Abstract
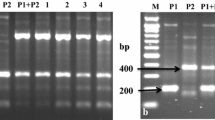
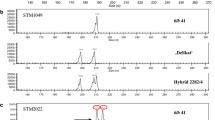
Interspecific somatic hybrids between the dihaploid Solanum tuberosum and the wild species S. pinnatisectum Dun. were produced via protoplast fusion. Protoplast isolation, electrofusion, culture of post-fusion products and regeneration of calli/shoots were undertaken following optimized protocols. Regenerants were characterized for hybridity, ploidy and resistance to Phytophthora infestans (Mont.) de Bery, causal fungal pathogen of late blight disease. From a total of 126 regenerated macrocalli, 12 somatic hybrids were confirmed by possessing species-specific diagnostic bands of their corresponding parents as revealed by RAPD, SSRs and cytoplasmic-DNA analyses. Tetraploid status of the 12 hybrids was determined using flow cytometry analysis. Intermediate phenotypes for leaf, flower, and tuber characteristics and high male fertility were observed in field-grown hybrid plants. Hybrids were highly resistant to foliage late blight based on field assessment for two seasons. In contrast, moderate level of resistance to foliage blight was observed in hybrids based on the detached leaf assay under laboratory conditions. Overall, somatic hybrids with moderate levels of resistance to foliage blight were identified, and these will be useful for in situ hybridization in potato breeding efforts.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AUDPC:
-
Area under the disease progress curve
- CRBC:
-
Chicken red blood cell
- CTAB:
-
Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide
- DAP:
-
Days after planting
- nDNA:
-
Nuclear DNA
- EBN:
-
Endosperm balance number
- FC:
-
Flow cytometry
- HEPES:
-
4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog
- MAS:
-
Marker assisted selection
- PDS:
-
Protoplast digestion solution
- RAPD:
-
Random amplified polymorphic DNA
- RAUDPC:
-
Relative area under the disease progress curve
- RCBD:
-
Randomized complete block design
- SSR:
-
Simple sequence repeat
- TPS:
-
True potato seed
References
Anonymous (2007) Procedures for standard evaluation trials of advanced potato clones. An International Cooperators’ Guide. International Potato Center, Lima, pp 41–53
Arumuganathan K, Earle ED (1991) Estimation of nuclear DNA content of plants by flow cytometry. Plant Mol Biol Rep 9:229–241
Bastia T, Carotenuto N, Basile B, Zonia A, Cardi T (2000) Induction of novel organelle DNA variation and transfer of resistance to frost and Verticillium wilt in Solanum tuberosum through somatic hybridization with 1 EBN S. commersonii. Euphytica 116:1–10
Behnke M (1975) Regeneration in Gewebekulturen einiger dihaplider Solanum tuberosum-Klone. Z Pflanzenziicht 75:262–265
Bidani A, Nouri-Ellouz O, Lakhoua L, Sihachakr D, Cheniclet C, Mahjoub A, Drira N, Gargouri-Bouzid R (2007) Interspecific potato somatic hybrids between Solanum berthaultii and Solanum tuberosum L. showed recombinant plastome and improved tolerance to salinity. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 91:179–189
Binding H, Nehls R (1977) Regeneration of isolated protoplast to plant Solanum dulcamara L. Z Pflanzenphysiol 85:279–280
Binding H, Nehls R, Schieder O, Sopory SK, Wenzel C (1978) Regeneration of mesophyll protoplast isolated from dihaploid clones of Solanum tuberosum L. Plant Physiol 43:52–54
Bradshaw JE, Bryan GJ, Ramsay G (2006) Genetic resources (including wild and cultivated Solanum species) and progress in their utilisation in potato breeding. Potato Res 49:49–65
Caetano-Anolles G, Bassam BJ, Gresshoff PM (1992) Primer template interactions during DNA amplification fingerprinting with single arbitrary oligonucleotides. Mol Gen Genet 235:157–165
Chimote VP, Chakrabarti SK, Pattanayak D, Pandey SK, Naik PS (2008) Molecular analysis of cytoplasm type in Indian potato varieties. Euphytica 162:69–80
Fry W (2008) Phytophthora infestans: the plant (and R gene) destroyer. Mol Plant Pathol 9:385–402
Ghislain M, Núñez J, Herrera MR, Pignataro J, Guzman F, Bonierbale M, Spooner DM (2009) Robust and highly informative microsatellite-based genetic identity kit for potato. Mol Breed 23:377–388
Gopal J, Oyama K (2005) Genetic base of Indian potato selections as revealed by pedigree analysis. Euphytica 142:23–31
Gopal J, Pandey SK, Kumar V, Kumar R, Pandey PC, Singh SV (2008) Morphological descriptors for DUS testing of potato varieties. Plant Gen Res New 154:40–47
Greplová M, Polzerová H, Vlastníková H (2008) Electrofusion of protoplasts from Solanum tuberosum, S. bulbocastanum and S. pinnatisectum. Acta Physiol Plant 30:787–796
Grosser JW, Gmitter FG Jr (2011) Protoplast fusion for production of tetraploids and triploids: applications for scion and rootstock breeding in citrus. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 104:343–357
Haverkort A, Struik P, Visser R, Jacobsen E (2009) Applied biotechnology to combat late blight in potato caused by Phytophthora infestans. Potato Res 52:249–264
Hawkes JG (1994) Origins of cultivated potatoes and species relationships. In: Bradshaw JE, Mackay GR (eds) Potato genetics. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 3–42
Kaushik SK, Bhardwaj V, Singh PH, Singh BP (2007) Evaluation of potato germplasm for adaptability and resistance to late blight. Potato J 34:443–444
Lema-Rumińska J (2011) Flow cytometric analysis of somatic embryos, shoots, and calli of the cactus Copiapoa tenuissima Ritt. forma monstruosa. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult. doi:10.1007/s11240-011-9941-7
Liu J, Xu X, Deng X (2005) Intergeneric somatic hybridization and its application to crop generic improvement. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 82:19–44
Lössl A, Götz M, Braun A, Wenzel G (2000) Molecular markers for cytoplasm in potato: male sterility and contribution of different plastid-mitochondrial configurations to starch production. Euphytica 116:221–230
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue culture. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Orrillo M, Bonierbale M (2009) Biología reproductiva y citogenética de la papa. International Potato Center, Lima, pp 9–17
Ovcharenko O, Momot V, Cherep N, Sheludko Y, Komarnitsky I, Rudas V, Kuchuk N (2011) Transfer of transformed Lesquerella fendleri (Gray) Wats. chloroplasts into Orychophragmus violaceus (L.) O.E. Schulz by protoplast fusion. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 105:21–27
Pehu E, Karp A, Moore K, Steele S, Dunckley R, Jones MGK (1989) Molecular, cytogenetic and morphological characterization of somatic hybrids of dihaploid Solanum tuberosum and diploid S. brevidens. Theor Appl Genet 78:696–704
Pinto DLP, Barros BA, Viccini LF, de Campos JMS, da Silva ML, Otoni WC (2010) Ploidy stability of somatic embryogenesis-derived Passiflora cincinnata Mast. plants as assessed by flow cytometry. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 103:71–79
Polzerová H, Patzak J, Greplová M (2011) Early characterization of somatic hybrids from symmetric protoplast electrofusion of Solanum pinnatisectum Dun. and Solanum tuberosum L. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 104:163–170
Saghai-Maroof MA, Soliman KM, Jorgensen RA, Allard RW (1984) Ribosomal DNA spacer-length polymorphisms in barley: Mendelian inheritance, chromosomal locations, and population dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci 81:8014–8018
Sarkar D, Sharma S, Chandel P, Pandey SK (2010) Evidence for gametoclonal variation in potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). Plant Growth Regul 61:109–117
Serraf I, Sihachakr D, Ducreux G, Brown SC, Allot M, Barghi N, Rossignol L (1991) Interspecific somatic hybridization in potato by protoplast electrofusion. Plant Sci 76:115–126
Sharma S, Sarkar D, Pandey SK (2010) Phenotypic characterization and nuclear microsatellite analysis reveal genomic changes and rearrangements underlying androgenesis in tetraploid potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.). Euphytica 171:313–326
Spooner DM, Salas A (2006) Structure, biosystematics, and genetic resources. In: Gopal J, Khurana SMP (eds) Handbook of potato production, improvement and postharvest management. Food Product Press, New York, pp 1–40
Sree Ramulu K (1986) Case histories of genetic variability in vitro: potato. In: Vasil IK (ed) Cell, culture and somatic cell genetics of plants. Academic Press, Minnesota, pp 449–473
Stancheva N, Weber J, Schulze J, Alipieva K, Ludwig-Müller J, Haas C, Georgiev V, Bley T, Georgiev M (2011) Phytochemical and flow cytometric analyses of Devil’s claw cell cultures. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 105:79–84
Sun Y, Liu S, Wang Y, Jones BJ, Wang H, Zhu S (2011) An interspecific somatic hybrid between upland cotton (G. hirsutum L. cv. ZDM-3) and wild diploid cotton (G. klotzschianum A.). Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult. doi:10.1007/s11240-011-9939-1
Szczerbakowa A, Boltowicz D, Lebecka R, Radomski P, Wielgat B (2005) Characteristics of the interspecific somatic hybrids Solanum pinnatisectum (+) S. tuberosum H-8105. Acta Physiol Plant 3:265–273
Szczerbakowa A, Tarwacka J, Oskiera M, Jakuczun H, Wielgat B (2010) Somatic hybridization between the diploids of S. × michoacanum and S. tuberosum. Acta Physiol Plant 32:867–873
Szczerbakowa A, Tarwacka J, Sliwinska E, Wielgat B (2011) Nuclear DNA content and chromosomal number in somatic hybrid allopolyploid of Solanum. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult. doi:10.1007/s11240-011-9932-8
Thieme R, Darsow U, Gavrilenko T, Dorokhov D, Tiemann H (1997) Production of somatic hybrids between S. tuberosum L. and late blight resistant Mexican wild potato species. Euphytica 97:189–200
Thieme R, Darsow U, Rakosy-Tican L, Kang Z, Gavrilenko T, Antonova O, Heimbach U, Thieme T (2004) Use of somatic hybridization to transfer resistance to late blight and potato virus Y (PVY) into cultivated potato. Plant Breed Seed Sci 50:113–118
Thieme R, Rakosy-Tican E, Gavrilenko T, Antonova O, Schubert J, Nachtigall M, Heimbach U, Thieme T (2008) Novel somatic hybrids (Solanum tuberosum L. + Solanum tarnii) and their fertile BC1 progenies express extreme resistance to potato virus Y and late blight. Theor Appl Genet 116:691–700
Thieme R, Rakosy-Tican E, Nachtigall M, Schubert J, Hammann T, Antonova O, Gavrilenko T, Heimbach U, Thieme T (2010) Characterization of the multiple resistance traits of somatic hybrids between Solanum cardiophyllum Lindl. and two commercial potato cultivars. Plant Cell Rep 29:1187–1201
Tiwari JK, Poonam B, Sarkar D, Pandey SK, Gopal J, Kumar SR (2010) Molecular and morphological characterization of somatic hybrids between Solanum tuberosum L. and S. etuberosum Lindl. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 103:175–187
Vleeshouwers VGAA, van Dooijeweert W, Keizer LCP, Sijpkes L, Govers F, Colon LT (1999) A laboratory assay for Phytophthora infestans resistance in various Solanum species reflects the field situation. Eur J Plant Pathol 105:241–250
Wenzel G (1994) Tissue culture. In: Bradshaw JE, Mackey GR (eds) Potato genetics. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 173–195
Yang Y, Guan S, Zhai H, He S, Liu Q (2009) Development and evaluation of a storage root-bearing sweetpotato somatic hybrid between Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam. and I. triloba L. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 99:83–89
Zhou A, Xia G, Zhang X, Chen H, Hu H (2001) Analysis of chromosomal and organellar DNA of somatic hybrids between Triticum aestivum and Haynaldia villosa Schur. Mol Genet Genomics 265:387–393
Acknowledgments
Authors are grateful to Dr. PS Ahuja, Director, Institute of Himalayan Bioresource and Technology (IHBT), Palampur, Himachal Pradesh, India for the facility provided for flow cytometry analysis. Authors thank to Mr. Sheeshram Thakur for the in vitro multiplication and field management. The financial assistance received in the form of an ad-hoc research project (F. No. 8-45/2004-Hort. II) from the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), New Delhi is also acknowledged. Useful comments and suggestions on the manuscript from the editor, associate editor and two anonymous reviewers are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix
Appendix
See Tables 4, 5, 6 and Fig. 4.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarkar, D., Tiwari, J.K., Sharma, S. et al. Production and characterization of somatic hybrids between Solanum tuberosum L. and S. pinnatisectum Dun.. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 107, 427–440 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-011-9993-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11240-011-9993-8