Abstract
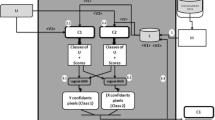
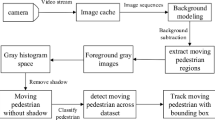
Cast shadow detection and removal is one of the key problems in vision-based systems for accurate and robust segmentation of moving objects. This paper proposes a co-training-based adaptive method for detecting moving shadows in video sequences. Shadow detection based on static methods cannot adapt to changing environment such as gradual illumination changes. In order to solve this problem, we have proposed an online sequential extreme learning machine (OS-ELM)-based semi-supervised technique for moving cast shadow detection. Online learning of OS-ELM is much faster and provides better generalization performance compared to other popular online learning algorithms. First, we extracted color, texture, gradient, and image patch similarity features using a background model and input video frame, which are useful for discriminating moving shadows and objects. Co-training scheme is used for online updating of the OS-ELM classifier in order to adapt to the dynamic environment. Experimental results on different benchmark video sequences shows that the proposed method performs better shadow detection and discrimination compared with other methods.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Blum A, Mitchell T (1998) Combining labeled and unlabeled data with co-training. 11th Annual Conference on Computation Learning Theory, pp 92–100
Cavallaro A, Salvador E, Ebrahimi T (2005) Shadow-aware object-based video processing. IEEE Proc Vision Image Signal Process 152(4):398–406
Chen CC, Aggarwal JK (2010) Human shadow removal with unknown light source. International Conference on Pattern Recognition, pp 2407–2410
Cucchiara R, Grana C, Piccardi M, Prati A (2003) Detecting moving objects, ghosts, and shadows in video streams. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 25(10):1337–1342
El-Zahhar MM, Karali A, ElHelw M (2011) A semi supervised learning-based method for adaptive shadow detection. IEEE International Conference on Signal and Image Processing Applications, pp 348–353
Grest D, Frahm JM, Koch R (2003) A color similarity measure for robust shadow removal in real-time. Vision Modeling and Visualization, pp 253–260
Hsieh JW, Hu WF, Chang CJ, Chen YS (2003) Shadow elimination for effective moving object detection by Gaussian shadow modeling. Image Vis Comput 21:505–516
Huang JB, Chen CS (2009) Moving cast shadow detection using physics-based features. IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 2310–2317
Huang GB, Zhu QY, Siew CK (2006) Extreme learning machine: theory and applications. Neurocomputing 70:489–501
Jalal AS, Singh V (2014) A framework for background modeling and shadow suppression for moving object detection in complex wavelet domain. Multimedia Tools Appl 73:779–801
Jarraya SK, Boukhriss RR, Hammami M, Ben-Abdallah H (2012) Cast shadow detection based on semi supervised learning. LNCS 7324:19–26
Jia Y, Yu X, Dai J, Hu W (2012) A novel moving cast shadow detection of vehicles in traffic scene. Proceedings of the Third Sino-foreign-Interchange Conference on Intelligent Science and Intelligent Data Engineering, pp 115–124
Jiang K, Li A, Cui Z, Wang T, Su Y (2013) Adaptive shadow detection using global texture and sampling detection. IET Comput Vis 7(2):115–122
Joshi AJ, Atev S, Masoud O, Papanikolopoulos N (2007) Moving shadow detection with low and mid level reasoning. IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation, pp 4827–4832
Joshi AJ, Papanikolopoulos NP (2008) Learning to detect moving shadows in dynamic environments. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 30(11):2055–2063
Leone A, Distance C (2007) Shadow detection for moving objects based on texture analysis. Pattern Recogn 40:1222–1233
Li G, Qin L, Huang Q (2013) Adaptive moving cast shadow detection. The Era of Interactive Media, pp 399–409
Liang NY, Huang GB, Saratchandran P, Sundararajan N (2006) A fast and accurate online sequential learning algorithms for feedforwards networks. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 17:1411–1423
Nigam K, Ghani R (2000) Analyzing the effectiveness and applicability of co-training. 9th International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management, pp 86–93
Prati A, Mikic I, Trividi M, Cucchira R (2003) Detecting moving shadows: algorithms and evaluation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 25(7):918–923
Salvador E, Cavallaro A, Ebrahimi T (2004) Cast shadow segmentation using invariant color features. Comput Vis Image Underst 95:238–259
Sanin A, Sanderson C, Lovell BC (2010) Improved shadow removal for robust person tracking in surveillance scenarios. International Conference on Pattern Recognition, pp 141–144
Sanin A, Sanderson C, Lovell BC (2012) Shadow detection: a comparative evaluation of recent methods. Pattern Recogn 45:1684–1695
Song KT, Tai JC (2007) Image-based traffic monitoring with shadow suppression. Proc IEEE 95(2):413–426
Staufer C, Grimson WEL (1999) Adaptive background mixture model for real-time tracking. IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, pp 246–252
Yang MT, Lo KH, Chiang CC, Tai WK (2007) Moving cast shadow detection by exploiting multiple cues. IET Image Process 2(2):95–104
Yang Y, Ming Y, Yongchao M (2009) A Strategy to detect the moving vehicle shadows based on gray-scale information. Second International Conference on Intelligent Networks and Intelligent Systems, pp 358–361
Yuan C, Yang C, Xu Z (2010) Simple vehicle detection with shadow removal at intersection. Second International Conference on Multimedia and Information Technology, pp 188–191
Zhigang L, Xiao L, Yaonan W, Xi H (2013) Adaptive moving cast shadow detection by integrating multiple cues. Chin J Electron 22(4):757–762
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghimire, D., Lee, J. Online sequential extreme learning machine-based co-training for dynamic moving cast shadow detection. Multimed Tools Appl 75, 11181–11197 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-2839-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-015-2839-3