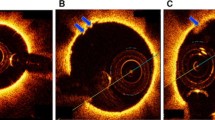
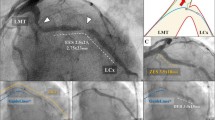
Abstract
In this feasibility study, a novel catheter prototype for laser thrombolysis under the guidance of optical coherence tomography (OCT) was designed and evaluated in a preclinical model. Human arteries and veins were integrated into a physiological flow model and occluded with thrombi made from the Chandler Loop. There were four experimental groups: placebo, 20 mg alteplase, laser, 20 mg alteplase + laser. The extent of thrombolysis was analyzed by weighing, OCT imaging and relative thrombus size. In the alteplase group, thrombus size decreased to 0.250 ± 0.036 g (p < 0.0001) and 14.495 ± 0.526 mm2 (p < 0.0001) at 60 min. The relative thrombus size decreased to 73.6 ± 4.1% at 60 min (p < 0.0001). In the laser group, thrombus size decreased significantly to 0.145 ± 0.028 g (p < 0.0001) and 11.559 ± 1.034 mm2 (p < 0.0001). In the alteplase + laser group, thrombus size decreased significantly (0.051 ± 0.026 g; p < 0.0001; 9.622 ± 0.582 mm2; p < 0.0001; 47.4 ± 6.1%; p < 0.0001) in contrast to sole alteplase and laser application. The reproducibility and accuracy of the OCT imaging was high (SD <10%). Histological examination showed no relevant destruction of the vascular layers after laser ablation (arteries: 745.8 ± 5.5 μm; p = 0.69; veins: 448.3 ± 4.5 μm; p = 0.27). Thus, laser ablation and OCT imaging are feasible with the novel catheter and thrombolysis combining alteplase with laser irradiation appears highly efficient.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vandvik PO, Lincoff AM, Gore JM, Gutterman D D, Sonnenberg FA, Alonso-Coello P, Akl EA, Lansberg MG, Guyatt GH, Spencer FA (2012). Primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease: antithrombotic therapy and prevention of thrombosis. American College of Chest Physicians evidence-based clinical practice guidelines. CHEST J, 141(2_suppl), e637S–e668S
Meissner MH, Gloviczki P, Comerota AJ, Dalsing MC, Eklof BG, Gillespie DL, Lohr JM, McLafferty RB, Murad MH, Padberg F, Pappas P, Raffetto JD, Wakefield TW (2012) Early thrombus removal strategies for acute deep venous thrombosis: clinical practice guidelines of the Society for Vascular Surgery and the American Venous Forum. J vasc surg 55(5):1449–1462
Dave RM, Patlola R, Kollmeyer K, Bunch F, Weinstock BS, Dippel E, Jaff MR, Popma J, Weissman N (2009) Excimer laser recanalization of femoropopliteal lesions and 1-year patency: results of the CELLO registry. J Endovasc Ther 16(6):665–675
Bidinger J, Ackermann R, Cattaneo G, Kammel R, Nolte S (2014) A feasibility study on femtosecond laser thrombolysis. Photomed Laser Surg 32(1):17–22
Shammas NW, Weissman NJ, Coiner D, Shammas GA, Dippel E, Jerin M (2012) Treatment of subacute and chronic thrombotic occlusions of lower extremity peripheral arteries with the excimer laser: a feasibility study. Cardiovasc Revasc Med 13(4):211–214
Soest CG, Goderie T, Regar E, Koljenovic S, van Leenders GL, Gonzalo N, van Noorden S, Okamura T, Bourma BE, Tearny GJ, Oosterhuis JW, Serruys PW, van der Steen AF (2010) Atherosclerotic tissue characterization in vivo by optical coherence tomography attenuation imaging. J Biomed Opt 15(1):011105
Jorge E, Baptista R, Calisto J, Faria H, Monteiro P, Pan M, Pêgo M (2016) Optical coherence tomography of the pulmonary arteries: a systematic review. J Cardiol 67(1):6–14
Koustenis A, Harris A, Gross J, Januleviciene I, Shah A, Siesky B (2016). Optical coherence tomography angiography: an overview of the technology and an assessment of applications for clinical research. Br J Ophthalmol, doi:10.1136/bjophthalmol-2016-309389.
Kubo T, Akasaka T, Shite J, Suzuki T, Uemura S, Yu B, Kozuma K, Kitabata H, Shinke T, Habara M, Saito Y, Hou J, Suzuki N, Zhang S (2013). OCT compared with IVUS in a coronary lesion assessment: the OPUS-CLASS study. JACC, 6(10), 1095–1104.
Caiazzo G, Longo G, Giavarini A, Kilic ID, Fabris E, Serdoz R, Mattesini A, Foin N, Secco GG, De Rosa S, Indolfi C, Di Mario C (2016) Optical coherence tomography guidance for percutaneous coronary intervention with bioresorbable scaffolds. Int J Cardiol 221:352–358
Van der Steenhoven TJ, Bosman PF, Tersteeg C, Jacobs MJ, Moll FL, de Groot PG, Heyligers JM (2012) Thrombogenicity of a new injectable biocompatible elastomer for aneurysm exclusion, compared to expanded polytetrafluoroethylene in a human ex vivo model. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 43(6):675–680
Tien WH, Chen HY, Berwick ZC, Krieger J, Chambers S, Dabiri D, Kassab GS (2014) Characterization of a bioprosthetic bicuspid venous valve hemodynamics: implications for mechanism of valve dynamics Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 48(4):459–464
Diamond, Scott L. (1999) Engineering design of optimal strategies for blood clot dissolution. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 1(1):427–461
Tsetis DK, Katsamouris AN, Giannoukas AD, Hatzidakis AA, Kostas T, Chamalakis K, Ioannou C, Gourtsoyiannis NC (2003) Potential benefits from heating the high-dose rtPA boluses used in catheter-directed thrombolysis for acute/subacute lower limb ischemia. J Endovasc Ther 10(4):739–744
Marczynski-Bühlow M, Gro J, Berndt R, Röcken C, Wedel T, Böttner M, Cremer J, Lutter G, Petzina R (2014) Comparison of different resection tools for human calcified aortic valves. Innovations 9(4):312–316
Yamashita T, Sato T, Sakamoto K, Ishii H, Yamamoto J (2015) The free-radical scavenger edaravone accelerates thrombolysis with alteplase in an experimental thrombosis model. Thromb Res 135(6):1209–1213
Lee K, Istl A, Dubois L, DeRose G, Forbes TL, Wiseman D, Mujoomdar A, Kribs S, Power AH (2015) Fibrinogen Level and bleeding risk during catheter-directed thrombolysis using tissue plasminogen activator. Vasc Endovascular Surg 49(7):175–179
Du GC, Zhang MC, Zhao JC (2015). Catheter-directed thrombolysis plus anticoagulation versus anticoagulation alone in the treatment of proximal deep vein thrombosis—a meta-analysis. Vasa 44(3): 195–202.
Kahn SR, Galanaud JP, Vedantham S, Ginsberg JS (2016) Guidance for the prevention and treatment of the post-thrombotic syndrome. J Thromb Thrombolysis 41:144–153
Blackwood S, Dietzek AM (2016) Pharmacomechanical thrombectomy: 2015 update. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 14(4):463–475
Park KM, Moon IS, Kim JI, Yun SS, Hong KC, Jeon YS, Cho SG, Kim JY (2014) Mechanical thrombectomy with Trerotola compared with catheter-directed thrombolysis for treatment of acute iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis. Ann Vasc Surg 28(8):1853–1861
Wilkoff BL, Byrd CL, Love CJ, Hayes DL, Sellers TD, Schaerf R, Parsonnet V, Epstein LM, Sorrentino RA, Reiser C (1999) Pacemaker lead extraction with the laser sheath: results of the pacing lead extraction with the excimer sheath (PLEXES) trial. J Am Coll Cardiol 33(6):1671–1676
Malskat WS, Poluektova AA, van der Geld CW, Neumann HM, Weiss RA, Bruijninckx CM, van Gemert MJ (2014) Endovenous laser ablation (EVLA): a review of mechanisms, modeling outcomes, and issues for debate. Lasers Med Sci 29(2):393–403
Mumme A, Heinen W, Geier B, Maatz W, Barbera L, Walterbusch G (2002) Regional hyperthermic fibrinolytic perfusion after unsuccessful venous thrombectomy of extensive deep venous thrombosis. J Vasc Surg 36(6):1219–1224
Dippel EJ, Makam P, Kovach R, George JC, Patlola R, Metzger DC, Mena-Hurtado C, Beasley R, Soukas P, Colon-Hernandez PJ, Stark MA, Walker C (2015). Randomized controlled study of excimer laser atherectomy for treatment of femoropopliteal in-stent restenosis: initial results from the EXCITE ISR trial (EXCImer Laser Randomized Controlled Study for Treatment of FemoropopliTEal In-Stent Restenosis). JACC 8(1):92–101.
Huang C, Liu B, Brezinski ME (2008) Ultrasound-enhanced optical coherence tomography: improved penetration and resolution. J Opt Soc Am A 25(4):938–946
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Rouven Berndt and Rene Rusch have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berndt, R., Rusch, R., Hummitzsch, L. et al. Development of a new catheter prototype for laser thrombolysis under guidance of optical coherence tomography (OCT): validation of feasibility and efficacy in a preclinical model. J Thromb Thrombolysis 43, 352–360 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-016-1470-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-016-1470-0