Abstract
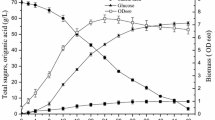
Sweet sorghum juice was a cheap and renewable resource, and also a potential carbon source for the fermentation production of lactic acid (LA) by a lactic acid bacterium. One newly isolated strain Lactobacillus salivarius CGMCC 7.75 showed the ability to produce the highest yield and optical purity of LA from sweet sorghum juice. Studies of feeding different concentrations of sweet sorghum juice and nitrogen source suggested the optimal concentrations of fermentation were 325 ml l−1 and 20 g l−1, respectively. This combination produced 142.49 g l−1 LA with a productivity level of 0.90 g of LA per gram of sugars consumed. The results indicated the high LA concentration achieved using L. salivarius CGMCC 7.75 not only gives cheap industrial product, but also broaden the application of sweet sorghum.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Patel S, Majumder A, Goyal A (2012) Potentials of exopolysaccharides from lactic acid bacteria. Indian J Microbiol 52:3–12
Thumu SCR, Halami PM (2012) Acquired resistance to macrolide–lincosamide–streptogramin antibiotics in lactic acid bacteria of food origin. Indian J Microbiol 52:530–537
Manisseri C, Gudipati M (2012) Prebiotic activity of purified xylobiose obtained from Ragi (Eleusine coracana, Indaf-15) Bran. Indian J Microbiol 52:251–257
Özdemir GB, Biyik HH (2012) Isolation and characterization of a bacteriocin-like substance produced by Geobacillus toebii strain HBB-247. Indian J Microbiol 52:104–108
Wang LM, Zhao B, Liu B, Yu B, Ma CQ, Su F, Hua DL, Li QG, Ma YH, Xu P (2010) Efficient production of l-lactic acid from corncob molasses, a waste by-product in xylitol production, by a newly isolated xylose utilizing Bacillus sp. strain. Bioresour Technol 20:7908–7915
Gnansounou E, Dauriat A, Wyman CE (2005) Refining sweet sorghum to ethanol and sugar: economic trade-offs in the context of North China. Bioresour Technol 96:985–1002
Rooney WL, Blumenthal J, Bean B, Mullet JE (2007) Designing sorghum as a dedicated bioenergy feedstock. Biofuels Bioprod Bioref 1:147–157
Berthier F, Ehrlich SD (1998) Rapid species identification within two groups of closely related lactobacilli using PCR primers that target the 16S/23S rRNA spacer region. FEMS Microbiol Lett 161:97–106
Dumbrepatil A, Adsul M, Chaudhari S, Khire J, Gokhale D (2008) Utilization of molasses sugar for lactic acid production by Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. delbrueckii mutant Uc-3 in batch fermentation. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:333–335
Kim JH, Shoemaker SP, Mills DA (2009) Relaxed control of sugar utilization in Lactobacillus brevis. Microbiology 155:1351–1359
Cock LS, de Stouvenel AR (2006) Lactic acid production by a strain of Lactococcus lactis subs lactis isolated from sugar cane plants. Electron J Biotechnol 9:40–45
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Science & Technology Pillar Program in 12th Five-year Plan of China (2011BAD17B04).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic Supplementary Material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
12088_2013_377_MOESM1_ESM.doc
Kinetics of lactic acid and residual sugars produced by L. salivarius CGMCC 7.75 using different concentrations of sweet sorghum juice at the fixed 15 g l-1 nitrogen source. (A) yields of lactic acid; (B) amounts of residual reducing sugars; (C) amounts of residual sucrose. Numbers following groups correspond to the groups in the first column in the Electronic supplementary Table S1 and were represented by different symbols. Supplementary material 1 (DOC 73 kb)
12088_2013_377_MOESM2_ESM.doc
Kinetics of lactic acid and residual sugars produced by L. salivarius CGMCC 7.75 using different concentrations of nitrogen source at the fixed 300 ml l-1 sweet sorghum juice. (A) Yields of lactic acid; (B) amounts of residual reducing sugars; (C) amounts of residual sucrose. Numbers following groups correspond to the groups in the first column in the Electronic supplementary Table S2 and were represented by different symbols. Supplementary material 2 (DOC 72 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Wang, S., Zhi, JF. et al. Efficient Production of Lactic Acid from Sweet Sorghum Juice by a Newly Isolated Lactobacillus salivarius CGMCC 7.75. Indian J Microbiol 53, 332–336 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-013-0377-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-013-0377-0