Abstract
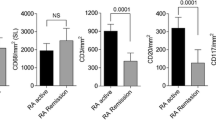
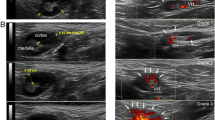
To develop quantitative imaging biomarkers of synovial tissue perfusion by pixel-based contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS), we studied the relationship between CEUS synovial vascular perfusion and the frequencies of pathogenic T helper (Th)-17 cells in psoriatic arthritis (PsA) joints. Eight consecutive patients with PsA were enrolled in this study. Gray scale CEUS evaluation was performed on the same joint immediately after joint aspiration, by automatic assessment perfusion data, using a new quantification approach of pixel-based analysis and the gamma-variate model. The set of perfusional parameters considered by the time intensity curve includes the maximum value (peak) of the signal intensity curve, the blood volume index or area under the curve, (BVI, AUC) and the contrast mean transit time (MTT). The direct ex vivo analysis of the frequencies of SF IL17A-F+CD161+IL23+ CD4+ T cells subsets were quantified by fluorescence-activated cell sorter (FACS). In cross-sectional analyses, when tested for multiple comparison setting, a false discovery rate at 10%, a common pattern of correlations between CEUS Peak, AUC (BVI) and MTT parameters with the IL17A-F+IL23+ - IL17A-F+CD161+ - and IL17A-F+CD161+IL23+ CD4+ T cells subsets, as well as lack of correlation between both peak and AUC values and both CD4+T and CD4+IL23+ T cells, was observed. The pixel-based CEUS assessment is a truly measure synovial inflammation, as a useful tool to develop quantitative imaging biomarker for monitoring target therapeutics in PsA.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gladman DD, Antoni C, Mease P, Clegg DO, Nash P (2005) Psoriatic arthritis: epidemiology, clinical features, course, and outcome. Ann Rheum Dis 64(Suppl 2):ii14–ii17
Scarpa R, Ayala F, Caporaso N, Olivieri I (2006) Psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, or psoriatic disease? J Rheumatol 33:210–212
Bowes J, Budu-Aggrey A, Huffmeier U, Uebe S, Steel K, Hebert HL, Wallace C, Massey J, Bruce IN, Bluett J, Feletar M, Morgan AW, Marzo-Ortega H, Donohoe G, Morris DW, Helliwell P, Ryan AW, Kane D, Warren RB, Korendowych E, Alenius GM, Giardina E, Packham J, McManus R, FitzGerald O, McHugh N, Brown MA, Ho P, Behrens F, Burkhardt H, Reis A, Barton A (2015) Dense genotyping of immune-related susceptibility loci reveals new insights into the genetics of psoriatic arthritis. Nat Commun 6:6046
Budu-Aggrey A, Bowes J, Loehr S, Uebe S, Zervou MI, Helliwell P, Ryan AW, Kane D, Korendowych E, Giardina E, Packham J, McManus R, FitzGerald O, McHugh N, Behrens F, Burkhardt H, Huffmeier U, Ho P, Martin J, Castañeda S, Goulielmos G, Reis A, Barton A (2016) Replication of a distinct psoriatic arthritis risk variant at the IL23R locus. Ann Rheum Dis 75:1417–1418
Kirkham BW, Kavanaugh A, Reich K (2014) Interleukin-17A: a unique pathway in immune-mediated diseases: psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Immunology 141:133–142
Fitzgerald O, Winchester R (2009) Psoriatic arthritis: from pathogenesis to therapy. Arthritis Res Ther 11:214
Tan WS, Kelly S, Pitzalis C (2016) Targeted therapies: what they teach us about the pathogenesis of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. doi:10.1080/1744666X.2017.1241710
van Kuijk AW, Reinders-Blankert P, Smeets TJ, Dijkmans BA, Tak PP (2006) Detailed analysis of the cell infiltrate and the expression of mediators of synovial inflammation and joint destruction in the synovium of patients with psoriatic arthritis: implications for treatment. Ann Rheum Dis 15(65):1551–1557
Fiocco U, Sfriso P, Oliviero F, Roux-Lombard P, Scagliori E, Cozzi L, Lunardi F, Calabrese F, Vezzù M, Dainese S, Molena B, Scanu A, Nardacchione R, Rubaltelli L, Dayer JM, Punzi L (2010) Synovial effusion and synovial fluid biomarkers in psoriatic arthritis to assess intraarticular tumor necrosis factor-α blockade in the knee joint. Arthritis Res Ther 12:R148
Leipe J, Grunke M, Dechant C, Reindl C, Kerzendorf U, Schulze-Koops H, Skapenko A (2010) Role of Th17 cells in human autoimmune arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 62:2876–2885
Celis R, Planell N, Fernández-Sueiro JL, Sanmartí R, Ramírez J, González-Álvaro I, Pablos JL, Cañete JD (2012) Synovial cytokine expression in psoriatic arthritis and associations with lymphoid neogenesis and clinical features. Arthritis Res Ther 14:R93
Raychaudhuri SP, Raychaudhuri SK, Genovese MC (2012) IL-17 receptor and its functional significance in psoriatic arthritis. Mol Cell Biochem 359:419–429
Jandus C, Bioley G, Rivals JP, Dudler J, Speiser D, Romero P (2008) Increased numbers of circulating polyfunctional Th17 memory cells in patients with seronegative spondylarthritides. Arthritis Rheum 58:2307–2317
Benham H, Norris P, Goodall J, Wechalekar MD, FitzGerald O, Szentpetery A, Smith M, Thomas R, Gaston H (2013) Th17 and Th22 cells in psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis. Arthritis Res Ther 15:R136
Fiocco U, Accordi B, Martini V, Oliviero F, Facco M, Cabrelle A, Piva L, Molena B, Caso F, Costa L, Scanu A, Pagnin E, Atteno M, Scarpa R, Basso G, Semenzato G, Punzi L, Doria A, Dayer JM (2014) JAK/STAT/PKCδ molecular pathways in synovial fluid T lymphocytes reflect the in vivo T helper-17 expansion in psoriatic arthritis. Immunol Res 58:61–69
Moran EM, Heydrich R, Ng CT, Saber TP, McCormick J, Sieper J, Appel H, Fearon U, Veale DJ (2011) IL-17A expression is localised to both mononuclear and polymorphonuclear synovial cell infiltrates. PLoS One 6:e24048
van Baarsen LG, Lebre MC, van der Coelen D, Aarrass S, Tang MW, Ramwadhdoebe TH, Gerlag DM, Tak PP (2014) Heterogeneous expression pattern of interleukin 17A (IL-17A), IL-17F and their receptors in synovium of rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis and osteoarthritis: possible explanation for nonresponse to anti-IL-17 therapy? Arthritis Res Ther 16:426
Dolcino M, Ottria A, Barbieri A, Patuzzo G, Tinazzi E, Argentino G, Beri R, Lunardi C, Puccetti A (2015) Gene expression profiling in peripheral blood cells and synovial membranes of patients with psoriatic arthritis. PLoS One 10:e0128262
Menon B, Gullick NJ, Walter GJ, Rajasekhar M, Garrood T, Evans HG, Taams LS, Kirkham BW (2014) Interleukin-17+CD8+ T cells are enriched in the joints of patients with psoriatic arthritis and correlate with disease activity and joint damage progression. Arthritis Rheumatol 66:1272–1281
Cosmi L, De Palma R, Santarlasci V, Maggi L, Capone M, Frosali F, Rodolico G, Querci V, Abbate G, Angeli R, Berrino L, Fambrini M, Caproni M, Tonelli F, Lazzeri E, Parronchi P, Liotta F, Maggi E, Romagnani S, Annunziato F (2008) Human interleukin 17-producing cells originate from a CD161+CD4+ T cell precursor. J Exp Med 205:1903–1916
Korn T, Bettelli E, Oukka M, Kuchroo VK (2009) IL-17 and Th17 cells. Annu Rev Immunol 27:485–517
Muranski P, Restifo NP (2013) Essentials of Th17 cell commitment and plasticity. Blood 121:2402–2414
Caso F, Del Puente A, Peluso R, Caso P, Girolimetto N, Del Puente A, Scarpa R, Costa L (2016) Emerging drugs for psoriatic arthritis. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs 21:69–79
Ritchlin CT, Krueger JG (2016) New therapies for psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol 28:204–210
Morel DR, Schwieger I, Hohn L, Terrettaz J, Llull JB, Cornioley YA, Schneider M (2000) Human pharmacokinetics and safety evaluation of SonoVue, a new contrast agent for ultrasound imaging. Investig Radiol 35:80–85
Rednic N, Tamas MM, Rednic S (2011) Contrast-enhanced ultrasonography in inflammatory arthritis. Med Ultrason 13:220–227
Reece RJ, Canete JD, Parsons WJ, Emery P, Veale DJ (1999) Distinct vascular patterns of early synovitis in psoriatic, reactive, and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 42:1481–1484
McGonagle D, Lories RJ, Tan AL, Benjamin M (2007) The concept of a “synovio-entheseal complex” and its implications for understanding joint inflammation and damage in psoriatic arthritis and beyond. Arthritis Rheum 56:2482–2491
Fiocco U, Cozzi L, Chieco-Bianchi F, Rigon C, Vezzù M, Favero E, Ferro F, Sfriso P, Rubaltelli L, Nardacchione R, Todesco S (2011) Vascular changes in psoriatic knee joint synovitis. J Rheumatol 28:2480–2486
Rizzo G, Raffeiner B, Coran A, Ciprian L, Fiocco U, Botsios C, Stramare R, Grisan E (2015) Pixel-based approach to assess contrast-enhanced ultrasound kinetics parameters for differential diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. J Med Imaging (Bellingham) 2:034503
Taylor W, Gladman D, Helliwell P, Marchesoni A, Mease P, Mielants H, CASPAR Study Group (2006) Classification criteria for psoriatic arthritis: development of new criteria from a large international study. Arthritis Rheum 54:2665–2673
Fiocco U, Stramare R, Coran A, Grisan E, Scagliori E, Caso F, Costa L, Lunardi F, Oliviero F, Bianchi FC, Scanu A, Martini V, Boso D, Beltrame V, Vezzù M, Cozzi L, Scarpa R, Sacerdoti D, Punzi L, Doria A, Calabrese F, Rubaltelli L (2015) Vascular perfusion kinetics by contrast-enhanced ultrasound are related to synovial microvascularity in the joints of psoriatic arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 34:1903–1912
Patil V, Johnson G (2011) An improved model for describing the contrast bolus in perfusion MRI. Med Phys 38:6380–6383
G. Rizzo, M. Tonietto, M. Castellaro, A. Coran, B. Raffeiner, U. Fiocco, R. Stramare, E. Grisan (2017) Detection of a slow-flow component in contrast-enhanced ultrasound of the synovia for the differential diagnosis of arthritis’, SPIE Conference on Medical Imaging, Orlando (FL). Paper 10134–143
Dunn OJ (1961) Multiple comparisons among means. J Am Stat Assoc 56:52–64
Chappell MA, Groves AR, Whitcher B, Woolrich MW (2009) Variational Bayesian inference for a nonlinear forward model. IEEE Trans Signal Process 57:223–236
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) J R Stat Soc Ser B Methodol 57:289–300
Prescott JW (2013) Quantitative imaging biomarkers: the application of advanced image processing and analysis to clinical and preclinical decision making. J Digit Imaging 26:97–108
Ehling J, Lammers T, Kiessling F (2013) Non-invasive imaging for studying anti-angiogenic therapy effects. Thromb Haemost 109:375–390
Ferrari M, Onuoha SC, Pitzalis C (2016) Going with the flow: harnessing the power of the vasculature for targeted therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Drug Discov Today 21:172–179
Nistala K, Adams S, Cambrook H, Ursu S, Olivito B, de Jager W, Evans JG, Cimaz R, Bajaj-Elliott M, Wedderburn LR (2010) Th17 plasticity in human autoimmune arthritis is driven by the inflammatory environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:14751–14756
Komatsu N, Okamoto K, Sawa S, Nakashima T, Oh-hora M, Kodama T, Tanaka S, Bluestone JA, Takayanagi H (2014) Pathogenic conversion of Foxp3+ T cells into TH17 cells in autoimmune arthritis. Nat Med 20:62–68
Fiocco U, Martini V, Accordi B, Caso F, Costa L, Oliviero F, Scanu A, Facco M, Boso D, Gatto M, Felicetti M, Frallonardo P, Ramonda R, Piva L, Zambello R, Agostini C, Scarpa R, Basso G, Semenzato G, Dayer JM, Punzi L, Doria A (2015) Transcriptional network profile on synovial fluid T cells in psoriatic arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 34:1571–1580
Miossec P (2003) Interleukin-17 in rheumatoid arthritis: if T cells were to contribute to inflammation and destruction through synergy. Arthritis Rheum 48:594–601
Paulissen SM, van Hamburg JP, Dankers W, Lubberts E (2015) The role and modulation of CCR6+ Th17 cell populations in rheumatoid arthritis. Cytokine 74:43–53
van Hamburg JP, Asmawidjaja PS, Davelaar N, Mus AM, Cornelissen F, van Leeuwen JP, Hazes JM, Dolhain RJ, Bakx PA, Colin EM, Lubberts E (2012) TNF blockade requires 1,25(OH)2D3 to control human Th17-mediated synovial inflammation. Ann Rheum Dis 71:606–612
Basdeo SA, Moran B, Cluxton D, Canavan M, McCormick J, Connolly M, Orr C, Mills KH, Veale DJ, Fearon U, Fletcher JM (2015) Polyfunctional, pathogenic CD161+ Th17 lineage cells are resistant to regulatory T cell-mediated suppression in the context of autoimmunity. J Immunol 195:528–540
Bai A, Robson S (2015) Beyond ecto-nucleotidase: CD39 defines human Th17 cells with CD161. Purinergic Signal 11:317–319
Fergusson JR, Fleming VM, Klenerman P (2011) CD161-expressing human T cells. Front Immunol 2:36
Naredo E, Möller I, de Miguel E, Batlle-Gualda E, Acebes C, Brito E, Mayordomo L, Moragues C, Uson J, de Agustín JJ, Martínez A, Rejón E, Rodriguez A, Daudén E, Ultrasound School of the Spanish Society of Rheumatology and Spanish ECO-Aps Group (2011) High prevalence of ultrasonographic synovitis and enthesopathy in patients with psoriasis without psoriatic arthritis: a prospective case-control study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 50:1838–1848
Freeston JE, Coates LC, Nam JL, Moverley AR, Hensor EM, Wakefield RJ, Emery P, Helliwell PS, Conaghan PG (2014) Is there subclinical synovitis in early psoriatic arthritis? A clinical comparison with gray-scale and power Doppler ultrasound. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 66:432–439
Gullick NJ, Evans HG, Church LD, Jayaraj DM, Filer A, Kirkham BW, Taams LS (2010) Linking power Doppler ultrasound to the presence of th17 cells in the rheumatoid arthritis joint. PLoS One 5(9)
Kelly S, Bombardieri M, Humby F, Ng N, Marrelli A, Riahi S, DiCicco M, Mahto A, Zou L, Pyne D, Hands RE, Pitzalis C (2015) Angiogenic gene expression and vascular density are reflected in ultrasonographic features of synovitis in early rheumatoid arthritis: an observational study. Arthritis Res Ther 17:58
Fearon U, Griosios K, Fraser A, Reece R, Emery P, Jones PF, Veale DJ (2003) Angiopoietins, growth factors, and vascular morphology in early arthritis. J Rheumatol 30:260–268
Fiocco U, Ferro F, Cozzi L, Vezzù M, Sfriso P, Checchetto C, Bianchi FC, Nardacchione R, Piccoli A, Todesco S, Rubaltelli L (2003) Contrast medium in power Doppler ultrasound for assessment of synovial vascularity: comparison with arthroscopy. J Rheumatol 30:2170–2176
Klauser AS, De Zordo T, Bellmann-Weiler R, Feuchtner GM, Sailer-Höck M, Sögner P, Gruber J (2009) Feasibility of second-generation ultrasound contrast media in the detection of active sacroiliitis. Arthritis Rheum 61:909–916
Mouterde G, Aegerter P, Correas JM, Breban M, D’Agostino MA (2014) Value of contrast-enhanced ultrasonography for the detection and quantification of enthesitis vascularization in patients with spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 66:131–138
Espinoza LR, Vasey FB, Espinoza CG, Bocanegra TS, Germain BF (1982) Vascular changes in psoriatic synovium. A light and electron microscopic study. Arthritis Rheum 25:677–684
Pickens SR, Volin MV, Mandelin AM II, Kolls JK, Pope RM, Shahrara S (2010) IL-17 contributes to angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol 184:3233–3241
Numasaki M, Watanabe M, Suzuki T, Takahashi H, Nakamura A, McAllister F, Hishinuma T, Goto J, Lotze MT, Kolls JK, Sasaki H (2005) IL-17 enhances the net angiogenic activity and in vivo growth of human non-small cell lung cancer in SCID mice through promoting CXCR-2-dependent angiogenesis. J Immunol 175:6177–6189
Honorati MC, Meliconi R, Pulsatelli L, Canè S, Frizziero L, Facchini A (2001) High in vivo expression of interleukin-17 receptor in synovial endothelial cells and chondrocytes from arthritis patients. Rheumatology (Oxford) 40:522–527
Moran EM, Connolly M, Gao W, McCormick J, Fearon U, Veale DJ (2011) Interleukin-17A induction of angiogenesis, cell migration, and cytoskeletal rearrangement. Arthritis Rheum 63:3263–3273
Hot A, Lenief V, Miossec P (2012) Combination of IL-17 and TNFα induces a pro-inflammatory, pro-coagulant and pro-thrombotic phenotype in human endothelial cells. Ann Rheum Dis 71:768–776
Cañete JD, Pablos JL, Sanmartí R, Mallofré C, Marsal S, Maymó J, Gratacós J, Mezquita J, Mezquita C, Cid MC (2004) Antiangiogenic effects of anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha therapy with infliximab in psoriatic arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 50:1636–1641
Izquierdo E, Cañete JD, Celis R, Santiago B, Usategui A, Sanmartí R, Del Rey MJ, Pablos JL (2009) Immature blood vessels in rheumatoid synovium are selectively depleted in response to anti-TNF therapy. PLoS One 4:e8131
Fiocco U, Ferro F, Vezzù M, Cozzi L, Checchetto C, Sfriso P, Botsios C, Ciprian L, Armellin G, Nardacchione R, Piccoli A, Todesco S, Rubaltelli L (2005) Rheumatoid and psoriatic knee synovitis: clinical, grey scale, and power Doppler ultrasound assessment of the response to etanercept. Ann Rheum Dis 64:899–905
Abou-Elkacem L, Bachawal SV, Willmann JK (2015) Ultrasound molecular imaging: moving toward clinical translation. Eur J Radiol 84:1685–1693
Put S, Westhovens R, Lahoutte T, Matthys P (2014) Molecular imaging of rheumatoid arthritis: emerging markers, tools, and techniques. Arthritis Res Ther 16:208
Klauser A, Frauscher F, Schirmer M, Halpern E, Pallwein L, Herold M, Helweg G, ZurNedden D (2002) The value of contrast-enhanced color Doppler ultrasound in the detection of vascularization of finger joints in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 46:647–653
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Italian Ministry of Education, University and Research (MIUR-2009EE3SWA; FIRB 2011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was approved by the local ethic committee of the University Hospital of Padova (Italy) (number 52723; October 11, 2010).
Disclosures
None.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOCX 20.2 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fiocco, U., Stramare, R., Martini, V. et al. Quantitative imaging by pixel-based contrast-enhanced ultrasound reveals a linear relationship between synovial vascular perfusion and the recruitment of pathogenic IL-17A-F+IL-23+ CD161+ CD4+ T helper cells in psoriatic arthritis joints. Clin Rheumatol 36, 391–399 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-016-3500-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-016-3500-x