Abstract
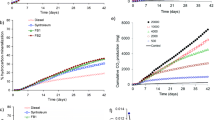
Processes that control the distribution and natural attenuation (NA) of petroleum hydrocarbons dissolved from the released diesel fuel in a bench-scale model aquifer were evaluated. The experimental results obtained in two-dimensional aqueous-phase petroleum hydrocarbon concentrations indicated that the total petroleum hydrocarbon (TPH) in the aquifer migrated in longitudinal and lateral directions. The TPH plume of 2 mg L−1 spread to the entire area of the aquifer, and the maximum concentration at the center of the plume was 44.15 mg L−1 after 90 days of release. After diesel fuel release, the NA of TPH was evaluated and quantified. Experimental data indicated that the NA of TPH was immediately implemented to prevent migration of the plume into the downgradient of the aquifer, but controlling the TPH plumes using NA mechanisms requires a long time.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atkinson R (1990) Gas-phase tropospheric chemistry of organic compounds: a review. Atmos Environ 24:1–41
Barker JF, Wilson JT (1997) Natural biological attenuation of aromatic hydrocarbons under anaerobic conditions. In: Ward CH, Cherry JA, Scalf MR (eds) Subsurface restoration. BIOS Ann Arbor Press, Chelsea, MI, pp 289–300
Barker JF, Patrick GC, Major D (1987) Natural attenuation of aromatic hydrocarbons in a shallow sand aquifer. Groundw Monit Remediat 7:64–71
Chapelle FH (1999) Bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated ground water: the perspectives of history and hydrology. groundw 37:122–132
Cho JS, Wilson JT, DiGiulio DC, Vardy JA, Choi W (1997) Implementation of natural attenuation at a JP-4 jet fuel release after active remediation. Biodegradation 8:265–273
Chrysikopoulos CV, Kim TJ (2000) Local mass transfer correlations for nonaqueous phase liquid pool dissolution in saturated porous media. Transp Porous Med 38:167–187
Chrysikopoulos CV, Lee KY, Harmon TC (2000) Dissolution of a well-defined trichloroethylene pool in saturated porous media: experimental design and aquifer characterization. Water Resour Res 36:1687–1696
Cozzarelli IM, Eganhouse RP, Baedecker MJ (1990) Transformation of monoaromatic hydrocarbons to organic acids in anoxic groundwater environment. Environ Geol 16:135–141
Gelman F, Binstock R (2008) Natural attenuation of MTBE and BTEX compounds in a petroleum contaminated shallow coastal aquifer. Environ Chem Lett 6:259–262
Jamison VW, Raymond RL, Hudson JO (1975) Biodegradation of high-octane gasoline in groundwater. Dev Ind Microbiol 16:305–312
Khan FI, Husain T (2003) Evaluation of a petroleum hydrocarbon contaminated site for natural attenuation using ‘RBMNA’methodology. Environ Model Softw 18:179–194
Kim TJ, Chrysikopoulos CV (1999) Mass transfer correlations for nonaqueous phase liquid pool dissolution in saturated porous media. Water Resour Res 35:449–459
Kostecki BP, Nascaewlla M (2003) LUST Cleanup landscape changing: landfilling still in, pump and treat on the way out. Contaminated Soil Sediment Water 9–11
Lee KY, Chrysikopoulos CV (2002) Dissolution of a well-defined trichloroethylene pool in saturated porous media: experimental results and model simulations. Water Res 36:3911–3918
Lee JY, Lee KK (2001) Viability of natural attenuation in a petroleum-contaminated shallow sandy aquifer. Environ Pollut 126:201–212
Liebeg EW, Cutright TJ (1999) The investigation of enhanced bioremediation through the addition of macro and micronutrients in a PAH contaminated soil. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 44:55–64
Luthy RG, Aiken RG, Brusseau ML et al (1997) Sequestration of hydrophobic organic contaminants by geosorbents. Environ Sci Technol 31:3341–3347
McAllister PM, Chiang CY (1994) A practical approach to evaluating natural attenuation of contaminants in ground water. Groundw Monit Remediat 14:161–173
Nobre RCM, Nobre MMM (2004) Natural attenuation of chlorinated organics in a shallow sand aquifer. J Hazard Mater 110:129–137
Rifai HS, Rittaler T (2005) Modeling natural attenuation of benzene with analytical and numerical models. Biodegradation 16:291–304
Sarkar D, Ferguson M, Datta R, Birnbaum S (2005) Bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbons in contaminated soils: comparison of biosolids addition, carbon supplementation, and monitored natural attenuation. Environ Pollut 136:187–195
Smith MR (1990) The biodegradation of aromatic hydrocarbons by bacteria. Biodegradation 1:191–206
Stempvoort DV, Biggar K (2008) Potential for bioremediation of petroleum hydrocarbons in groundwater under cold climate conditions: a review. Cold Reg Sci Technol 53:16–41
Suarez MP, Rifai HS (2002) Evaluation of BTEX remediation by natural attenuation at a coastal facility. Groundw Monit Remediat 22:62–77
Uçankuş T, Ünlü K (2008) The effect of aquifer heterogeneity on natural attenuation rate of BTEX. Environ Geol 54:759–776
Vasudevan N, Rajaram P (2001) Bioremediation of oil sludge-contaminated soil. Environ Int 26:409–411
Wiedemeier TH, Swanson MA, Wilson JT, Kampbell DH, Miller RN, Hansen JE (1996) Approximation of biodegradation rate constants for monoaromatic hydrocarbons (BTEX) in ground water. Groundw Monit Remediat 16:186–194
Acknowledgments
This study was supported as by the National High-Tech Research Development Program of China (“863” Project, 2008AA06A410) and Cooperation and Innovation Research Project for Oil Shale Exploration and Exploitation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qu, Zh., Zhao, Ys., Zhou, R. et al. Laboratory-scale analysis of transportation and natural attenuation of diesel fuel in aquifer. Environ Earth Sci 68, 1555–1561 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1849-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-012-1849-y