Abstract
Background and Aim
Previous studies evaluating the safety of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) undergoing hemodialysis reported an increased risk of post-procedural bleeding. We investigated the safety and efficacy of ERCP for the treatment of choledocholithiasis in patients with ESRD undergoing long-term dialysis.
Methods
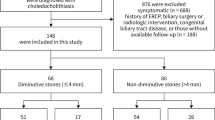
A total of 3466 patients who underwent ERCP due to choledocholithiasis between January 2000 and Feb 2018 were reviewed and analyzed retrospectively. Patients were divided into dialysis and non-dialysis group, and propensity score matching was used to minimize selection bias.
Results
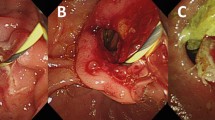
Patients of dialysis group (n = 39) and non-dialysis group (n = 78) were compared after propensity score matching. Among 39 patients of dialysis group, hemodialysis was used in 28 (71.8%) patients for renal replacement therapy, while 11 (28.2%) patients received peritoneal dialysis. The median duration of dialysis was 8 years (range 1–24 years). Overall success rate of ERCP was not different between two groups. The overall prevalence of post-procedural complications in dialysis group and non-dialysis group was 28.2 and 15.4%, respectively (p = 0.100). Post-procedural bleeding occurred more frequently in dialysis group than non-dialysis group (23.1 vs 5.1%, p = 0.004). All procedure-related bleeding episodes were successfully controlled using endoscopic management. Prevalence of post-ERCP pancreatitis, infection, and perforation were not significantly different between two groups (p > 0.05).
Conclusions
Overall success rate of complete ductal clearance was not different between dialysis and non-dialysis groups. The risk of post-procedural bleeding seems to be increased in patients with ESRD undergoing long-term dialysis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Everhart JE, Khare M, Hill M, Maurer KR. Prevalence and ethnic differences in gallbladder disease in the United States. Gastroenterology. 1999;117:632–639.
Houdart R, Perniceni T, Darne B, Salmeron M, Simon JF. Predicting common bile duct lithiasis: determination and prospective validation of a model predicting low risk. Am J Surg. 1995;170:38–43.
Jin DC, Han JS. Renal replacement therapy in Korea, 2012. Kidney Res Clin Pract. 2014;33:9–18.
Kazama JJ, Kazama S, Koda R, Yamamoto S, Narita I, Gejyo F. The risk of gallbladder stone formation is increased in patients with predialysis chronic kidney disease but not those undergoing chronic hemodialysis therapy. Nephron Clin Pract. 2009;111:c167–c172.
Genctoy G, Ayidaga S, Ergun T, Lakadamyali H, Erbayrak M, Sezer S. Increased frequency of gallbladder stone and related parameters in hemodialysis patients. Turk J Gastroenterol. 2014;25:54–58.
Frossard JL, Morel PM. Detection and management of bile duct stones. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010;72:808–816.
Andriulli A, Loperfido S, Napolitano G, et al. Incidence rates of post-ERCP complications: a systematic survey of prospective studies. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102:1781–1788.
Hori Y, Naitoh I, Nakazawa T, et al. Feasibility of endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography-related procedures in hemodialysis patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;29:648–652.
Nelson DB, Freeman ML. Major hemorrhage from endoscopic sphincterotomy: risk factor analysis. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1994;19:283–287.
Williams EJ, Taylor S, Fairclough P, et al. Risk factors for complication following ERCP; results of a large-scale, prospective multicenter study. Endoscopy. 2007;39:793–801.
Wang P, Li ZS, Liu F, et al. Risk factors for ERCP-related complications: a prospective multicenter study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2009;104:31–40.
Escolar G, Diaz-Ricart M, Cases A. Uremic platelet dysfunction: past and present. Curr Hematol Rep. 2005;4:359–367.
Skorecki K, Chertow GM, Marsden PA, et al. Brenner and Rector’s The Kidney E-Book. New York: Elsevier; 2011.
Takahara N, Isayama H, Sasaki T, et al. Endoscopic papillary balloon dilation for bile duct stones in patients on hemodialysis. J Gastroenterol. 2012;47:918–923.
Baron TH, Harewood GC. Endoscopic balloon dilation of the biliary sphincter compared to endoscopic biliary sphincterotomy for removal of common bile duct stones during ERCP: a metaanalysis of randomized, controlled trials. Am J Gastroenterol. 2004;99:1455–1460.
Kaneva K, Bansal V, Hoppensteadt D, Cunanan J, Fareed J. Variations in the circulating heparin levels during maintenance hemodialysis in patients with end-stage renal disease. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2013;19:449–452.
Vandervoort J, Soetikno RM, Tham TC, et al. Risk factors for complications after performance of ERCP. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002;56:652–656.
Rutsky EA, Robards M, Van Dyke JA, Rostand SG. Acute pancreatitis in patients with end-stage renal disease without transplantation. Arch Intern Med. 1986;146:1741–1745.
Araki T, Ueda M, Ogawa K, Tsuji T. Histological pancreatitis in end-stage renal disease. Int J Pancreatol. 1992;12:263–269.
Minnaganti VR, Cunha BA. Infections associated with uremia and dialysis. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2001;15:385–406.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no potential conflict of interest to declare.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S.B., Kim, K.H. & Kim, T.N. Safety and Efficacy of Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography for Choledocholithiasis in Long-Term Dialysis: A Propensity Score Analysis. Dig Dis Sci 63, 3141–3146 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-018-5112-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-018-5112-6