Abstract
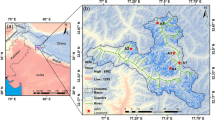
Annual thawing/freezing indices (TIs and FIs) for ten meteorological stations in the China Tianshan Mountains (CTM) are analyzed based on the daily maximum and minimum temperature records during 1961–2010. These indices are submitted for trend analysis and change-point analysis. The correlations between the TIs and FIs and the annual mass balance (AMB) for the No. 1 glacier, a rapid regressing small-scale glacier with the solely longest observed time series of the AMB at the headwater of the Urumqi River in the CTM, were analyzed in order to demonstrate the implication behind variations in the TIs and FIs. Furthermore, to explain atmospheric controls of the TI and FI variations, correlations between large-scale climatic forcing, e.g., the mean NAO indices and the mean Arctic Oscillation (AO) and the TIs and the FIs were analyzed. The results show that there were obvious upward trends in the TIs and downward trends in the FIs occurred, which demonstrates an increasing thawing and decreasing freezing potential in the CTM during the period of 1961–2010. Change-point analysis revealed evident change point around the year 1997 for the TIs at most of the stations, while various change points for the FIs. Obvious negative relationships between the TIs and the AMB for the No. 1 glacier have been found. Also, significant change point around the year 1996/1997 has been detected for the AMB time series. The revealed tight links between the TIs and the AMB, and also temporal consistency of change points indicates that changes in the TIs could be one of the main factors resulted in changes in the AMB of No. 1 glacier. Furthermore, significant negative correlation between the TIs and FIs and the mean summer NAO index for most stations are also found, demonstrating that the variations in TIs and FIs in the CTM were possibly related with changes in NAO.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aizen VB, Aizen EM, Melack JM, Dozier J (1997) Climatic and Hydrologic Changes in the Tien Shan, Central Asia. J Clim 10:1393–1404
Aizen VB, Kuzmichenok VA, Surazakov AB, Aizen EM (2007) Glacier changes in the Tien Shan as determined from topographic and remotely sensed data. Glob Planet Change 56:328–340
Beniston M (1997) Variations of snow depth and duration in the Swiss Alps over the last 50 years: link to changes in the large-scale climatic forcings. Clim Change 36:281–300
Beniston M (2003) Climatic change in mountain regions: a review of possible impacts. Clim Change 59:5–31
Bolch T (2007) Climate change and glacier retreat in northern Tien Shan (Kazakhstan/Kyrgyzstan) using remote sensing data. Glob Planet Change 56(1–2):1–12
Chen R, Kang E, Ji X, Yang J, Yang Y (2006) Cold regions in China. Cold Reg Sci Technol 45:95–102
Cheng G, Jiang H, Wang K (2003) Thawing index and freezing index on the embankment surface in permafrost regions. J Glaciol Geocryol 25(6):603–607 (in Chinese)
Croitoru A, Drignei D, Holobaca I, Dragota C (2012) Change-point analysis for serially correlated summit temperatures in the Romanian Carpathians. Theor Appl Climatol 108:9–18. doi:10.1007/s00704-011-0508-7
del Rio S, Iqbal M, Cano-ortiz A, Herrero L, Hassan A, Penas A (2012) Recent mean temperature trends in Pakistan and links with teleconnection patterns. Int J Climatol. doi:10.1002/joc.3423
Easterling D, Horton B, Jones P, Peterson T, Karl T, Parker D, Salinger M, Razuvayev V, Plumer N, Jamason P, Foland C (1997) Maximum and minimum temperature trends for the globe. Science 277:364–367
Feng S, Hu Q, Qian W (2004) Quality control of daily meteorological data in China, 1951–2000: a new dataset. Int J Climatol 24:853–870. doi:10.1002/joc.1047
Fischer T, Gemmer M, Liu L, Su B (2011) Change-points in climate extremes in the Zhujiang River Basin, South China, 1961–2007. Clim Change. doi:10.1007/s10584-011-0123-8
Frauenfeld OW, Zhang T, Mccreight JL (2007) Northern hemisphere freezing/thawing index variations over the twentieth century. Int J Climatol 27:47–63
Gao R, Wei Z, Dong W (2003) Interannual variation of the beginning date and the ending date of soil freezing in the Tibetan plateau. J Glaciol Geocryol 25(1):49–54 (in Chinese)
Gong D, Wang S, Zhu J (2004) Arctic oscillation influence on daily temperature variance in winter over China. Chin Sci Bull 49(6):637–642
Han T, Ding Y, Ye B, Liu S, Jiao K (2006) Mass-balance characteristics of Urumqi glacier No. 1, Tien Shan, China. Ann Glaciol 43:323–327
Hatzaki M, Flocas H, Asimakopoulos D, Maheras P (2007) The eastern Mediterranean teleconnection pattern: identification and definition. Int J Climatol 27(6):727–737
Hoelzle M, Chinn T, Stumm D, Paul F, Zemp M, Haeberli W (2007) The application of glacier inventory data for estimating past climate change effects on mountain glaciers: a comparison between the European Alps and the Southern Alps of New Zealand. Global Planet Change 56(1–2):69–82
Houghton J, Ding Y (eds) (2001) Climate Change 2000. The Scientific Basis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Hu R (ed) (2004) Physical geography of the Tianshan Mountain in China. China Environmental Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Hu R, Ma H, Fan Z, Yang Q, Wu S, Huang Y (2002a) Response of water resources to climate change in Xinjiang. J Nat Resour 17(1):22–26 (in Chinese)
Hu R, Jiang F, Wang Y (2002b) Signal and impact of climatic shift from warm-dry to warm-wet in Xinjiang. Arid land Geography 25(3):194–200 (in Chinese)
Hurrell J (1995) Decadal trends in the North-Atlantic Oscillation- regional temperatures and precipitation. Science 269(5224):676–679
Hurrell J, Van Loon H (1997) Decadal variations in climate association with the North Atlantic Oscillation. Clim Change 36(3):301–326
IPCC (2007) The fourth assessment report: climate change 2007. Cambridge University Press, New York
Jiang F, Zhu C, Mu G, Hu R, Meng Q (2005) Magnification of flood disasters and its relation to regional precipitation and local human activities since the 1980s in Xinjiang, Northwestern China. Nat Hazards 36(3):307–330
Jiang F, Hu R, Li Z (2008) Variations and trends of the freezing and thawing index along the Qinghai-Xizang Railway for 1966-2004. J Geog Sci 18:3–16
Jin H, Li S, Wang S (2000) Effects of climate change on permafrost and environment in cold region of China. Acta Geographica Sinica 55(2):161–173 (in Chinese)
Jing Z, Jiao K, Yao T, Wang N, Li Z (2006) Mass balance and recession of Urumqi glacier No. 1, Tien Shan, China, over the last 45 years, pp 214–217
King L, Herza T, Hartmanna H (2006) The PACE monitoring strategy: a concept for permafrost research in Qinghai-Tibet. Quat Int 154–155:149–157
Li Z, Jiang F (2007) A study of abrupt climate change in Xinjiang region during 1961-2004. J Glaciol Geocryol 29(3):351–359 (in Chinese)
Li Z, Yan Z (2009) Homogenized daily mean/maximum/minimum temperature series for China from 1960-2008. Atmos Ocean Sci Lett 2(4):1–7
Li J, Yu R, Zhou T (2008) Teleconnection between NAO and climate downstream of the Tibetan Plateau. J Clim 21:4680–4690
Liu X, Chen B (2000) Climatic warming in the Tibetan Plateau during recent decades. Int J Climatol 20:1729–1742
Liu S, Ding Y, Shangguan D, Zhang Y, Li J, Han H, Wang J, Xie C (2006) Glacier retreat as a result of climate warming and increased precipitation in the Tarim river basin, northwest China. Ann Glaciol 43:91–96
Marchenko SS, Gorbunov AP, Romanovsky VE (2007) Permafrost warming in the Tien Shan Mountains, Central Asia. Global Planet Change 56:311–327
Paul F, Kääb A, Haeberli W (2007) Recent glacier changes in the Alps observed by satellite: consequences for future monitoring strategies. Global Planet Change 56(1–2):111–122
Pu Z, Zhang S, Li J, Wang S (2008) Facts and features of climate change into warmth and damp in the Tianshan Mountains in recent 36 years. Arid Land Geography 31(3):409–415 (in Chinese)
She Y, Li Z, Zhang M, Wang S, Sun M (2012) Response of streamflow to climate change at the headwaters of Urumqi River in the Tianshan mountains over the recent 51 years. J Arid Land Resour Environ 26(12):113–118 (in Chinese)
Shi Y, Shen Y, Li D, Zhang G, Ding Y, Hu R, Kang E (2003) Discussion on the present climate change from warm-day to warm-wet in northwest China. Quat Sci 23:152–164 (in Chinese)
Sorg A, Bolch T, Stoffel M, Solomina O, Beniston M (2012) Climate change impacts on glaciers and runoff in Tien Shan (Central Asia). Nat Clim Change 2:725–731
Su B, Jiang T, Jin W (2006) Recent trends in observed temperature and precipitation extremes in the Yangtze River Basin, China. Theor Appl Climatol 83:139–151
Tao H, Gemmer M, Bai Y, Su B, Mao W (2011) Trends of stream flow in the Tarim River Basin during the past 50 years: human impact or climate change? J Hydrol 400:1–9
Taylor W (2000) Change-point analysis: a powerful new tool for detecting changes. http://www.variation.com/cpa/tech/changepoint.html
Turkes M, Erlat E (2008) Influence of the Arctic Oscillation on the variability of winter mean temperature in Turkey. Theor Appl Climatol 92:75–85
Walther GR, Post E, Convey P, Menzel A, Parmesan C, Beebee TJC, Fromentin JM, Hoegh-Guldberg O, Bairlein F (2002) Ecological responses to recent climate change. Nature 416:389–395
Wang S, Jin H, Li S (2000) Permafrost degradation on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and its environmental impacts. Permafrost Periglac Process 11:43–54
Wang G, Shen Y, Mao W (2005) Climate warming and its effects on glacier in recent 44 years in the head waters of Urumuqi River. J Glaciol Geocryol 27(6):813–819 (in Chinese)
Wanner H, Rickli R, Salvisberg E, Schmutz C, Schiiepp M (1997) Global climate change and variability and its influence on alpine climate-concepts and observations. Theor Appl Climatol 58:221–243
Wu Q, Liu Y (2004) Ground temperature monitoring and its recent change in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Cold Reg Sci Technol 38:85–92
Xie Z, Wang X, Feng Q (2006) Modeling the response of glaciers to climate warming in China. Ann Glaciol 43(1):313–316
Xu X, Pan B, Hu E, Li Y, Liang Y (2011) Responses of two branches of Glacier No. 1 to climate change from 1993 to 2005, Tianshan, China. Quat Int 236:143–150
Yang H, Li Z, Ye B, Jiao K, Jing Z, Zhao Z (2005) Study on mass balance and process of glacier no. 1 at the headwaters of the Urumqi River in the past 44 years. Arid Land Geography 28(1):76–80 (in Chinese)
Yuan Q, Wei W (2006) Annual climate change in Tianshan Mountains since recent 40 years. Arid Land Geography 23(1):115–118 (in Chinese)
Yuan Y, Wei W, Mu G (2004) Features of autumn climate change in Tianshan mountainous area for the recent 40 years and comparison with those in the southern and northern Xinjiang. Chin Geogr Sci 24(6):674–679
Zhang J, Shi Y (2002) Research for climate change and short-term forecast in Xinjiang. Meteorology Press, Beijing (in Chinese)
Zhang T, Osterkamp TE, Stamnes K (1997) Effects of climate on the active layer and permafrost on the north slope of Alaska, USA. Permafrost Periglac Process 8:45–67
Zhou Y (1999) The hydrology and water resources of rivers in Xinjiang. Xinjiang Science, Technology and Health Press, Urumqi (in Chinese)
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by the Knowledge Innovation Key Project of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant No.: KZCX2-YW-GJ04) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.41171378). The authors thank the editor, Prof. Dr. Wolfgang Cramer, and two anonymous reviewers for their valuable suggestions that helped to improve the quality of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editor: Wolfgang Cramer.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jiang, Fq., Jilili, Aw., Wang, Sp. et al. Annual thawing and freezing indices changes in the China Tianshan Mountains. Reg Environ Change 15, 227–240 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-014-0610-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10113-014-0610-3