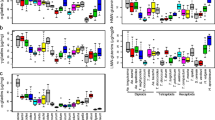
Abstract
Ubiquitous nature of prolamin proteins dubbed gluten from wheat and allied cereals imposes a major challenge in the treatment of celiac disease, an autoimmune disorder with no known treatment other than abstinence diet. Administration of hydrolytic glutenases as food supplement is an alternative to deliver the therapeutic agents directly to the small intestine, where sensitization of immune system and downstream reactions take place. The aim of the present research was to evaluate the capacity of wheat grain to express and store hydrolytic enzymes capable of gluten detoxification. For this purpose, wheat scutellar calli were biolistically transformed to generate plants expressing a combination of glutenase genes for prolamin detoxification. Digestion of prolamins with barley endoprotease B2 (EP-HvB2) combined with Flavobacterium meningosepticum prolyl endopeptidase (PE-FmPep) or Pyrococcus furiosus prolyl endopeptidase (PE-PfuPep) significantly reduced (up to 67%) the amount of the indigestible gluten peptides of all prolamin families tested. Seven of the 168 generated lines showed inheritance of transgene to the T2 generation. Reversed phase high-performance liquid chromatography of gluten extracts under simulated gastrointestinal conditions allowed the identification of five T2 lines that contained significantly reduced amounts of immunogenic, celiac disease-provoking gliadin peptides. These findings were complemented by the R5 ELISA test results where up to 72% reduction was observed in the content of immunogenic peptides. The developed wheat genotypes open new horizons for treating celiac disease by an intraluminal enzyme therapy without compromising their agronomical performance.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alaedini A, Green PH (2005) Narrative review: celiac disease: understanding a complex autoimmune disorder. Ann Intern Med 142:289–298
Altenbach SB, Allen PV (2011) Transformation of the US bread wheat ‘Butte 86’ and silencing of omega-5 gliadin genes. GM Crops 2:66–73
Arranz-Otaegui A, Gonzalez Carretero L, Ramsey MN, Fuller DQ, Richter T (2018) Archaeobotanical evidence reveals the origins of bread 14,400 years ago in northeastern Jordan. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115:7925–7930
Barro F, Iehisa JC, Giménez MJ, García-Molina MD, Ozuna CV, Comino I, Sousa C, Gil-Humanes J (2016) Targeting of prolamins by RNAi in bread wheat: effectiveness of seven silencing-fragment combinations for obtaining lines devoid of coeliac disease epitopes from highly immunogenic gliadins. Plant Biotechnol J 14:986–996
Bethune MT, Khosla C (2012) Oral enzyme therapy for celiac sprue. Methods Enzymol 502:241–271
Bethune MT, Strop P, Tang Y, Sollid LM, Khosla C (2006) Heterologous expression, purification, refolding, and structural-functional characterization of EP-B2, a self-activating barley cysteine endoprotease. Chem Biol 13:637–647
Botterman J, Gosselé V, Thoen C, Lauwereys M (1991) Characterization of phosphinothricin acetyltransferase and C-terminal enzymatically active fusion proteins. Gene 102:33–37
Cambra I, Hernández D, Diaz I, Martinez M (2012) Structural basis for specificity of propeptide-enzyme interaction in barley C1A cysteine peptidases. PLoS One 7:e37234
Cameron-Mills V, Ingversen J (1978) In vitro synthesis and transport of barley endosperm proteins: reconstitution of functional rough microsomes from polyribosomes and stripped microsomes. Carlsb Res Commun 43:471–489
Cappetta M, Roth I, Díaz A, Tort J, Roche L (2002) Role of the prosegment of Fasciola hepatica cathepsin L1 in folding of the catalytic domain. Biol Chem 383:1215–1221
Cheng M, Fry J, Pang S, Zhou H, Hironaka C, Duncan D et al (1997) Genetic transformation of wheat mediated by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Physiol 115:971–980
Comino I, Real A, Vivas S, Síglez MÁ, Caminero A, Nistal E, Casqueiro J, Rodríguez-Herrera A, Cebolla A, Sousa C (2012) Monitoring of gluten-free diet compliance in celiac patients by assessment of gliadin 33-mer equivalent epitopes in feces. Am J Clin Nutr 95:670–677
Davy A, Sorensen MB, Svendsen I, Cameron-Mills V, Simpson DJ (2000) Prediction of protein cleavage sites by the barley cysteine endoproteases EP-A and EP-B based on the kinetics of synthetic peptide hydrolysis. Plant Physiol 122:137–145
Desai P, Shrivastava N, Padh H (2010) Production of heterologous proteins in plants: strategies for optimal expression. Biotechnol Adv 28:427–435
Dominguez F, Cejudo FJ (1999) Patterns of starchy endosperm acidification and protease gene expression in wheat grains following germination. Plant Physiol 119:81–88
Fasano A (2009) Surprises from celiac disease. Sci Am 301:54–61
Fleckenstein B, Molberg O, Qiao SW, Schmid DG, von der Mulbe F, Elgstoen K, Jung G, Sollid LM (2002) Gliadin T cell epitope selection by tissue transglutaminase in celiac disease. Role of enzyme specificity and pH influence on the transamidation versus deamidation process. J Biol Chem 277:34109–34116
Gao L, Ma W, Chen J, Wang K, Li J, Wang S, Bekes F, Appels R, Yan Y (2010) Characterization and comparative analysis of wheat high molecular weight glutenin subunits by SDS-PAGE, RP-HPLC, HPCE, and MALDI-TOF-MS. J Agr Food Chem 58:2777–2786
Gass J, Khosla C (2007) Prolyl endopeptidases. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:345–355
Gass J, Ehren J, Strohmeier G, Isaacs I, Khosla C (2005) Fermentation, purification, formulation, and pharmacological evaluation of a prolyl endopeptidase from Myxococcus xanthus: implications for Celiac Sprue therapy. Biotechnol Bioeng 92:674–684
Gass J, Vora H, Bethune MT, Gray GM, Khosla C (2006) Effect of barley endoprotease EP-B2 on gluten digestion in the intact rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 318:1178–1186
Gilissen LJWJ, van der Meer IM, Smulders MJM (2014) Reducing the incidence of allergy and intolerance to cereals. J Cereal Sci 59:337–353
Gordon-Kamm WJ, Spencer TM, Mangano ML, Adams TR, Daines RJ, Start WG, O'Brien JV, Chambers SA, Adams WR Jr, Willetts NG, Rice TB, Mackey CJ, Krueger RW, Kausch AP, Lemaux PG (1990) Transformation of maize cells and regeneration of fertile transgenic plants. Plant Cell 2:603–618
Gorokhovets NV, Makarov VA, Petushkova AI, Prokopets OS, Rubtsov MA, Savvateeva LV, Zernii EY, Zamyatnin AA (2017) Rational design of recombinant papain-like cysteine protease: optimal domain structure and expression conditions for wheat-derived enzyme triticain-α. Int J Mol Sci 18:1395
Gujral N, Freeman HJ, Thomson AB (2012) Celiac disease: prevalence, diagnosis, pathogenesis and treatment. World J Gastroenterol 18:6036–6059
Hamamatsu N, Aita T, Nomiya Y, Uchiyama H, Nakajima M, Husimi Y, Shibanaka Y (2005) Biased mutation-assembling: an efficient method for rapid directed evolution through simultaneous mutation accumulation. Protein Eng Des Sel 18:265–271
Harris MN, Madura JD, Ming LJ, Harwood VJ (2001) Kinetic and mechanistic studies of prolyl oligopeptidase from the hyperthermophile Pyrococcus furiosus. J Biol Chem 276:19310–19317
Hartmann G, Koehler P, Wieser H (2006) Rapid degradation of gliadin peptides toxic for coeliac disease patients by proteases from germinating cereals. J Cereal Sci 44:368–371
Juhász A, Belova T, Florides CG, Maulis C, Fischer I, Gell G, Birinyi Z, Ong J, Keeble-Gagnère G, Maharajan A, Ma W, Gibson P, Jia J, Lang D, Mayer KFX, Spannagl M, International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium, Tye-Din JA, Appels R, Olsen O-A (2018) Genome mapping of seed-borne allergens and immunoresponsive proteins in wheat. Sci Adv 4:eaar8602
Kaukinen K, Lindfors K (2015) Novel treatments for celiac disease: glutenases and beyond. Dig Dis 33:277–281
Keil B (1992) Specificity of proteolysis. Springer-Verlag, Berlin-Heidelberg-NewYork
Kim S (2011) Production of composites by using gliadin as a bonding material. J Cereal Sci 54:168–172
König J, Holster S, Bruins MJ, Brummer RJ (2017) Randomized clinical trial: effective gluten degradation by Aspergillus niger-derived enzyme in a complex meal setting. Sci Rep 7:13100
Kumlehn J, Hensel G (2009) Genetic transformation technology in the Triticeae. Breed Sci 59:553–560
Lähdeaho ML, Kaukinen K, Laurila K, Vuotikka P, Koivurova OP, Kärjä-Lahdensuu T et al (2012) The Glutenase ALV003 attenuates gluten-induced mucosal injury in patients with celiac disease. Gastroenterology 146:1649–1658
Large EC (1954) Growth stages in cereals illustration of the Feekes scale. Plant Path 3:128–129
Leenhardt F, Levrat-Verny MA, Chanliaud E, Rémésy C (2005) Moderate decrease of pH by sourdough fermentation is sufficient to reduce phytate content of whole wheat flour through endogenous phytase activity. J Agric Food Chem 53:98–102
Loc N, Tinjuangjun P, Gatehouse A, Christou P, Gatehouse J (2002) Linear transgene constructs lacking vector backbone sequences generate transgenic rice plants which accumulate higher levels of proteins conferring insect resistance. Mol Breed 9:231–244
Løvik A, Skodje G, Bratlie J, Brottveit M, Lundin K (2017) Diet adherence and gluten exposure in coeliac disease and self-reported non-coeliac gluten sensitivity. Clin Nutr 36:275–280
Matysiak-Budnik T, Candalh C, Cellier C, Dugave C, Namane A, Vidal-Martinez T et al (2005) Limited efficiency of prolyl-endopeptidase in the detoxification of gliadin peptides in celiac disease. Gastroenterology 129:786–796
Mejías JH, Lu X, Osorio C, Ullman JL, von Wettstein D, Rustgi S (2014) Analysis of wheat prolamins, the causative agents of celiac sprue, using reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography (RP-HPLC) and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS). Nutrients 6:1578–1597
Mitea C, Havenaar R, Drijfhout JW, Edens L, Dekking L, Koning F (2007) Efficient degradation of gluten by a prolyl endoprotease in a gastrointestinal model: implications for coeliac disease. Gut 57:1–2
Molberg O, McAdam SN, Korner R, Quarsten H, Kristiansen C, Madsen L, Fugger L, Scott H, Norén O, Roepstorff P, Lundin KE, Sjöström H, Sollid LM (1998) Tissue transglutaminase selectively modifies gliadin peptides that are recognized by gut-derived T cells in celiac disease. Nat Med 4:713–717
Okubara P, Blechl A, McCormick S, Alexander N, Dill-Macky R, Hohn T (2002) Engineering deoxynivalenol metabolism in wheat through the expression of a fungal trichothecene acetyltransferase gene. Theor Appl Genet 106:74–83
Osorio C, Wen N, Gemini R, Zemetra R, von Wettstein D, Rustgi S (2012) Targeted modification of wheat grain protein to reduce the content of celiac causing epitopes. Funct Integr Genomics 12:417–438
Quarsten H, McAdam SN, Jensen T, Arentz-Hansen H, Molberg O, Lundin KEA, Sollid LM (2001) Staining of celiac disease-relevant T cells by peptide-DQ2 multimers. J Immunol 167:4861–4868
Rasheed A, Xia X, Yan Y, Appels R, Mahmood T, He Z (2014) Wheat seed storage proteins: advances in molecular genetics, diversity and breeding applications. J Cereal Sci 60:11–24
Rey M, Yang M, Lee L, Zhang Y, Sheff JG, Sensen CW, Mrazek H, Halada P, Man P, McCarville JL, Verdu EF, Schriemer DC (2016) Addressing proteolytic efficiency in enzymatic degradation therapy for celiac disease. Sci Rep 6:30980
Ribeiro M, Nunes FM, Rodriguez-Quijano M, Carrillo JM, Branlard G, Igrejas G (2018) Next-generation therapies for celiac disease: the gluten-targeted approaches. Trends Food Sci Tecnol 75:56–71
Rood J (2017) Pouring a pitcher of celiac relief. The Scientist 31:20–22
Rosell CM, Barro F, Sousa C, Mena MC (2014) Cereals for developing gluten-free products and analytical tools for gluten detection. J Cereal Sci 59:354–364
Rustgi S, Wen N, Osorio C, Brew-Appiah RAT, Wen S, Gemini R, Mejias JH, Ankrah N, Moehs CP, von Wettstein D (2014) Natural dietary therapies for the ‘gluten syndrome’. Scientia Danica, Series B, Biologica 3:1–87
Saberianfar R, Menassa R (2017) Protein bodies: how the ER deals with high accumulation of recombinant proteins. Plant Biotechnol J 15:671–673
Salden B, Monserrat V, Troost F, Bruins M, Edens L, Bartholomé R, Haenen GR, Winkens B, Koning F, Masclee AA (2015) Randomised clinical study: Aspergillus niger-derived enzyme digests gluten in the stomach of healthy volunteers. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 42:273–285
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, USA
Sánchez-León S, Gil-Humanes J, Ozuna CV, Giménez MJ, Sousa C, Voytas DF, Barro F (2018) Low-gluten, nontransgenic wheat engineered with CRISPR/Cas9. Plant Biotechnol J 16:902–910
Savvateeva LV, Gorokhovets NV, Makarov VA, Serebryakova MV, Solovyev AG, Morozov SY, Reddy VP, Zernii EY, Zamyatnin AA, Aliev G (2015) Glutenase and collagenase activities of wheat cysteine protease Triticain-α: feasibility for enzymatic therapy assays. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 62:115–124
Scherf KA, Wieser H, Koehler P (2018) Novel approaches for enzymatic gluten degradation to create high-quality gluten-free products. Food Res Int 110:62–72
Schilling K, Körner A, Sehmisch S, Kreusch A, Kleint R, Benedix Y, Schlabrakowski A, Wiederanders B (2009) Selectivity of propeptide-enzyme interaction in cathepsin L-like cysteine proteases. Biol Chem 390:167–174
Shan L, Molberg Ø, Parrot I, Hausch F, Filiz F, Gray GM, Sollid LM, Khosla C (2002) Structural basis for gluten intolerance in celiac sprue. Science 297:2275–2279
Shan L, Martin T, Sollid LM, Gray GM, Khosla C (2004) Comparative biochemical analysis of three bacterial prolyl endopeptidases: implications for coeliac sprue. Biochem J 383:311–318
Shewry PR, Tatham AS (2016) Improving wheat to remove coeliac epitopes but retain functionality. J Cereal Sci 67:12–21
Siegel M, Garber ME, Spencer AG, Botwick W, Kumar P, Williams RN, Kozuka K, Shreeniwas R, Pratha V, Adelman DC (2012) Safety, tolerability, and activity of ALV003: results from two phase 1 single, escalating-dose clinical trials. Dig Dis Sci 57:440–450
Siegel M, Bethune MT, Gass J, Ehren J, Xia J, Johannsen A, Stuge TB, Gray GM, Lee PP, Khosla C (2006) Rational design of combination enzyme therapy for celiac sprue. Chem Biol 13:649–658
Sollid LM, Khosla C (2011) Novel therapies for coeliac disease. J Intern Med 269:604–613
Spaenij-Dekking L, Kooy-Winkelaar Y, van Veelen P, Drijfhout JW, Jonker H, van Soest L, Smulders MJ, Bosch D, Gilissen LJ, Koning F (2005) Natural variation in toxicity of wheat: potential for selection of nontoxic varieties for celiac disease patients. Gastroenterology 129:797–806
Stern M, Ciclitira PJ, van Eckert R, Feighery C, Janssen FW, Mendez E, Mothes T, Troncone R, Wieser H (2001) Analysis and clinical effects of gluten in coeliac disease. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 13:741–747
Szeltner Z, Polgar L (2008) Structure, function and biological relevance of prolyl oligopeptidase. Curr Prot Peptide Sci 9:96–107
Tack GJ, Van de Water JM, Bruins MJ, Kooy-Winkelaar EM, van Bergen J, Bonnet P, Vreugdenhil AC, Korponay-Szabo I, Edens L, von Blomberg BM, Schreurs MW, Mulder CJ, Koning F (2013) Consumption of gluten with gluten-degrading enzyme by celiac patients: a pilot-study. World J Gastroenterol 19:5837
Thompson L, Slife FW, Butler HS (1970) Environmental influence on the tolerance of corn to Atrazine. Weed Sci 18:509–514
Tye-Din JA, Anderson RP, Ffrench RA, Brown GJ, Hodsman P, Siegel M, Botwick W, Shreeniwas R (2010) The effects of ALV003 pre-digestion of gluten on immune response and symptoms in celiac disease in vivo. Clin Immunol 134:289–295
Venalainen JI, Juvonen RO, Mannisto PT (2004) Evolutionary relationships of the prolyl oligopeptidase family enzymes. Eur J Biochem 271:2705–2715
Verdu EF, Caminero A (2017) How infection can incite sensitivity to food. Science 356:29–30
Wang G-P, Yu X-D, Sun Y-W, Jones HD, Xia L-Q (2016) Generation of marker-and/or backbone-free transgenic wheat plants via Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Front Plant Sci 7:1–16
Wen S, Wen N, Pang J, Langen G, Brew-Appiah RA, Mejias JH, Osorio C, Yang M, Gemini R, Moehs CP, Zemetra RS, Kogel KH, Liu B, Wang X, von Wettstein D, Rustgi S (2012) Structural genes of wheat and barley 5-methylcytosine DNA glycosylases and their potential applications for human health. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:20543–20548
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Ellison Mackenzie and Rhoda Brew-Appiah for laboratory assistance, Richa Gemini for the bioinformatics support, Pat Reisenauer for greenhouse assistance, Robert Zemetra for help with the wheat genetic transformation, and the two anonymous reviewers whose comments helped us in improving the manuscript.
Funding
This work received financial support by NIH grants 1R01 GM080749-01A2, and Clemson Faculty Succeeds grant 15-202-EQUIP-5701-430-1502211.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
S. Rustgi, D.v.W., S. Reinbothe, and B.L. designed the research; C.E.O., N.W., J.H.M., and S. Rustgi performed the research; C.E.O., N.W., J.H.M., D.v.W., and S. Rustgi analyzed the data; and S. Rustgi, C.E.O., B.L. and S. Reinbothe wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 4.30 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Osorio, C.E., Wen, N., Mejias, J.H. et al. Development of wheat genotypes expressing a glutamine-specific endoprotease from barley and a prolyl endopeptidase from Flavobacterium meningosepticum or Pyrococcus furiosus as a potential remedy to celiac disease. Funct Integr Genomics 19, 123–136 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-018-0632-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-018-0632-x