Abstract
Purpose
This study aims to examine the findings of 99mTc-diphosphonate bone scans in cancer patients with a history of HIFU treatment.
Methods
Bone scan images of patients with a history of HIFU treatment for primary or metastatic cancer from January 2006 to July 2010 were retrospectively reviewed. Cases of primary bone tumor or HIFU treatment reaching only the superficial soft tissue layer were excluded.
Results
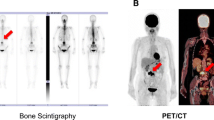
Bone scan images of 62 patients (26 female, 36 male; mean age 57 ± 9 years) were studied. HIFU treatment was performed in the liver (n = 40), pancreas (n = 16), and breast (n = 6). Mean interval time between HIFU treatment and bone scan was 106 ± 105 days (range: 1–572 days). Of 62 scans, 43 showed diffusely decreased uptake of bone within the path of HIFU treatment: antero-axillary and/or posterior arcs of right 5th to 11th ribs in 34 cases after treatment of hepatic lesions; anterior arcs of 2nd to 5th ribs in 5 cases after treatment for breast tumors; and posterior arcs of left 9th to 11th ribs or thoraco-lumbar vertebrae in 4 cases after treatment for pancreas tumor. Of 20 patients who had bone scans more than twice, five showed recovered uptake of the radiotracer in the involved ribs in the follow-up bone scan.
Conclusion
Of 62 bone scans in patients with a history of HIFU treatment for primary or metastatic cancer, 69% presented diffusely decreased uptake in the bone in the path of HIFU treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Park MY, Jung SE, Cho SH, Piao XH, Hahn ST, Han JY, et al. Preliminary experience using high intensity focused ultrasound for treating liver metastasis from colon and stomach cancer. Int J Hyperthermia. 2009;25(3):180–8.
Jung SE, Cho SH, Jang JH, Han JY. High-intensity focused ultrasound ablation in hepatic and pancreatic cancer: complications. Abdom Imaging. 2011;36(2):185–95.
Kennedy JE, Wu F, ter Haar GR, Gleeson FV, Phillips RR, Middleton MR, et al. High-intensity focused ultrasound for the treatment of liver tumours. Ultrasonics. 2004;42(1–9):931–5.
Kim YS, Rhim H, Choi MJ, Lim HK, Choi D. High-intensity focused ultrasound therapy: an overview for radiologists. Korean J Radiol. 2008;9(4):291–302.
Zhang L, Zhu H, Jin C, Zhou K, Li K, Su H, et al. High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU): effective and safe therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma adjacent to major hepatic veins. Eur Radiol. 2009;19(2):437–45.
Marmor JB, Pounds D, Hahn GM. Clinical studies with ultrasound-induced hyperthermia. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1982;61:333–7.
Dubinsky TJ, Cuevas C, Dighe MK, Kolokythas O, Hwang JH. High-intensity focused ultrasound: current potential and oncologic applications. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008;190(1):191–9.
Haar GT, Coussios C. High intensity focused ultrasound: physical principles and devices. Int J Hyperthermia. 2007;23(2):89–104.
Furusawa H, Namba K, Thomsen S, Akiyama F, Bendet A, Tanaka C, et al. Magnetic resonance-guided focused ultrasound surgery of breast cancer: reliability and effectiveness. J Am Coll Surg. 2006;203(1):54–63.
Stewart EA, Rabinovici J, Tempany CM, Inbar Y, Regan L, Gostout B, et al. Clinical outcomes of focused ultrasound surgery for the treatment of uterine fibroids. Fertil Steril. 2006;85(1):22–9.
Li JJ, Xu GL, Gu MF, Luo GY, Rong Z, Wu PH, et al. Complications of high intensity focused ultrasound in patients with recurrent and metastatic abdominal tumors. World J Gastroenterol. 2007;13(19):2747–51.
Mitchell MJ, Logan PM. Radiation-induced changes in bone. Radiographics. 1998;18(5):1125–36. quiz 1242–3.
Bell EG, McAfee JG, Constable WC. Local radiation damage to bone and marrow demonstrated by radioisotopic imaging. Radiology. 1969;92(5):1083–8.
Delon-Martin C, Vogt C, Chignier E, Guers C, Chapelon JY, Cathignol D. Venous thrombosis generation by means of high-intensity focused ultrasound. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1995;21(1):113–9.
Wu F, Chen WZ, Bai J, Zou JZ, Wang ZL, Zhu H, et al. Tumor vessel destruction resulting from high-intensity focused ultrasound in patients with solid malignancies. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2002;28(4):535–42.
Hynynen K, Chung AH, Colucci V, Jolesz FA. Potential adverse effects of high-intensity focused ultrasound exposure on blood vessels in vivo. Ultrasound Med Biol. 1996;22(2):193–201.
Kennedy JE, Ter Haar GR, Cranston D. High intensity focused ultrasound: surgery of the future? Br J Radiol. 2003;76(909):590–9.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, Y.Y., O, J.H., Sohn, H.S. et al. Whole-Body Bone Scan Findings after High-Intensity Focused Ultrasound (HIFU) Treatment. Nucl Med Mol Imaging 45, 268–275 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13139-011-0102-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13139-011-0102-z