Abstract
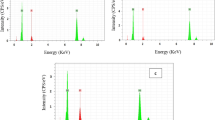
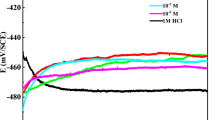
Corrosion rates of mild steel were measured in oxygen-free, CO2-saturated brines as a function of NaCl concentration employing electrochemical techniques. Decreased corrosion rates were observed as salt concentration increased. However, at high salt concentration (≥20 wt% NaCl), corrosion rates were independent of the flow rate of CO2-saturated brine. To understand this phenomenon, corrosion surfaces were analyzed by scanning electron microscopy and X-ray diffraction and showed only residual iron carbide for salt concentrations of 0.5–5 wt%. However, at 20 wt% NaCl, a porous corrosion scale with embedded crystals, possibly magnetite, was observed. No iron carbonate was observed and water chemistry showed it was 10,000 times below saturation. A numerical model of corrosion in CO2–NaCl systems was able to predict the reduced corrosion rates with salt concentration increase as a consequence of reduced solubility of CO2 (“salting-out”). However, the model did not predict that corrosion rates were flow-independent at high salt concentration. These results demonstrate that flow-independent corrosion is a consequence of a diffusion barrier created by magnetite scale, present only at high salt concentrations.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pachauri RK, Reisinger A (2007) Climate change 2007: Synthesis report. Contribution of working groups I, II and III to the fourth assessment report of the intergovernmental panel on climate change. IPCC, Geneva
Bachu S (2000) Energy Convers Manag 41:953
Bachu S (2002) Energy Convers Manag 43:87
Carey JW, Wigand M, Chipera S et al (2007) Int J of Greenh Gas Con 1:75
Crow W, Carey JW, Gasda S et al (2010) Int J of Greenh Gas Con 4:186
Carey JW, Svec R, Grigg R et al (2010) Int J of Greenh Gas Con 4:272
Han J, Carey JW, Zhang J (2010) 9th Annual Conference for Carbon Capture and Sequestration, paper no# 361
Woollam RC, Hernandez SE (2006) SPE international oilfield corrosion symposium, paper no. 100673. Society of Petroleum Engineers, Aberdeen, UK
Nyborg R (2010) NACE CORROSION/2010, paper no. 10371.
Han J, Carey JW, Zhang J (2011) Int J of Greenh Gas Con. doi:10.1016/j.ijggc.2011.02.005
Chin RJ, Nobe K (1972) J Electrochem Soc 119:1457
Darwish NA, Hilbert F, Lorenz WJ et al (1973) Electrochim Acta 18:421
Kuo HC, Nobe K (1978) J Electrochem Soc 125:853
MacFarlane DR, Smedley IS (1986) J Electrochem Soc 133:2240
Asakura S, Nobe K (1971) J Electrochem Soc 118:13
Burstein GT, Davies DH (1980) Corros Sci 20:1143
Burstein GT, Davies DH (1980) J Electrochem Soc 128:33
Ashley GW, Burstein GT (1991) Corrosion 47:908
Wang Z, Moore RC, Felmy AR et al (2001) Waste Manag 21:335
Cid M, Penuela A, Pett MC (1985) Mater Chem Phys 13:139
Foley RT (1970) Corrosion 26:58
Kirby GN (1995) Chem Eng Prog 91:47
Fang H, Nešić S, Brown BN (2007) NACE CORROSION/2007, paper no. 06372
Fang H, Brown BN, Nešić S (2010), NACE CORROSION/2010, paper no. 10276
Nešić S, Postlethwaite J, Olsen S (1996) Corrosion 54:280
Conway BE (1985). In: Conway BE, White RE, Bockris JO’M (eds) Modern aspects of electrochemistry, no. 16. Plenum Press, New York
Bockris JO’M, Drazic D, Despic AR (1961) Electrochim Acta 4:325
Harrington SP, Devine TM (2008) J Electrochem Soc 155:C381
De Waard C, Williams DE (1975) Corrosion 31:177
Norsok Standard M-506, CO2 corrosion rate calculation model (Rev. 2). Available via DIALOG. http://www.standard.no/en/Sectors/Petroleum/NORSOK-Standard-Categories/M-Material/M-5061/. Accessed 15 Jan 2011
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Fossil Energy Program of the Department of Energy (FE-10-001) for funding support. The authors would like to acknowledge Michael S. Rearick from GGRL Lab (Geology Geochemistry Research Lab), Earth and Environmental Sciences Division, Los Alamos National Laboratory for his water chemistry analysis. The manuscript was significantly improved by comments from anonymous reviewers.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, J., Carey, J.W. & Zhang, J. Effect of sodium chloride on corrosion of mild steel in CO2-saturated brines. J Appl Electrochem 41, 741–749 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-011-0290-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-011-0290-3