Abstract
Objective
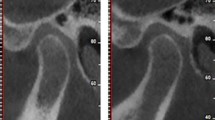
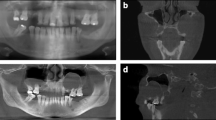
The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence and characteristics of pneumatization of the articular tubercle (PAT) and pneumatization of the roof of the glenoid fossa (PRGF) in a large population using cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT).
Materials and Methods
This study was designed to evaluate the CBCT images of 1000 patients. The prevalences of the pneumatizations by age, sex, locularity, and laterality were determined. The significance of differences between variables was evaluated by the Chi-square test and analysis of variance.
Results
PAT was detected in 28.4% of the zygomatic bone sides and PRGF in 29.6%. Bilateral PAT was detected in 176 (17.6%) patients and bilateral PRGF in 195 (19.5%). The mean age of patients with PAT was 47.33 years and that of patients with PRGF was 45.62 years. Multilocular appearance was observed significantly more often than unilocular type for both pneumatizations (p < 0.01). Unilateral PAT cases were slightly, but significantly, higher than bilateral PAT cases (p = 0.047), while no significant difference was observed between unilateral and bilateral PRGF cases.
Conclusions
In conclusion, PAT and PRGF can be assessed more accurately on CBCT images than on plain radiographs. During routine radiological investigations, maxillofacial radiologists should be aware of zygomatic air cells.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ladeira DB, Barbosa GL, Nascimento MC, Cruz AD, Freitas DQ, Almeida SM. Prevalence and characteristics of pneumatization of the temporal bone evaluated by cone beam computed tomography. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013;42(6):771–5.
de Rezende Barbosa GL, Nascimento MC, Ladeira DB, Bomtorim VV, da Cruz AD, Almeida SM. Accuracy of digital panoramic radiography in the diagnosis of temporal bone pneumatization: a study in vivo using cone-beam-computed tomography. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2014;42(5):477–81.
Virapongse C, Sarwar M, Bhimani S, Sasaki C, Shapiro R. Computed tomography of temporal bone pneumatization: 1. Normal pattern and morphology. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1985;145(3):473–81.
Schlager S, Rüdell A. Sexual dimorphism and population affinity in the human zygomatic structure-comparing surface to outline data. Anat Rec. 2017;300(1):226–37.
Nkenke E, Hahn M, Lell M, Wiltfang J, Schultze-Mosgau S, Stech B, et al. Anatomic site evaluation of the zygomatic bone for dental implant placement. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2003;14(1):72–9.
Ujigawa K, Kato Y, Kizu Y, Tonogi M, Yamane GY. Three-dimensional finite elemental analysis of zygomatic implants in craniofacial structures. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2007;36(7):620–5.
da Costa Ribeiro R, dos santos BJ Jr, Provenzano N, de Freitas PH. Dautrey’s procedure: an alternative for the treatment of recurrent mandibular dislocation in patients with pneumatization of the articular eminence. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2014;43(4):465–9.
Sunwoo W, Nam DW, Kim YH. Zygomatic mastoiditis with extracranial complications: an extremely rare cause of cheek swelling. Korean J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018;61(2):110–3.
İlgüy M, Dölekoğlu S, Fişekçioğlu E, Ersan N, İlgüy D. Evaluation of pneumatization in the articular eminence and roof of the glenoid fossa with cone-beam computed tomography. Balkan Med J. 2015;32(1):64–8.
Miloglu O, Yilmaz AB, Yildirim E, Akgul HM. Pneumatization of the articular eminence on cone beam computed tomography: prevalence, characteristics and a review of the literature. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2011;40(2):110–4.
Tyndall DA, Matteson SR. The zygomatic air cell defect (ZACD) on panoramic radiographs. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1987;64(3):373–6.
Singh V, Krishna Chaitanya D, Chauhan BKS, Kumar IDV. A comparative study of pneumatization of temporal bone. J Anat Soc India. 2017;66(1):78–81.
Allam AF. Pneumatization of the temporal bone. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 1969;78(1):49–64.
Orhan K, Delilbasi C, Cebeci I, Paksoy C. Prevalence and variations of pneumatized articular eminence: a study from Turkey. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005;99(3):349–54.
Orhan K, Delilbasi C, Orhan AI. Radiographic evaluation of pneumatized articular eminence in a group of Turkish children. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2006;35(5):365–70.
Yavuz MS, Aras MH, Gungor H, Buyukkurt MC. Prevalence of the pneumatized articular eminence in the temporal bone. J Craniomaxillofac Surg. 2009;37(3):137–9.
Orhan K, Oz U, Orhan AI, Ulker AE, Delilbasi C, Akcam O. Investigation of pneumatized articular eminence in orthodontic malocclusions. Orthod Craniofac Res. 2010;13(1):56–60.
Nagaraj T, Nigam H, Balraj L, Santosh H, Ghouse N, Tagore S. A population-based retrospective study of zygomatic air cell defect in Bengaluru. J Med Radiol Pathol Surg. 2016;3(6):5–8.
Broonosh P, Shakibafard A, Mokhtare MR, Munesi Rad T. Temporal bone pneumatisation: a computed tomography study of pneumatized articular tubercle. Clin Radiol. 2014;69(2):151–6.
Mosavat F, Ahmadi A. Pneumatized articular tubercle and pneumatized roof of glenoid fossa on cone beam computed tomography: prevalence and characteristics in selected Iranian population. J Dentomaxillofac Radiol Pathol Surg. 2015;4(3):10–4.
Groell R, Fleischmann B. The pneumatic spaces of the temporal bone: relationship to the temporomandibular joint. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 1999;28(2):69–72.
Jadhav AB, Fellows D, Hand AR, Tadinada A, Lurie AG. Classification and volumetric analysis of temporal bone pneumatization using cone beam computed tomography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol. 2014;117(3):376–84.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Cansu Buyuk, Kaan Gunduz, and Hakan Avsever declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human rights statements
All procedures followed were in accordance with the ethical standards of the responsible committee on human experimentation (institutional and national) and with the Helsinki Declaration of 1964 and later versions.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients for being included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Buyuk, C., Gunduz, K. & Avsever, H. Prevalence and characteristics of pneumatizations of the articular eminence and roof of the glenoid fossa on cone-beam computed tomography. Oral Radiol 35, 171–176 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-018-0334-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11282-018-0334-z