416–422
Viana BF, Neves EL, Silva FO (2001) Aspectos da biologia de nidificação de Euplusia mussitans (Fabricius) (Hymenoptera, Apidae, Euglossini). Rev Bras Zool 18:1081–1087
Wolda H (1980) Seasonality of tropical insects. I. Leafhoppers (Homoptera) in Las Cumbres, Panama. J Anim Ecol 49:277–290
Wolda H (1981) Similarity indices, sample sizes and diversity. Oecologia 50:296–302
Acknowledgments
The authors want to thank Yasmine Antonini for lending some chemical scents; Izabela Moreira Franco, André R.S. Garraffoni, Matheus M. Teixeira Cota, Stéfane Novais Neves, and Cristiana A. Pereira Souza for helping with sampling. We also thank Prof. Dr. André Nemésio for helping with the identification of Euglossina species, providing valuable literature, and reading and commenting on the manuscript, and two anonymous referees for helpful comments. This work was supported by Fundação de Amparo do Estado de Minas Gerais (FAPEMIG-CBB-APQ-00680-0) and MCTI-Rede ComCerrado (50.6121/2008-09).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Edited by: Fernando B Noll – UNESP
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Viotti, M.A., Moura, F.R. & Lourenço, A.P. Species Diversity and Temporal Variation of the Orchid-Bee Fauna (Hymenoptera, Apidae) in a Conservation Gradient of a Rocky Field Area in the Espinhaço Range, State of Minas Gerais, Southeastern Brazil. Neotrop Entomol 42, 565–575 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-013-0164-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13744-013-0164-y