Abstract
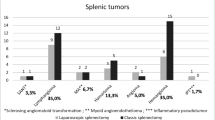
Laparoscopic splenectomy (LS) is nowadays considered as the gold standard for most hematological diseases where splenectomy is necessary, but many questions still remain. The aim of this study was to analyze our 5-years experiences consisting of 48 consecutive LS cases in order to assess the optimal approach and the feasibility of the procedure also in malignant diseases and unusual cases such as a primary spleen lymphoma, a big splenic artery aneurism, or a spleen infarct due to a huge pancreatic pseudo-cyst. Forty-eight consecutive patients underwent LS from January 2006 to January 2011 with at least 1-year follow-up. Clinical data and immediate outcome were retrospectively recorded; age, diagnosis, operation time, perioperative transfusion requirement, conversion rate, accessory incision, hospital stay, and complications were analyzed. We had 14 cases of malignant splenic disease, the most frequent malignant diagnosis was non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (12/14, 85.7 %). Splenomegaly (interpole diameter (ID) >20 cm) was observed in 12 cases (25 %) and massive splenomegaly (ID >25 cm) in 3 cases (6.25 %). Conversion to laparotomy occurred in two patients (4.16 %), both associated to uncontrollable bleeding in patients with splenomegaly. Mean operative time was 138 ± 22 min. Mean hospital stay was 4.5 days. Postoperative morbidity rate was 8.8 % for the benign group and 35.7 % in the malignant group. Mortality occurred in 1/48 patients (2.08 %), as a result of overwhelming post-splenectomy infection (OPSI). LS can be performed safely for malignant splenic disease and splenomegaly without any statistically significant increase of morbidity and mortality rate. Conversion rate is increased for massive splenomegaly. LS should be considered as the preferential approach even in patients with malignant disease, splenomegaly, or unusual cases. Massive splenomegaly should be considered as relative contraindication to LS even at experienced centers.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gigot JF, Lengele B, Gianello P, Etienne J, Claeys N (1998) Present status of laparoscopic splenectomy for hematological diseases: certitudes and unresolved issues. Semin Laparosc Surg 5:147–167
Delaitre B, Maignien B (1991) Splenectomy by the laparoscopic approach. Report of a case. Presse Med 20:2263
Cogliandolo A, Berland-Dai B, Pidoto RR (2001) Saint Marc O. Results of laparoscopic and open splenectomy for nontraumatic diseases. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech 11:256–261
Smith BM, Schropp KP, Lobe TE, Rogers DA, Presbury GJ, Wilimas JA, Wong WC (1994) Laparoscopic splenectomy in childhood. J Pediatr Surg 29:975–977
Terrosu G, Baccarani U, Bresadola V, Sistu MA, Uzzau A, Bresadola F (2002) The impact of splenic weight on laparoscopic splenectomy for splenomegaly. Surg Endosc 16(1):103–107
Silecchia G, Boru CE, Fantini A, Raparelli L, Greco F, Rizzello M, Pecchia A, Fabiano P, Basso N (2006) Laparoscopic splenectomy in the management of benign and malignant hematologic Diseases. JSLS 10:199–205
Coignard-Biehler H, Lanternier F, Hot A, Salmon D, Berger A, de Montalebert M, Suarez F, Launay O, Lecuit M, Lortholary O (2011) Adherence to preventive measures after splenectomy in the hospital setting and in the Community. J Infect Public Health 4(4):187–194
Wang H, Kopac D, Brisebois R, Sample C, Shapiro AM (2011) Randomized controlled trial to investigate the impact of anticoagulation on the incidence of splenic or portal vein thrombosis after laparoscopic splenectomy. Can J Surg 54(4):227–231
Habermalz B, Sauerland S, Decker G, Delaitre B, Gigot JF, Leandros E, Lechner K, Rhodes M, Silecchia G, Szold A, Targarona E, Torelli P, Neugebauer E (2008) Laparoscopic splenectomy: the clinical practice guidelines of the European Association for Endoscopic Surgery (EAES). Surg Endosc 22(4):821–848
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA (2004) Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg 240(2):205–213
Carr SC, Mahvi BM, Hoch JR, Archer CW, Turnipseed WD (2001) Visceral artery aneurism rupture. J Vasc Surg 33:806–811
Trastek VF, Pairolero PC, Joyce JW, Hollier LH, Bernatz PE (1982) Splenic artery aneurism. surgery 91:694–699
Wu Z, Zhou J, Pankaj P, Peng B (2012) Comparative treatment and literature review for laparoscopic splenectomy alone versus preoperative splenic artery embolization splenectomy. Surg Endosc 26(10):2758–2766
Neunert C, Lim W, Crowther M, Cohen A, Solberg L Jr, Crowther MA (2011) The American Society of Hematology 2011 evidence-based practice guideline for immune thrombocytopenia. Blood 117(16):4190–4207
Corcione F, Pirozzi F, Aragiusto G, Galante F, Sciuto A (2012) Laparoscopic splenectomy: experience of a single center in a series of 300 cases. Surg Endosc 26(10):2870–2876
Bonnard A, Benkerrou M, Rorlich P, de Ribier A, Aigrain Y (2004) Pediatric laparoscopic splenectomy: benefits of the anterior approach. Surg Endosc 18:80–82
Park A, Gagner M, Pomp A (1997) The lateral approach to laparoscopic splenectomy. Am J Surg 173:126–130
Casaccia M, Torelli P, Squarcia S, Sormani MP, Savelli A, Troilo B, Santori G, Valente U (2006) Laparoscopic splenectomy for hematologic diseases: a preliminary analysis performed on the Italian Registry of Laparoscopic Surgery of the Spleen (IRLSS). Surg Endosc 20:1214–1220
Stanek A, Stefaniak T, Makarewicz W, Kaska L, Podgorczyk H, Hellman A, Lachinski A (2005) Accessory spleens: preoperative diagnostics limitations and operational strategy in laparoscopic approach to splenectomy in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura patients. Langenbecks Arch Surg 390:47–51
Romano F, Gelmini R, Caprotti R, Andreotti A, Guaglio M, Franzoni C, Uggeri F, Saviano M (2007) Laparoscopic splenectomy: ligasure versus EndoGIA: a comparative study. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech A. 17(6):763–767
Shabahang H, Maddah G, Tavassoli A (2012) Jangjoo, Alvandipour M, Abdollahi A, Noorshafiee S. Laparoscopic splenectomy: ligasure or clip ligation? Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutan Tech. 22(2):136–138
Targarona EM, Cerdàn G, Gracia E, Rodriguez M, Trias M (2001) Results of laparoscopic splenectomy for treatment of malignant conditions. HPB (Oxford) 3(4):251–255
Bai YN, Jiang H, Prasoon P (2012) A meta-analysis of perioperative outcomes of laparoscopic splenectomy for hematological disorders. World J Surg 36(10):2349–2358
Nursal TA, Ezer A, Belli S, Parlakgumus A, Caliskan K, Noyan T (2009) Reaching proficiency in laparoscopic splenectomy. World J Gastroenterol 15(32):4005–4008
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marte, G., Scuderi, V., Rocca, A. et al. Laparoscopic splenectomy: a single center experience. Unusual cases and expanded inclusion criteria for laparoscopic approach. Updates Surg 65, 115–119 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13304-013-0197-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13304-013-0197-0