Abstract
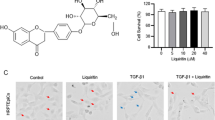
Salvianolic acid B (Sal B) is the most abundant bioactive molecule from Radix Salviae Miltiorrhizae, and has recently been used for treating renal fibrosis in traditional Chinese medicine. Here we investigated the ability reversal of Sal B to reverse the transdifferentiation of human kidney proximal tubular epithelial cells that was induced by transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGF-β1). The effects of Sal B on HK-2 cell morphology were observed by phase contrast microscopy, while alpha smooth muscle actin and E-cadherin were studied by immunocytochemistry and real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, respectively. Exposure of HK-2 cells to TGF-β1 for 72 h induced a complete conversion of the epithelial cells to myofibroblasts. When HK-2 cells were co-incubated with Sal B and TGF-β1 for a further 72 h, the morphology of myofibroblasts returned to that of proximal tubular epithelial cells, whereas the myofibroblast phenotype was maintained after exposure of cells to TGF-β1 for 144 h. Sal B reduced alpha smooth muscle actin levels and increased E-cadherin levels compared with their epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition controls. The reversal effect of Sal B was dose-dependent. That Sal B reverses the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in vitro suggests that it could possibly facilitate the repair of tubular epithelial structures and the regression of renal fibrosis in injured kidneys.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Border, W. A. and Noble, N. A., TGF-beta in kidney fibrosis: a target for gene therapy. Kidney Int., 51, 1388–1396 (1997).
Border, W. A. and Noble, N. A., Interactions of transforming growth factor beta and angiotensin II in renal fibrosis. Hypertension, 31, 181–188 (1998).
Bottinger, E. P. and Bitzer, M., TGF-beta signaling in renal disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol., 13, 2600–2610 (2002).
Cao, C. M., Xia, Q., Zhang, X., Xu, W. H., Jiang, H. D., and Chen, J. Z., Salvia miltiorrhiza attenuates the changes in contraction and intracellular calcium induced by anoxia and reoxygenation in rat cardiomyocytes. Life Sci., 72, 2451–2463 (2003).
Chen, C. G. and Wang, Y. P., Magnesium lithospermate B ameliorates renal cortical microperfusion in rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin., 27, 217–222 (2006).
Chen, Y. H., Du, G. H., and Zhang, J. T., Salvianolic acid B protects brain against injuries caused by ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin., 21, 463–466 (2000).
Copeland, J. W., Beaumont, B. W., Merrilees, M. J., and Pilmore, H. L., Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of human proximal tubular epithelial cells: effects of rapamycin, mycophenolate, cyclosporin, azathioprine and methylprednisolone. Transplantation, 83, 809–814 (2007).
Docherty, N. G., Sullivan, D. E., Healy, D. A., Murphy, M., Fitzpatrick, T. M., and Watson, R. W., TGF-beta 1-induced EMT can occur independently of its proapoptotic effects and is aided by EGF receptor activation. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol., 290, 1202–1212 (2006).
Eddy, A. A., Molecular basis of renal fibrosis. Pediatr. Nephrol., 15, 290–301 (2000).
Fan, J. M., Ng, Y. Y., Hill, P. A., Nikolic-Paterson, D. J., Mu, W., Atkins, R. C., and Lan, H. Y., Transforming growth factor-beta regulates tubular epithelial-myofibroblast transdifferentiation in vitro. Kidney Int., 56, 1455–1467 (1999).
Fioretto, P., Steffes, M. W., Sutherland, D. E., Goetz, F. C., and Mauer, M., Reversal of lesions of diabetic nephropathy after pancreas transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med., 339, 69–75 (1998).
Fioretto, P., Sutherland, D. E., Najafian, B., and Mauer, M., Remodeling of renal interstitial and tubular lesions in pancreas transplant recipients. Kidney Int., 69, 907–912 (2006).
Hase, K., Kasimu, R., Basnet, P., Kadota, S., and Namba, T., Preventive effect of lithospermate B from Salvia miltiorhiza on experimental hepatitis induced by carbon tetrachloride or D-galactosamine/lipopolysaccharide. Planta Med., 63, 22–26 (1997).
He, H., Shi, M., Zeng, X., Yang, J., Li, Y., Wu, L., and Li, L., Cardioprotective effect of salvianolic acid B on large myocardial infarction mediated by reversing upregulation of leptin, endothelin pathways and abnormal expression of SERCA2a, phospholamban in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol., 118, 35–45 (2008).
Hsu, Y. C., Lin, Y. L., Chiu, Y. T., Shiao, M. S., Lee, C. Y., and Huang, Y. T., Antifibrotic effects of Salvia miltiorrhiza on dimethylnitrosamine intoxicated rats. J. Biomed. Sci., 12, 185–195 (2005).
Iwano, M., Plieth, D., Danoff, T. M., Xue, C., Okada, H., and Neilson, E. G., Evidence that fibroblasts derive from epithelium during tissue fibrosis. J. Clin. Invest., 110, 341–350 (2002).
Jiang, R. W., Lau, K. M., Hon, P. M., Mak, T. C., and Woo, K. S., Chemistry and biological activities of caffeic acid derivatives from Salvia miltiorrhiza. Curr. Med. Chem., 12, 237–246 (2005).
Jung, M., Lee, H. C., Ahn, C. W., Park, W., Choi, S., Kim, H., Cho, D., Lee, G. T., and Li, H. R., Effective isolation of magnesium lithospermate B and its inhibition of aldose reductase and fibronectin on mesangial cell line. Chem. Pharm. Bull., 50, 1135–1136 (2002).
Kalluri, R. and Neilson, E. G., Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and its implications for fibrosis. J. Clin. Invest., 112, 1776–1784 (2003).
Kang, D. G., Oh, H., Sohn, E. J., Hur, T. Y., Lee, K. C., Kim, K. J., Kim, T. Y., and Lee, H. S., Lithospermic acid B isolated from Salvia miltiorrhiza ameliorates ischemia/reperfusion-induced renal injury in rats. Life Sci., 75, 1801–1816 (2004).
Kang, E. S., Lee, G. T., Kim, B. S., Kim, C. H., Seo, G. H., Han, S. J., Hur, K. Y., and Ahn, C. W., Lithospermic acid B ameliorates the development of diabetic nephropathy in OLETF rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 579, 418–425 (2008).
Lee, G. T., Ha, H., Jung, M., Li, H., Hong, S. W., Cha, B. S., Lee, H. C., and Cho, Y. D., Delayed treatment with lithospermate B attenuates experimental diabetic renal injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol., 14, 709–720 (2003).
Lin, Y. L., Wu, C. H., Luo, M. H., Huang, Y. J., Wang, C. N., Shiao, M. S., and Huang, Y. T., In vitro protective effects of salvianolic acid B on primary hepatocytes and hepatic stellate cells. J. Ethnopharmacol., 105, 215–222 (2006).
Liu, P., Hu, Y. Y., and Liu, C., Clinical observation of salvianolic acid B in treatment of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B. World J. Gastroenterol., 8, 679–685 (2002a).
Liu, P., Liu, C. H., Wang, H. N., HU, Y. Y., and Liu, C., Effect of salvianolic acid B on collagen production and mitogenactivated protein kinase activity in rat hepatic stellate cells1. Acta Pharmacol. Sin., 23, 733–738 (2002b).
Luft, F. C., Transforming growth factor beta-angiotensin II interaction: Implications for cardiac and renal disease. J. Mol. Med., 77, 517–518 (1999).
Nan, J. X., Park, E. J., Kang, H. C., Park, P. H., Kim, J. Y., and Sohn, D. H., Anti-fibrotic effects of a hot-water extract from Salvia miltiorrhiza roots on liver fibrosis induced by biliary obstruction in rats. J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 53, 197–204 (2001).
Nqai, H. H., Sit, W. H., and Wan, J. M., The nephroprotective effects of the herbal medicine preparation, WH30+, on the chemical-induced acute and chronic renal failure in rats. Am. J. Chin. Med., 33, 491–500 (2005).
Peters, H., Noble, N. A., and Border, W. A., Transforming growth factor-beta in human glomerular injury. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens., 6, 389–393 (1997).
Soung, D. Y., Rhee, S. H., Kim, J. S., Lee, J. Y., Yang, H. S., Choi, J. S., Yokozawa, T., Han, Y. N., and Chung, H. Y., Peroxynitrite scavenging activity of lithospermate B from Salvia miltiorrhiza. J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 55, 1427–1432 (2003).
Strutz, F., Okada, H., Lo, C. W., Danoff, T., Carone, R. L., Tomaszewski, J. E., and Neilson, E. G., Identification and characterization of a fibroblast marker: FSP1. J. Cell Biol., 130, 393–405 (1995).
Tian, L. L., Wang, X. J., Sun, Y. N., Li, C. R., Xing, Y. L., Zhao, H. B., Duan, M., Zhou, Z., and Wang, S. Q., Salvianolic acid B, an antioxidant from Salvia miltiorrhiza, prevents 6-hydroxydopamine induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y cells. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol., 40, 409–422 (2008).
Wasser, S., Ho, J. M. S., Ang, H. K., and Tan, C. E. L., Salvia miltiorrhiza reduced experimentally induced hepatic fibrosis in rats. J. Hepatol., 29, 760–771 (1998).
Watzke, A., O'Malley, S. J., Bergman, R. G., and Ellman, J. A., Reassignment of the configuration of salvianolic acid B and establishment of its identity with lithospermic acid B. J. Nat. Prod., 69, 1231–1233 (2006).
Wojcikowski, K., Johnson, D. W., and Gobe, G., Medicinal herbal extracts-renal friend or foe? Part two: herbal extracts with potential renal benefits. Nephrology (Carlton, 9, 400–405 (2004).
Wojcikowski, K., Johnson, D. W., and Gobe, G., Herbs or natural substances as complementary therapies for chronic kidney disease: ideas for future studies. J. Lab. Clin. Med., 147, 160–166 (2006).
Yang, J. and Liu, Y., Dissection of key events in tubular epithelial to myofibroblast transition and its implications in renal interstitial fibrosis. Am. J. Pathol., 159, 1465–1475 (2001).
Yang, J. and Liu, Y., Blockage of tubular epithelial to myofibroblast transition by hepatocyte growth factor prevents renal interstitial fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol., 13, 96–107 (2002).
Yang, J. and Liu, Y., Delayed administration of hepatocyte growth factor reduces renal fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol., 284, 349–357 (2003).
Yang, J., Dai, C., and Liu, Y., A novel mechanism by which hepatocyte growth factor blocks tubular epithelial to mesenchymal transition. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol., 16, 68–78 (2005).
Yao, G., Xu, L., Wu, X., Xu, L., Yang, J., and Chen, H., Preventive effects of salvianolic acid B on transforming growth factor-β1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of human kidney cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull., 32, 882–886 (2009).
Zeisberg, M., Hanai, J., Sugimoto, H., Mammoto, T., Charytan, D., Strutz, F., and Kalluri, R., BMP-7 counteracts TGFbeta1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and reverses chronic renal injury. Nat. Med., 9, 964–968 (2003).
Zeng, R., Yao, Y., Han, M., Zhao, X. Q., Liu, X. C., and Wei, J. C., Biliverdin reductase mediates hypoxia-induced EMT via PI3-kinase and Akt. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol., 19, 380–387 (2008).
Zhang, A., Wang, M. H., Dong, D., and Yang, T. X., Prostaglandin E2 is a potent inhibitor of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition: interaction with hepatocyte growth factor. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol., 291, 1323–1331 (2006).
Zhou, L., Zuo, Z., and Chow, M. S., Danshen: an overview of its chemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and clinical use. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 45, 1345–1359 (2005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, Rh., Xie, Fy., Chen, Hm. et al. Salvianolic acid B reverses the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of HK-2 cells that is induced by transforming growth factor-β. Arch. Pharm. Res. 34, 477–483 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0317-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-011-0317-7