Abstract
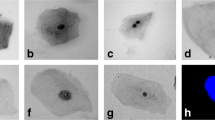
The main objective of the present study was to screen the genotoxicity caused by individual and combined habits of smoking, tobacco chewing, and alcohol consumption in human population of North India. Study recruited 67 male subjects aged 25 to 65 years. Buccal mucosal cells were subjected to micronucleus (MN) assay, and 8-hydroxyl-2-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) was estimated in their urine samples. Number and shape of the MN cells varied in the buccal epithelium of different groups. Maximum number of MN (0.47%) were found in tobacco chewers followed by smokers (0.45%) and alcoholics (0.44%) (P < 0.05). These results reciprocated the concentration of urinary 8-OHdG. Maximum value for 8-OHdG was also recorded in tobacco chewers (21.07 ± 5.51 mg/mg creatinine) followed by smokers (20.25 ± 3.96 mg/mg creatinine) and alcoholics (19.06 ± 3.41 mg/mg creatinine) (P < 0.05). Combined effects of these agents were found to be statistically different from individual effects. Carcinogenic compounds present in cigarette smoke, nitrosamines found in solid tobacco, and acetaldehyde, a metabolic product of alcohol, induce oxidative stress that manifests into genotoxicity. In conclusion, demographical differences occur in the genotoxicity caused by these three habits. MN assay and urinary 8-OHdG are simple, noninvasive, and reliable biomarkers of genotoxicity.






Similar content being viewed by others

References
Babu, S., Bhat, R. V., Kumar, P. U., Sesikaran, B., Rao, K. V., Aruna, P., & Reddy, P. R. (1996). A comparative clinico-pathological study of oral submucous fibrosis in habitual chewers of pan masala and betel quid. Journal of Toxicology. Clinical Toxicology, 34, 317–322.
Bagwe, A. N., & Bhisey, R. A. (1993). Occupational exposure to tobacco and resultant genotoxicity. Mutation Research, 299, 103–109.
Bansal, H., Sandu, V. S., Bhandari, R., & Sharma, D. (2012). Evaluation of micronuclei in tobacco users: a study in Punjabi population. Comtemporary Clinical Trials, 3, 184–187.
Blot, W. J. (1992). Alcohol and cancer. Cancer Research, 52, 2119S–2123S.
Chandirasekar, R., Suresh, K., Sasikala, K., Kumar, B. L., Venkatesan, R., Ganesh, G. K., & Jacob, R. (2013). Genotoxicity assessment in smokeless tobacco users: a case control study. Toxicology and Industrial Health, 29, 216–223.
De Marini, D. M. (2004). Genotoxicity of tobacco smoke and tobacco smoke condensate: a review. Mut Res, 567, 447–474.
Feulgen, R., & Rosenbeck, H. (1924). NachweiseinerNukleinsäurevomTypus der Thymonukleinsäure und die daraufberuhendeelektiveFärbung von Zellkernen in mikroskopischenPräparaten. Zeitschrift für Physikalische Chemie, 135, 203–248.
Hanahan, D., & Weinberg, R. A. (2000). The hallmarks of cancer. Cell, 100, 57–70.
Harty, L. C., Capsaraso, N. E., Hayes, R. B., Win, D. M., Bravo-Otero, E., Blot, W. J., et al. (1997). Alcohol dehydrogenase 3 genotype and risk of oral cavity and pharyngeal cancer. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 89, 1698–1705.
Heddle, J. A., Cimino, M. C., Hayashi, M., Romagna, F., Shelby, M. D., Tucker, J. D., Vanparys, P., & Macgregor, J. T. (1991). Micronuclei as an index of cytogenetic damage: past, present and future. Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, 18, 277–291.
International agency for research on cancer. (2011). Global cancer facts and figures (2nd ed.pp. 1–57). Atlanta: Am Cancer Soc P.
International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) working group on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. (2004). Tobacco smoke and involuntary smoking. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, 83, 1–1473.
International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC) working group on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans. (2010). Alcohol consumption and ethyl carbamate. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans, 96, 1–1428.
Ishizakai, M., Yoshida, K., Nishimoto, N., Saleh, A. M., Ishii, C., Handa, H., et al. (2004). 8-Hydroxyl-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) in patients with chronic liver diseases. Rinsho Byori, 52, 732–736.
Jyoti, S., Khan, S., Afzal, M., Naz, F., & Siddique, Y. H. (2013). Evaluation of micronucleus frequency by acridine orange fluorescent staining in buccal epithelial cells of oral submucosus fibrosis (OSMF) patients. Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics, 14, 189–193.
Kayal, J. J., Trivedi, A. H., Dave, B. J., Nair, J., Nair, U. J., Bhide, S. V., et al. (1993). Incidence of micro- nuclei in oral mucosa of users of tobacco products singly or in various combinations. Mutagenesis, 8, 31–33.
Kissling, G. E., Dertinger, S. D., Hayashi, M., & Macgregor, J. T. (2007). Sensitivity of erythrocyte micronucleus assay: dependence on number of cells scored and inter animal variability. Mutation Research, 634, 235–240.
Kulikowska-Karpinska, E., & Czerw, K. (2015). Estimation of 8-hydroxyl-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) concentration in the urine of cigarette smokers. Wiadomo ci Lekarskie, 68, 32–38.
Kumar, S., & Rana, S. V. S. (1993). Influence of age, alcohol and smoking on the excretion of hippuric acid in painters. Journal of Environmental Biology, 14, 293–299.
Lippman, S. M., Peters, E. J., Wargovich, M. J., Stadnyk, A. N., Dixon, D. O., Dekmezian, R. H., et al. (1990). Bronchial micronuclei as a marker of an early stage of carcinogenesis in the human tracheobronchial epithelium. International Journal of Cancer, 45, 811–815.
Livingston, G. K., Reed, R. N., Olson, B. L., & Lockey, J. E. (1990). Induction of nuclear aberrations by smokeless tobacco in epithelial cells of human oral mucosa. Environmental and Molecular Mutagenesis, 15, 136–144.
Manikantan, P., Balachandar, V., Sashikala, K., & Mohanadevi, S. (2010). Lymphocyte DNA damage in chewing tobacco users of Coimbatore, Tamil Nadu, by using comet assay. Journal of Human Ecology, 31, 53–58.
Mansoori, A. A., & Jain, S. K. (2015). Molecular links between alcohol and tobacco induced DNA damage, gene polymorphisms and pathophysiological consequences: a systemic review of hepatic carcinogenesis. Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention, 16, 4803–4812.
Mojidra, B. N., Archana, K., Gautam, A. K., Verma, Y., & Lakkad, B. C. (2009). Evaluation of genotoxicity of pan masala employing chromosomal aberration and micronucleus assay in bone marrow cells of the mice. Toxicology and Industrial Health, 25, 467–471.
Nagler, R., & Dayan, D. (2006). The dual role of saliva in oral carcinogenesis. Oncology, 71(1–2), 10–17.
Nair, U. J., Obe, G., Maru, G. B., Bhide, S. V., Pieper, R., & Bartsch, H. (1991). Evaluation of frequency of micronucleated oral mucosa cells as a marker for genotoxic damage in chewers of betel quid with or without tobacco. Mutation Research, 261, 163–168.
Patel, B. P., Trivedi, P. J., Brahmbhatt, M. M., Shukla, S. N., Shah, P. M., & Bakshi, S. R. (2009). Micronuclei and chromosomal aberrations in healthy tobacco chewers and controls: a study from Gujarat, India. Archive of Oncology, 17, 7–10.
Perera, F. P., Santella, R. M., Brenner, D., Poirier, M. C., Munshi, A. A., Fischman, H. K., et al. (1987). DNA adducts, protein adducts, and sister chromatid exchange in cigarette smokers and nonsmokers. Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 79, 449–456.
Prokopczyk, B., Revenson, A., Bertinato, P., Brunnemann, K. D., & Hoffmann, D. (1987). 3-(Methylnitrosamino)propionitrile: occurrence in saliva of betel quid chewers, carcinogenicity, and DNA methylation in F344 rats. Cancer Research, 47, 467–471.
Rossner, P., Boffetta, P., Ceppi, M., Bonassi, S., Smerhovsky, Z., Landa, K., et al. (2005). Chromosomal aberrations in lymphocytes of healthy subjects and risk of cancer. Environmental Health Perspectives, 113, 517–520.
Rubin, H. (2001). Synergistic mechanisms in carcinogenesis by polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and by tobacco smoke: a bio-historical perspective with updates. Carcinogenesis, 22, 1903–1930.
Santovito, A., Cervella, P., & Delpero, M. (2015). Evidence of genotoxicity in lymphocytes of non-smoking alcoholics. Molecular Biology Reports, 42, 53–59.
Sarto, F., Faccioli, M. C., Cominato, I., & Levis, A. G. (1985). Aging and smoking increase the frequency of sister-chromatid exchanges (SCE) in man. Mutation Research, 144, 183–187.
Sellappa, S., Balakrishnan, M., Raman, S., & Palanisamy, S. (2009). Introduction of micronuclei in buccal mucosa on chewing a mixture of betel leaf, areca nut and tobacco. Journal of Oral Science, 51, 289–292.
Stich, H. F., Curtis, J., & Parida, B. B. (1982). Application of the micronucleus test to exfoliated cells of high cancer risk groups: tobacco chewers. International Journal of Cancer, 30(5), 553–559.
Stich, H. F., Rosin, M. P., & Vallejera, M. O. (1984). Reduction with vitamin A and beta-carotene administration of proportion of micronucleated buccal mucosal cells in Asian betel nut and tobacco chewers. The Lancet, 2, 1204–1206.
Stich, H. F., Parida, B. B., & Brunnemann, K. D. (1992). Localized formation of micronuclei in the oral mucosa and tobacco-specific nitrosamines in the saliva of “reverse” smokers, khaini-tobacco chewers and gudakhu users. International Journal of Cancer, 50, 172–176.
Tolbert, P. E., Shy, C. M., & Allen, J. W. (1991). Micronuclei and other nuclear anomalies in buccal smears: a field test in snuff users. American Journal of Epidemiology, 134, 840–850.
Toro, G., & Ackermann, P.G. (1975). Practical clinical chemistry. Little Brown & Company, Boston, 154.
Valavanidis, A., Vlachogianni, T., & Fiotakis, C. (2009). 8-Hydroxyl-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG): a critical biomarker of oxidative stress and carcinogenesis. Journal Of Environmental Science and Health, Part C: Environmental Carcinogenesis & Ecotoxicology Reviews, 27, 120–139.
Webber, L. P., Pellicioli, A. C., Magnusson, A. S., Danilevicz, C. K., Bueno, C. C., Filho, S. A., et al. (2016). Nuclear changes in oral mucosa of alcoholics and crack cocaine users. Human and Experimental Toxicology, 35, 184–193.
Witt, K. L., Livanos, E., Kissling, G. E., Torous, D. K., Caspary, W., Tice, R. R., & Recio, L. (2008). Comparision of flow cytometery and microscopy based methods for measuring micronucleated reticulocyte frequencies in rodents treated with nongenotoxic and genotoxic chemicals. Mutation Research, 649, 101–113.
Yao, Q. H., Mei, S. R., Weng, Q. F., Zhang, P. D., Yang, Q., Wu, C. Y., et al. (2004). Determination of urinary oxidative DNA damage marker 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine and the association with cigarette smoking. Talanta, 63, 617–623.
Acknowledgements
GDS sincerely thanks University Grant Commission, New Delhi, for financial assistance (Grant No. F1-17.1/2015-16/RGNF-2015-17-SC-UTT-13500).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rana, S.V.S., Verma, Y. & Singh, G.D. Assessment of genotoxicity amongst smokers, alcoholics, and tobacco chewers of North India using micronucleus assay and urinary 8-hydroxyl−2′-deoxyguanosine, as biomarkers. Environ Monit Assess 189, 391 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6103-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-017-6103-3