Abstract
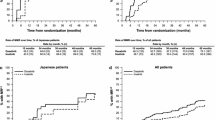
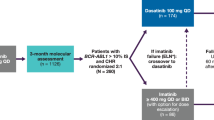
Dasatinib is a highly potent BCR-ABL kinase inhibitor with established efficacy and safety in imatinib-resistant or -intolerant patients with chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. In the global phase III DASISION trial in patients with newly diagnosed chronic phase CML (CML-CP), dasatinib was found to have an acceptable safety profile and demonstrated significantly faster and higher rates of complete cytogenetic response (CCyR) and major molecular response (MMR) compared with imatinib. Here, we report the results of a subset analysis of Japanese patients enrolled in the DASISION trial, showing safety and efficacy profiles generally consistent with patients enrolled worldwide, including higher response rates (CCyR, MMR) with dasatinib compared with imatinib and similar high rates of progression-free and overall survival with both therapies. However, the small sample size of the present study limits the strength of these conclusions, and further exploration is needed to confirm any differences observed in Japanese patients compared with the total treated population. These findings support the use of dasatinib 100 mg QD as a first-line treatment in Japanese patients with newly diagnosed CML-CP.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
de Lavallade H, Apperley JF, Khorashad JS, Milojkovic D, Reid AG, Bua M, et al. Imatinib for newly diagnosed patients with chronic myeloid leukemia: incidence of sustained responses in an intention-to-treat analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(20):3358–63.
Apperley JF. Part I: mechanisms of resistance to imatinib in chronic myeloid leukaemia. Lancet Oncol. 2007;8:1018–29.
Bauer S, Romvari E. Treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia following imatinib resistance: a nursing guide to second-line treatment options. Clin J Oncol Nurs. 2009;13(5):523–34.
Nestal de Moraes G, Souza PS, Costas FC, Vasconcelos FC, Reis FR, Maia RC. The interface between BCR-ABL-dependent and -independent resistance signaling pathways in chronic myeloid leukemia. Leuk Res Treatment. 2012;2012:671702.
Li S. Src-family kinases in the development and therapy of Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia and acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leuk Lymphoma. 2008;49(1):19–26.
Ng KP, Hillmer AM, Chuah CT, Juan WC, Ko TK, Teo AS, et al. A common BIM deletion polymorphism mediates intrinsic resistance and inferior responses to tyrosine kinase inhibitors in cancer. Nat Med. 2012;18(4):521–8.
O’Hare T, Walters DK, Stoffregen EP, Jia T, Manley PW, Mestan J, et al. In vitro activity of Bcr-Abl inhibitors AMN107 and BMS-354825 against clinically relevant imatinib-resistant Abl kinase domain mutants. Cancer Res. 2005;65(11):4500–5.
Breccia M, Alimena G. Activity and safety of dasatinib as second-line treatment or in newly diagnosed chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients. Biodrugs. 2011;25(3):147–57.
Hochhaus A, Baccarani M, Deininger M, Apperley JF, Lipton JH, Goldberg SL, et al. Dasatinib induces durable cytogenetic responses in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia in chronic phase with resistance or intolerance to imatinib. Leukemia. 2008;22(6):1200–6.
Kantarjian H, Pasquini R, Lévy V, Jootar S, Holowiecki J, Hamerschlak N, et al. Dasatinib or high-dose imatinib for chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia resistant to imatinib at a dose of 400 to 600 milligrams daily: two-year follow-up of a randomized phase 2 study (START-R). Cancer. 2009;115(18):4136–47.
Shah NP, Kim DW, Kantarjian H, Rousselot P, Llacer PE, Enrico A, et al. Potent, transient inhibition of BCR-ABL with dasatinib 100 mg daily achieves rapid and durable cytogenetic responses and high transformation-free survival rates in chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients with resistance, suboptimal response or intolerance to imatinib. Haematologica. 2010;95(2):232–40.
Kantarjian H, Shah NP, Hochhaus A, Cortes J, Shah S, Ayala M, et al. Dasatinib versus imatinib in newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(24):2260–70.
Kantarjian HM, Shah NP, Cortes JE, Baccarani M, Agarwal MB, Undurraga MS, et al. Dasatinib or imatinib in newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia: 2-year follow-up from a randomized phase 3 trial (DASISION). Blood. 2012;119(5):1123–9.
Saglio G, Kantarjian HM, Shah N, Jabbour EJ, Quintas-Cardama A, Steegmann JL. Early response (molecular and cytogenetic) and long-term outcomes in newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase (CML-CP): exploratory analysis of DASISION 3-year data. ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts. 2012;120:abstract 1675.
Ohnishi K, Nakaseko C, Takeuchi J, Fujisawa S, Nagai T, Yamazaki H, et al. Long-term outcome following imatinib therapy for chronic myelogenous leukemia, with assessment of dosage and blood levels: the JALSG CML202 study. Cancer Sci. 2012;103(6):1071–8.
Sakamaki H, Ishizawa K, Taniwaki M, Fujisawa S, Morishima Y, Tobinai K, et al. Phase 1/2 clinical study of dasatinib in Japanese patients with chronic myeloid leukemia or Philadelphia chromosome-positive acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Int J Hematol. 2009;89(3):332–41.
Kim DW, Goh YT, Hsiao HH, Caguioa PB, Kim D, Kim WS, et al. Clinical profile of dasatinib in Asian and non-Asian patients with chronic myeloid leukemia. Int J Hematol. 2009;89(5):664–72.
ClinicalTrials.gov. Phase II clinical trial of dasatinib first line therapy for patients with newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase. http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01464411. Accessed 7 Jan 2013.
Baccarani M, Cortes J, Pane F, Niederwieser D, Saglio G, Apperley J, et al. Chronic myeloid leukemia: an update of concepts and management recommendations of European LeukemiaNet. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(35):6041–51.
Druker BJ, Guilhot F, O’Brien SG, Gathmann I, Kantarjian H, Gattermann N, et al. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(23):2408–17.
Marin D, Ibrahim AR, Lucas C, Gerrard G, Wang L, Szydlo RM, et al. Assessment of BCR-ABL1 transcript levels at 3 months is the only requirement for predicting outcome for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia treated with tyrosine kinase inhibitors. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(3):232–8.
Hanfstein B, Muller MC, Hehlmann R, Erben P, Lauseker M, Fabarius A, et al. Early molecular and cytogenetic response is predictive for long-term progression-free and overall survival in chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). Leukemia. 2012;26(9):2096–102.
Marin D, Hedgley C, Clark RE, Apperley J, Foroni L, Milojkovic D, et al. Predictive value of early molecular response in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia treated with first-line dasatinib. Blood. 2012;120(2):291–4.
Nannya Y, Hatake K, Kurokawa M. A three-year follow-up report of dasatinib drug use results surveys for all cases treated in Japan. JSH Annual Meeting Abstracts. 2012;53:abstract OS-2-135.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all participating study sites for this Bristol-Myers Squibb-sponsored study. The authors would like to particularly thank the patients who participated in this study and acknowledge the efforts of study staff at the study centers in Japan: Osaka City University Hospital, Nagoya Daini Red Cross Hospital, Yokohama City University Medical Center, Tohoku University Hospital, University Hospital, Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine, Imamura Bun-in Hospital, Kameda Clinic of Medical Corporation Tesshokai, Fukuoka University Hospital, Kanto Medical Center NTT EC, Okayama University Hospital, Iwate Medical University Hospital, and Tokyo Metropolitan Komagome Hospital. StemScientific, funded by Bristol-Myers Squibb, provided writing and editorial support. The authors did not receive financial compensation for authoring the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
Shin Fujisawa has no conflict of interest to disclose. Hirohisa Nakamae has served as a consultant and lecturer for Novartis and Bristol-Myers Squibb and received from both: grants and payment for travel/accommodations/meeting expenses unrelated to activities listed. Michinori Ogura has received research funding from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eisai, Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd, Chugai, Pfizer, Novartis, Solasia, Celgene, SymBio, GlaxoSmithKline, Otsuka, Dainippon Sumitomo, MSD, and Janssen Pharma. Ken-ichi Ishizawa has no conflict of interest to disclose. Masafumi Taniwaki has no conflict of interest to disclose. Atae Utsunomiya has received consulting fees or honorarium from Bristol-Myers K.K. and Kyowa Hakko Kirin Co., Ltd. Kosei Matsue has no conflict of interest to disclose. Yasushi Takamatsu has no conflict of interest to disclose. Kensuke Usuki has no conflict of interest to disclose. Mitsune Tanimoto has no conflict of interest to disclose. Yoji Ishida has no conflict of interest to disclose. Hideki Akiyama has no conflict of interest to disclose. Shintaro Onishi is employed by Otsuka, and was formerly employed by Bristol-Myers Squibb throughout the manuscript development.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Fujisawa, S., Nakamae, H., Ogura, M. et al. Efficacy and safety of dasatinib versus imatinib in Japanese patients with newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia (CML-CP): Subset analysis of the DASISION trial with 2-year follow-up. Int J Hematol 99, 141–153 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-013-1470-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-013-1470-1