Abstract
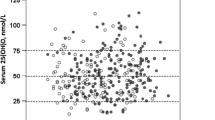
The majority of patients with dermatitis herpetiformis (DH) have small intestinal enteropathy that may result in bone loss. The objective of this study was to evaluate bone mineral density (BMD) in DH and to examine whether dietary treatment or degree of the small intestinal lesion correlate with BMD. Twenty-five patients with DH (18 men) were investigated. Detailed dietary assessment and duodenal biopsies were performed on all patients before entry into the study. BMD at lumbar spine and femur was determined by DXA scan. Bone biomarkers, vitamin D, and parathyroid status were assessed. Twenty patients had enteropathy. None of the patients had hypovitaminosis D or secondary hyperparathyroidism. Resorption and formation markers were within normal limits. BMD Z-scores were not significantly different from expected (−0.38; CI, −0.84 to 0.07) and femur (0.46; CI, −0.06 to 0.97). There was no relationship between BMD Z-scores and the severity of the degree of enteropathy. We conclude that enteropathy of differing severity is present in 80% of patients with DH, but this is not associated with bone disease.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fry L (1995) Dermatitis herpetiformis. Baillieres Clin Gastroenterol 9:371–393
Katz SI (1993) Dermatitis herpetiformis. In: Fitzpatrick TB, Eisen AZ, Wolff K, Freedberg IM, Austen KF (eds) Dermatology in general medicine, 4th ed. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 636–641
Egan CA, O’Loughlin S, Gormally S, Powell FC (1997) Dermatitis herpetiformis: a review of fifty-four patients. Ir J Med Sci 166:241–244
Gawkrodger DJ, McDonald C, O’Mahony S, Ferguson A (1991) Small intestinal function and dietary status in dermatitis herpetiformis. Gut 32:377–382
Scott BB, Young S, Rajah SM, Marks J, Losowsky MS (1976) Coeliac disease and dermatitis herpetiformis: further studies of their relationship. Gut 17:759–762
Garioch JJ, Lewis HM, Sargent SA, Leonard JN, Fry L (1994) 25 years experience of a gluten-free diet in the treatment of dermatitis herpetiformis. Br J Dermatol 131:541–545
Fry L, Riches D, Seah P, Hoffbrand A (1973) Clearance of skin lesions in dermatitis after gluten withdrawal. Lancet 1:288–291
Collin P, Pukkala E, Reunala T (1996) Malignancy and survival in dermatitis herpetiformis: a comparison with coeliac disease. Gut 38:528–530
Leonard JN, Tucker WF, Fry JS, Coulter CA, Boylston AW, McMinn RM, Haffenden GP, Swain AF, Fry L (1983) Increased incidence of malignancy in dermatitis herpetiformis. BMJ 286:16–18
Sigurgeirsson B, Agnarsson BA, Lindelof B (1994) Risk of lymphoma in patients with dermatitis herpetiformis. BMJ 308:13–15
Silk DB, Mowat NA, Riddell RH, Kirby JD (1977) Intestinal lymphoma complicating dermatitis herpetiformis. Br J Dermatol 96:555–560
Bose SK, Lacour JP, Bodokh I, Ortonne JP (1994) Malignant lymphoma and dermatitis herpetiformis. Dermatology 188:177–181
Lewis HM, Renaula TL, Garioch JJ, Leonard JN, Fry JS, Collin P, Evans D, Fry L (1996) Protective effect of gluten-free diet against development of lymphoma in dermatitis herpetiformis. Br J Dermatol 135:363–367
Sategna-Guidetti C, Grosso SB, Grosso S, Mengozzi G, Aimo G, Zaccaria T, Di Stefano M, Isaia GC (2000) The effects of 1-year gluten withdrawal on bone mass, bone metabolism and nutritional status in newly-diagnosed adult coeliac disease patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 14:35–43
Walters JRF, Banks LM, Butcher GP, Fowler CR (1995) Detection of low bone mineral density by dual energy x ray absorptiometry in unsuspected suboptimally treated celiac disease. Gut 37:220–224
Keaveny AP, Freaney R, McKenna MJ, Masterson J, O’Donoghue DP (1996) Bone remodelling indices and secondary hyperparathyroidism in celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol 91:1226–1231
Mustalahti K, Collin P, Sievanen H, Salmi J, Maki M (1999) Osteopenia in patients with clinically silent celiac disease warrants screening. Lancet 354:744–745
Valdimarsson T, Toss G, Ross I, Lofman O, Strom M (1994) Bone mineral density in celiac disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 29:457–461
De Boer WA, Tytgat GN (1992) A patient with osteomalacia as a single presenting symptom of gluten sensitive enteropathy. Arch Intern Med 232:81–85
Hajjar ET, Vincenti F, Salti CS (1979) Gluten induced enteropathy: osteomalacia as a principle manifestation. Arch Intern Med 131:565–566
Keaveny AP, Freaney R, McKenna MJ, O’Donoghue DP (1998) Coeliac bone disease: new strategies in management. Ir Med J 91:118–120
Marsh MN, Crowe PT (1995) Morphology of the mucosal lesion in gluten sensitivity. Baillieres Clin Gastroenterol 9:273–293
Looker AC, Wahner HW, Dunn WL, Calvo MS, Harris TB, Heyse SP, Johnston CC Jr, Lindsay R (1998) Updated data on proximal femur bone mineral levels of US adults. Osteoporosis Int 8:468–489
Lewiecki EM, Watts NB, McClung MR, Petak SM, Bachrach LK, Shepherd JA, Downs RW Jr, International Society for Clinical Densitometry (2004) Official positions of the International Society for Clinical Densitometry. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:3651–3655
Freaney R, Mc Brinn Y, McKenna MJ (1993) Secondary hyperparathyroidism in elderly people: combined effect of renal impairment and vitamin D deficiency. Am J Clin Nutr 58:187–191
McKenna MJ, Freaney R (1998) Secondary hyperparathyroidisrn in the elderly: means to defining hypovitaminosis D. Osteoporosis Int 8:S3–S6
Mazure R, Vazquez H, Gonzalez D, Mautalen C, Pedreira S, Boerr L, Bai JC (1994) Bone mineral affection in asymptomatic adult patients with celiac disease. Am J Gastroenterol 89:2130–2134
Di Stefano M, Jorizzo RA, Veneto G, Cecchetti L, Gasbarrini G, Corazza GR (1999) Bone mass and metabolism in dermatitis herpetiformis. Dig Dis Sci 44:2139–2143
McFarlane XA, Bhalla AK, Robertson DAF (1996) Effect of gluten free diet on osteopenia in adults with newly diagnosed coeliac disease. Gut 39:180–184
Valdimarsson T, Lofman O, Toss G, et al. (1996) Reversal of osteopenia with diet in adult coeliac disease. Gut 38:322–327
Mautalen C, Gonzalez D, Mazure R, Vazquez H, Lorenzetti MP, Maurino E, Niveloni S, Pedreira S, Smecuol E, Boerr LA, Bai JC (1997) Effect of treatment on bone mass, mineral metabolism, and body composition in untreated celiac disease patients. Am J Gastroenterol 92:313–318
Ciacci C, Maurelli L, Klain M, Savino G, Salvatore M, Mazzacca G, Cirillo M (1997) Effects of dietary treatment on bone mineral density in adults with celiac disease: factors predicting response. Am J Gastroenterol 92:992–996
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abuzakouk, M., Barnes, L., O’Gorman, N. et al. Dermatitis Herpetiformis: No Evidence of Bone Disease Despite Evidence of Enteropathy. Dig Dis Sci 52, 659–664 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9576-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-006-9576-4