Abstract
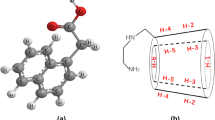
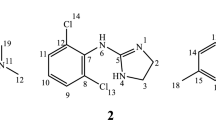
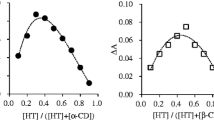
Inclusion complex of anionic nateglinide (NTG) with β-cyclodextrin (βCD) has been prepared to improve the water solubility of NTG. The mechanism of the complexation was elucidated using isothermal titration calorimetry and molecular modeling study. The solubility of NTG increased linearly with increasing the concentration of βCD and decreased gradually over 6 mM βCD in the solution. The maximum solubility of NTG in the presence of βCD was nine times more than that of NTG only. The stoichiometry (n), association constant (K), and thermodynamic parameters (ΔG, ΔH, ΔS) for the complexation were estimated: n = 1.0, K = 5.8 × 103 M−1, ΔG = −21.5 kJ mol−1, ΔH = −15.7 kJ mol−1, and ΔS = 19.5 J mol−1 K−1 at pH 7.0 and 298.15 K. The conformations and solvation energies for two types of the inclusion complex, type A penetrating the isopropyl cyclohexyl group of NTG into the βCD cavity and type B penetrating the phenyl group of NTG, were calculated. It was indicated that anionic NTG could strongly form the inclusion complex of type A complex with βCD at 1:1 molar ratio to increase the solubility in aqueous solution.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
International Diabetes Federation. IDF DIABETES ATLAS. In: POWER POINT 2014 IDF Diabetes Atlas 6th edition revision 2014. International Diabetes Federation. http://www.idf.org/diabetesatlas (2014). Accessed 15 Jan 2015.
Kataoka M, Itsubata S, Masaoka Y, Sakuma S, Yamashita S. In vitro dissolution/permeation system to predict the oral absorption of poorly water-soluble drugs: effect of food and dose strength on it. Biol Pharm Bull. 2011;34:401–7.
Yamamoto A. Improvement of gastrointestinal and transmucosal absorption of poorly absorbable drugs and development of novel dosage forms of these drugs. Tokyo: CMC; 2012. p. 4.
Higuchi T, Connors KA. Advances in analytical chemistry instrumentation, vol. 4. New Jersey: Wiley; 1965. p. 117–212.
The Japan Society of Calorimetry and Thermal Analysis. Handbook of calorimetry and thermal analysis. 2nd ed. Tokyo: The Japan Society of Calorimetry and Thermal Analysis; 2010. p. 63–5.
Wszelaka-Rylik M, Gierycz P. Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) study of natural cyclodextrins inclusion complexes with tropane alkaloids. J Therm Anal Calorim. Published online: 04 April 2015.
Liu Y, Han B, Li B, Zhang Y, Zhao P, Chen Y, Wada T, Inoue Y. Molecular recognition study on supramolecular system. 14. Synthesis of modified cyclodextrins and their inclusion complexation thermodynamics with l-tryptophan and some naphthalene derivatives. J Org Chem. 1998;63:1444–54.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The present article is based on the lecture presented at JCCTA50 conference in Osaka—Japan on 28–30 September, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ikeda, H., Fukushige, Y., Matsubara, T. et al. Improving water solubility of nateglinide by complexation of β-cyclodextrin. J Therm Anal Calorim 123, 1847–1850 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4714-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10973-015-4714-x