Abstract
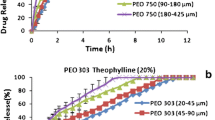
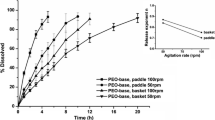
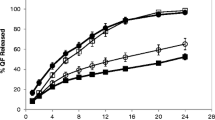
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of various in vitro test conditions, on the release properties of theophylline (TP) from aminophylline (AP) matrices based on different hydroxypropylmethylcellulose (HPMC) ratio and viscosity grades. The General full factorial experimental design 3 × 3 × 3 was used, based on three independent variables: applied in vitro test (X1), HPMC/drug ratio (X2) and polymer viscosity grade (X3). The drug release percent at 2h (Y2h), 4h (Y4h) and 8 h (Y8h) and time for 50% of TP release from matrices (YT50%) were response variables. Three in vitro tests were used: Test 1 and Test 4 (Theophylline Extended-release Capsules, USP 30) and Half-change method. According to factorial design analyses, in vitro test was the most significant factor influencing mechanism and amount of drug release. For Half Change method erosion was the predominant mechanism indicating Case — II transport, while for Test 1 the release mechanism were followed by both diffusion and erosion. The lowest release exponent n values, obtained from Ritger-Pepass equation, for Test 4 indicate diffusion process inclining from Fickian diffusion to Anomalous transport. Therefore, it is in the stage of development, useful to consider the influence of various in vitro test conditions on the formulation, in order to choose an optimal test for the purpose of future drug release examination.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Campos-Alderte, M. E. and Villafuerte-Robles, L., Influence of the viscosity grade and the particle size of HPMC on metrodinazole release from matrix tablets. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 43, 173–179 (1997).
Fassihi, A. R. and Munday, D. L., Dissolution of Theophylline from Film Coated Slow Release Mini Tablets in Various Dissolution media. J. Pharm. Sci., 41, 369–372 (1989).
Ford, J. L., Rubinstein, M. H., and Hogan, J. E., Formulation of sustained release promethazine hydrochloride tablets using hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose matrices. Int. J. Pharm., 24, 327–338 (1985a).
Ford, J. L., Rubinstein, M. H., and Hogan, J. E., Propranolol hydrochloride and aminophylline release from matrix tablets containing hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose. Int. J. Pharm., 24, 339–350 (1985b).
Ford, J. L., Rubinstein, M. H., Mc Caul, F., Hogan J. E., and Edgar, P. J., Importance of drug type, tablet shape and added diluents on drug release kinetics from hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose matrix tablets. Int. J. Pharm., 40, 223–234 (1987).
Furlanetto, S., Cirri, M., Maestrelli, F., Corti, G., and Mura, P., Study of formulation variables influencing the drug release rate from matrix tablets by experimental design. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm., 62, 77–84 (2006)
Gao, P. and Meury, R. H., Swelling of hydroxypropylmethylcelulose matrix tablet Part 1. Characterization of swelling using a novel optical imaging method. J. Pharm. Sci., 85, 725–731 (1996a).
Gao, P., Skoug, J. W., Nixon, P. R., Ju, R., Stemm, N. L., and Sung, K., Swelling of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose matrix tablets. 2. Mechanistic study of the influence of formulation variables on matrix performance and drug release. J. Pharm. Sci., 85, 732–740 (1996b).
Gohel, M. C. and Amin, A. F., Formulation optimization of controlled release diclofenac sodium microspheres using factorial design. J. Controlled Release., 51, 115–122 (1998).
Herzfeldt, C. D., Hellenbrecht, D., Yimmer, A., Brehm, R., Poor availability of sustained release theophylline coused by pH dependent biphasic release. Acta Pharm. Technol., 35, 79–81 (1989).
Huang, Y.-B., Tsai, Y.-H., Lee, S.-H., Chang, J.-S., Wu, P.-C., Optimization of pH-independent release of nicardipine hydrochloride extended-release matrix tablets usig response surface methodology. Int. J. Pharm., 289, 87–95 (2005)
Kim, C., Controlled Released Dosage Form Design, Technomic publication, Technomic Publishing Company Inc., Lancaster Pennsylvania USA (2000).
Li, C. L., Martini, L. G., Ford, J. L., and Roberts, M., The use of hypromellose in oral drug delivery. J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 57, 533–546 (2005).
Lin, S.-Y., Kao, Y.-H., and Chang, H.-N., Preliminary evaluation of the correlation between in vitro release and in vivo bioavailability of two aminophylline slow-release tablets. J. Pharm. Sci., 79, 326–330 (1990).
Paterakis, P. G., Korakianiti, E. S., Dallas, P. P., and Rekkas, D. M., Evaluation and simultaneous optimization of pellets characteristics using a 33 factorial design and the desirability function. Int. J. Pharm., 248, 51–60 (2002).
Petrovic, A., Vukicevic, J., and Djuric, Z., The influence of diluent concentration on release rate of theophylline from hydroxypropylmethylcellulose matrices. Proc. Internationa Meeting on Pharmaceutics, Biopharmaceutics, Pharmaceutical Technology, Florence 8–11 April., 83–84 (2002).
Reynold, T. D., Gehrke, S. H., Hussain, A. S., Shenouda, L. S., Polymer Erosion and Drug Release Characterization of Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose Matrices. J. Pharm. Sci., 87, 1115–1123 (1998).
Rinaki, E., Valsami, G., Macheras, P., The power law can describe the entire drug release curve from HPMC — based matrix tablets: a hypothesis. Int. J. Pharm., 255, 199–207 (2003).
Ritger, P. L., Peppas, N. S., A simple equation for disposition of solute release II: Fickian and anomalous release from swellable devices. J. Controlled Release., 5, 37–42 (1987).
Sako, K., Sawada, T., Nakashima, H., Yokohama, S., Sonobe, T., Influence of water soluble fillers on hydroxypropylmethylcellulose matrix on in vitro and in vivo drug release. J. Controlled Release., 81, 165–172 (2002).
Shoufeng, L., Senshang, L., Daggy, B. P., Mirchandani, H. L., and Chien Y. W., Effect of HPMC and Carbopol on the release and floating properties of Gastric Floating Drug Delivery System using factorial design. Int. J. Pharm., 253 13–253 22 (2003).
Siepmann, J. and Peppas, N., Modeling of drug release from delivery systems based on Hydrohypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC). Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev., 48, 139–157 (2001).
Simons, K. J., Estelle, F., Simons, R., Plett, K. D., and Scerbo, C., Dissolution studies of some sustained release theophylline dosage forms. J. Pharm. Sci., 73, 939–942 (1984).
Smart, J. D., Barnes, M. S., and Norris, M. J., An in vitro comparison of controlled release aminophylline tablets: Phyllocontin Continus and Pecram. J. Pham. Pharmacol., 44, 623–625 (1992).
Streubel, A., Siepmann, J., Peppas, N. A., and Bodemeier, R., Bimodal drug release achieved with multi-layer matrix tablets: transport mechanisms and device design. J. Control. Release., 69, 455–468 (2000).
Zuleger, S. and Lippold, B. C., Polymer particle erosion controlling drug release I. Factor influecing drug release and characterization of the release mechanism. Int. J. Pharm., 217, 139–152 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petrovic, A., Ibric, S., Trajkovic, S. et al. An investigation into effects of In Vitro Test condition on the release properties of theophylline from HPMC matrices using factorial design. Arch. Pharm. Res. 32, 1087–1096 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-009-1715-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-009-1715-y