Abstract
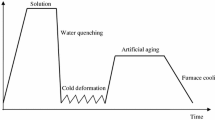
The influence of cooling rate (0.009–220 °C/s) after homogenization on the microstructure and mechanical properties of high strength aluminum alloy 7050 was investigated by tensile testing, optical microscope, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscope, and transmission electron microscope. A lower cooling rate after homogenization resulted in lower mechanical properties after aging. The drop in strength was significant when the cooling rate was decreased from 0.5 °C/s to 0.1 °C/s. A lower cooling rate gave rise to a larger amount of remnant S(Al2CuMg) phase and a higher fraction of recrystallization after solution heat treatment. Consequently, the increase in strength after aging due to precipitation hardening and substructure hardening was less significant in the case of slow cooling. This was supposed to be responsible for the lower mechanical properties due to a lower cooling rate after homogenization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. D. Anne, J. Light Met. 1, 133 (2001).
G. Itoh, H. Saitoh, and B. L. Ou, J. Jpn. Inst. Light Met. 36, 485 (1986).
Y. Miyagi and M. Hirano, J. Jpn. Inst. Light Met. 26, 501 (1976).
L. M. Wu, W. H. Wang, and Y. F. Hsu, J. Alloys Compd 456, 163 (2008).
J. D. Robson, Mater. Sci. Eng. A 382, 112 (2004).
D. Godard and P. Archambault, Acta Mater. 50, 2319 (2002).
X. G. Fan, D. M. Jiang, and Q. C. Meng, Mater. Lett. 60, 1475 (2006).
D. A. Porter and K. E. Easterling, Phase Transformation in Metals and Alloys, pp. 292, Alden Press, Oxford (1981)
J. D. Robson and P. B. Prangnell, Mater. Sci. Technol. 18, 607 (2002).
O. Engler, E. Sachot, and J. C. Ehrstrom, Mater. Sci. Technol. 12, 717 (1996).
T. Wang, Z. M. Yin, and K. Shen, Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China 17, 548 (2007).
M. J. Starink and S. C. Wang, Acta Mater. 51, 5131 (2003).
B. Morere, J. C. Ehrstrom, and P. J. Gregson, Metall. Mater. Trans. A 31, 2503 (2000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S.D., Yuan, Y.B., Li, C.B. et al. Influence of cooling rate after homogenization on microstructure and mechanical properties of aluminum alloy 7050. Met. Mater. Int. 18, 679–683 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-012-4016-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12540-012-4016-9